Welcome to the Virtual Education Wiki ~ Open Education Wiki
New Zealand
(Re.ViCa version by Theo Bastiaens, Paul Bacsich, Nikki Cortoos and Grégory Lucas.)
Put in merged template and prepared for update by Paul Bacsich, Sero.
Revised and updated for VISCED by James Kay.
For entities in New Zealand see Category:New Zealand
Partners and Experts situated in New Zealand
Partners
None - for any of Re.ViCa, VISCED and POERUP.
New Zealand members of VISCED IAC exist but have yet to be confirmed.
Experts
New Zealand in a nutshell
New Zealand (Maori: Aotearoa) is an geographically isolated island country in the south-western Pacific Ocean. It comprises two main landmasses (the North Island and the South Island), and numerous smaller islands, most notably Stewart Island/Rakiura and the Chatham Islands. The Realm of New Zealand also includes the Cook Islands and Niue (self-governing but in free association); Tokelau; and the Ross Dependency (New Zealand's territorial claim in Antarctica).
The population of New Zealand is around 4.1 million according to the CIA Factbook. This makes it rather similar in size to several European countries, rather larger than Lithuania, slightly smaller than Ireland and rather smaller than Norway. In UK terms, it is slightly smaller than Scotland (5.0 million) and slightly larger than Wales (3.0 million). Thus population-wise as well as politically and economically it is a good match to these countries/regions.
The indigenous Māori being the largest minority, the population is mostly of European descent. Also significant minorities are Asians and non-Māori Polynesians, especially in the urban areas. As a Commonwealth country with strong historic links with the UK in general and Scotland in particular, Elizabeth II is the Head of State. In her absence, she is represented by a non-partisan Governor-General. Actually the position of Queen Elizabeth II is essentially symbolic, and she has no real political influence. Political power is rather held by the democratically elected Parliament of New Zealand under the leadership of the Prime Minister, who is the head of government.
Education in New Zealand
In comparison with international standards New Zealand has a well performing education system. Therefore the focus of education policy lays on consolidation of education. This consolidation is carried out by creation of required infrastructure and in building up and support by institutions of quality-assurance. This way weaknesses in the educational system are to be identified at an early stage. Furthermore is the creation of an advantageous political environment for lecturers and learners intended. Special attention is paid to investments to peform better for and with Māori learners, Pasifika learners, children with specific barriers to learning and communities in lower socioeconomic areas.
The Ministry of Education’s Statement of Intent 2008-2013 (SOI) sets out key elements of appropriate priorities for education:
- All children develop strong learning foundations
- increasing participation in high-quality early childhood education - increasing literacy and numeracy achievement in primary school - earlier identification of and intervention for children with specific barriers to learning.
- All young people participate, engage and achieve in education
- increasing engagement and achievement in secondary education so that young people stay at school longer and leave with higher-level qualifications - more successful pathways into tertiary education and work - higher levels of achievement in tertiary education by the age of 25.
- Learners have access to high-quality Māori language education that delivers positive learning and language outcomes
- increasing numbers of high-quality teachers proficient in te reo Māori - increasing effectiveness of teaching and learning in and through te reo Māori.
- The education system produces the knowledge and develops people with the skills to drive New Zealand’s future economic and social success
- building an education system for the 21st-century - increasing education’s contribution to economic transformation and innovation through new knowledge, skills and research.
- Education agencies work effectively and efficiently to achieve education outcomes
- building leadership, accountability, relationships, competence and confidence.
In previous years the Ministry of Education focused on critical drivers of presence, engagement and achievement for all learners, namely:
- the effectiveness of the relationships that underpin teaching and learning
- family and community engagement
- providers focused on the use of evidence to support learning and achievement.
The New Zealand education system comprises following guiding principles: - culturally appropriate early childhood services - primary and secondary education that is free for New Zealand citizens and permanent residents - equitable and affordable access to tertiary education and quality assured and portable education qualifications - the provision of flexible pathways for study
Last item regards to the fact that students are not streamed or channeled through particular types of school from which future study options are determined.
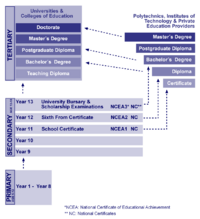
Generally the education system in New Zealand is divided into:
- pre-school education,
- primary education,
- secondary education,
- tertiary education.
Kindergarten education is usually run by private operators and not mandatory provided for all children. Primary school goes up to year 6, intermediate school finishes at year 8 and secondary school is the remaining five years of schooling. Between the ages of 6 and 16 Primary and Secondary education is compulsory for students.
Entry to university
Students who want to study at a New Zealand university need to meet a University Entrance (UE) standard. They need to achieve minimum standards at Levels 1, 2 and 3 of NCEA or the NQF.
They need to gain 42 or more credits at Level 3 or higher of the NQF from a specified range of subjects. Students must also gain specific literacy and numeracy standards.
Domestic students over 20 years of age may apply for entry without formal qualifications.
Equivalent international qualifications such as the International Baccalaureate and the Cambridge examinations are also accepted for UE. International students must fulfill minimum English language requirements for enrolment at tertiary institutions.
For more information on entry requirements go to the New Zealand Vice-Chancellors' Committee website.
Copied from: New Zealand Ministry of Education > NZ education system overview
Schools in New Zealand
((Needs to be completed.))
Further and Higher education
Universities in New Zealand
New Zealand has eight universities. Most used to be constituent colleges of the federal University of New Zealand but this was dissolved in 1961.
| Name | Location | Foundation |
|---|---|---|
| University of Otago | Dunedin | 1869 |
| University Canterbury | Christchurch | 1873 |
| University of Auckland | Auckland | 1883 |
| Victoria- University Wellington | Wellington | 1897 |
| Massey-University | Palmerston North, Auckland, Wellington | 1927 |
| University of Waikato | Hamilton | 1964 |
| Lincoln University | Lincoln, Canterbury | 1990 |
| Auckland University of Technology | Auckland | 2000 |
The total number of students at the Universities at New Zealand is about 170,000. The University of Otago is deemed to be the oldest University in the country. Auckland University of Technology as the youngest University was founded in the year 2000, whose origin as technical school lies in the year 1895. At the smallest University of New Zealand – Lincoln University – are 4.100 students registered, at the largest – Massey University – study 42.000 peeople (As at 2003).
Until the year of 1961 the sole University of New Zealand (1870-1961) as by law founded Organization concentrated several constituent colleges of higher education at various locations around New Zealand.
Polytechnics in New Zealand
There are also 23 polytechnics or institutes of technology in New Zealand. A useful NZQA observes:
- Polytechnics have traditionally specialised in vocational training, but that role has expanded over the last decade to meet the needs of learners and the economy. Many are involved in research activities, particularly in applied and technological areas and other degrees.
New Zealand has three public institutions designated as wānanga under the Education Act 1989. They are indigenous tertiary institutions that offer certificates (Levels 1-4), diplomas (Levels 5-6), and bachelors degrees (Level 7) at the minimum:
- Aotearoa or "Te Wananga o Aotearoa", which is Maori for the University of New Zealand but has nothing to do with the former university, offers courses such as Foundation, Maori studies, Humanities, Arts and Computing and Business. It also states on its web site that it has "over 75% of programmes with no fees and a one-on-one tauira (student)/kaiako (tutor) interaction".
- Awanuiarangi also offers courses that lead to a Master and even a Doctor of Philosophy diploma.
- Raukawa offers courses up to a Masters level.
Related Documents of the wānangas:
- Wikipedia's page on Wananga
- NEW ZEALAND: Maori institutions enjoy better times. 2008, University World News
- An address to the Australian Indigenous Higher Education Advisory Council (PDF), 2005, by Durie, M.
- NZ could limit Maori intake, 2003, Times Higher Education
Colleges in New Zealand
((Needs to be completed.))
Education reform
Schools
((Needs to be completed.))
Post-secondary
The Bologna Process
Regardless that New Zealand is not eligible to join the Bologna Process, it is engaged in these higher education reforms. The tertiary education system of New Zealand is already comparable to the Bologna ideal. Closely align with the key elements of the Bologna Process do the three-level degree structure, Register of Quality Assured Qualifications, quality assurance standards, efforts at increasing participation in tertiary education, and policies that promote institutional autonomy. Beyond that one has been undertaken further work across the tertiary education system to build on this high level of comparability. Thus New Zealand has acceded to the Lisbon Qualification Recognition Convention, is checking the introduction of an Diploma Supplement, and is verifying the comparability of the Register of Quality Assured Qualifications with Ireland’s National Framework of Qualifications.
Administration and finance
Schools
((Needs to be completed.))
Universities
Centralised, similar to England.
Quality assurance, inspection and accreditation
The administration and quality assurance of national qualifications in New Zealand is primary coordinated by the New Zealand Qualifications Authority (NZQA).
NZQA:
- registers and monitors all national qualifications on the National Qualifications Framework
- runs national senior secondary school examinations
- registers and monitors private providers of education and training to ensure they meet quality standards
- administers a qualifications recognition service for overseas people wanting to live, work or study in New Zealand
Its web site: http://www.nzqa.govt.nz
Schools
((Needs to be completed.))
Post-secondary
No information.
Information society
((Needs to be completed.))
ICT in education initiatives
Virtual initiatives in schools
((Needs to be completed.))
OER?
Virtual initiatives in post-secondary education
Distance learning providers
Open Polytechnic of New Zealand
The Open Polytechic is a specialist institution of distance learning based near Wellington, New Zealand, in the area of Lower Hutt, with Learning Centres in Auckland and Christchurch. It has just over 34,000 students, equating to around 7,000 equivalent full time students. There are rather more women than men students (57:43), and around 13% of students declare themselves to be of Maori ethnicity. It uses Moodle. Courses cover the full range of post-secondary provision, including college-level and university-level programmes.
The Open Polytechic web site is at http://openpolytechnic.ac.nz
Massey Univesity is New Zealand's only national university, with roughly 36,000 students. It has multiple campuses in Auckland, Wellington and Palmerston North and has a 50-year history as a leader in distance ('extramural') learning. In 2009, 18,000 enrolled students were distance learners. Massey provides distance students with a blend of print-based and electronic learning activities and resources and has recently adopted Moodle (rebranded Stream) as its official Learning Management System. It has a long history of innovation in teaching through new technologies and was the lead developer of the open source Mahara eportfolio system, now being used throughout the world.
Further information about distance education is available from http://extramural.massey.ac.nz.
The University of Otago in Dunedin, New Zealand, is that country's oldest university. It had over 20,000 students enrolled during the 2007 academic year. Since 1985, the University has supported distance learning, using a variety of learning materials and teaching media. A number of courses are available in purely online mode.
The University of Otago web site is at http://www.otago.ac.nz/
Southern Institute of Technology
The Southern Institute of Technology (SIT) is a Tertiary Education Institution in the province of Southland, New Zealand. Its main campus is situated in Invercargill, with satellite campuses are located in Gore and Christchurch. SIT offers over 130 programmes including certificates, diplomas, degrees and postgraduate study options. SIT has around 13,000 students. SIT2LRN is the multimedia "Flexible Mixed Mode Delivery" option offered by the Southern Institute of Technology. Its courses are delivered via their learning environment and may also include a combination of television, the internet, email and paper-based materials. Certificates and diplomas are available via SIT2LRN. The SIT web site is at http://www.sit.ac.nz
Campus-based universities with significant e-learning activity
These include:
Polytechnics
Colleges
OPNZ.
Benchmarking e-learning
New Zealand is the home of the eMM methodology, developed by Dr Stephen Marshall at the University of Wellington. He was a consultant to the UK Higher Education Academy Benchmarking Exercise. After a large amount of government-funded activity (see the 9 MB report) in 2004-2005, where nine institutions were benchmarked (six universities and three polytechnics), recently (up to summer 2007) there does not seem to be an externally funded benchmarking programme oriented to New Zealand tertiary institutions - but this situation may soon change.
Lessons learnt
General lessons
Notable practices
References
- Education Counts (government site - education statistics): http://www.educationcounts.govt.nz/
- The New Zealand Qualifications Authority (NZQA): http://www.nzqa.govt.nz/
See also Australia.