Welcome to the Virtual Education Wiki ~ Open Education Wiki
Chad: Difference between revisions
(added cats SSA and COI) |
(CSV import all low-income countries, except Yemen done manually already) |
||
| (24 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
== | ''by [[Graham Clarke]]'' | ||
''For entities in Chad see [[:Category:Chad]]'' | |||
== Experts situated in Chad== | |||
== Chad in a nutshell == | == Chad in a nutshell == | ||
<!--(please enter a few sentences - focus on name(s) of country, location, population, capital city)--> | |||
[[Image:Cd-map.gif|right|thumb|400px|Source : http://www.cia.gov]] | |||
''Chad'' (French: '''Tchad''', Arabic: تشاد '''Tshād'''), officially known as the '''Republic of Chad''', is a landlocked country in central Africa. It is bordered by [[Libya]] to the north, [[Sudan]] to the east, the [[Central African Republic]] to the south, [[Cameroon]] and [[Nigeria]] to the southwest, and [[Niger]] to the west. Due to its distance from the sea and its largely desert climate, the country is sometimes referred to as the "Dead Heart of Africa". | ''Chad'' (French: '''Tchad''', Arabic: تشاد '''Tshād'''), officially known as the '''Republic of Chad''', is a landlocked country in central Africa. It is bordered by [[Libya]] to the north, [[Sudan]] to the east, the [[Central African Republic]] to the south, [[Cameroon]] and [[Nigeria]] to the southwest, and [[Niger]] to the west. Due to its distance from the sea and its largely desert climate, the country is sometimes referred to as the "Dead Heart of Africa". | ||
Chad is divided into three major geographical regions: a desert zone in the north, an arid Sahelian belt in the centre and a more fertile Sudanese savanna zone in the south. Lake Chad, after which the country is named, is the largest wetland in Chad and the second largest in Africa. Chad's highest peak is the Emi Koussi in the Sahara, and N'Djamena,(formerly Fort-Lamy), the capital, is the largest city. Politically, Chad is divided since February 2008 into 22 regions. | The population of Chad is just over 10.7 million (CIA July 2011 est.): 26% live in urban areas and 74% in rural ones. The country's population is young: an estimated 47% is under 15. The birth rate is estimated at 42 births per 1,000 people, the mortality rate at 16.69. The life expectancy is 47.2 years | ||
Chad is divided into three major geographical regions: a desert zone in the north, an arid Sahelian belt in the centre and a more fertile Sudanese savanna zone in the south. Lake Chad, after which the country is named, is the largest wetland in Chad and the second largest in Africa. Chad's highest peak is the Emi Koussi in the Sahara, and N'Djamena,(formerly Fort-Lamy), the capital, is the largest city. | |||
Politically, Chad is divided since February 2008 into 22 regions. | |||
Chad is home to over 200 different ethnic and linguistic groups, which create diverse social structure. Arabic and French are the official languages. Islam is the most widely practiced religion. | Chad is home to over 200 different ethnic and linguistic groups, which create diverse social structure. Arabic and French are the official languages. Islam is the most widely practiced religion. | ||
== Education in Chad== | |||
<!-- overview of all sectors --> | |||
== School-level education == | |||
[http://education.stateuniversity.com/pages/255/Chad-PREPRIMARY-PRIMARY-EDUCATION.html] | |||
[http://www.bibl.u-szeged.hu/oseas_adsec/chad.htm] | |||
'''Primary level''' Primary education begins age six in larger cities, and seven in more rural areas. This level is a six year curriculum and is divided into three cycles of two years each. 1st level: cours préparatoire 1 (CP1), 2nd level: cours préparatoire 2 (CP2), 3rd level: cours élémentaire 1 (CE1), 4th level: cours élémentaire 2 (CE2), 5th level: cours moyen 1(CM1), 6th level: cours moyen 2 (CM2). the CEP, or Certificat d'Etudes Primaires (primary skills certification), is administered to all children. Those who successfully pass are admitted to secondary schools, while the others are directed to vocational and technical schools. | |||
'''Secondary level''' Secondary education is designed after the French system and comprises seven years divided into two stages. The first is four years and leads to the Brevet d'Etudes du Premier Cycle, (Junior High School Diploma) or BEPC. Students must pass this to continue to the next level. In the second stage of three years pupils enter into a stream of either humanities, economics, math, or natural sciences. These three years are usually spent in a lycée (an academic-track high school), and they end in the national Baccalauréat exam, a prerequisite for admission to the university. At the secondary level, instruction is in either French or Arabic, emphasis depending on the geographical location of the school. | |||
'''Vocational or Technical''' Chad has a two-tier system of vocational and technical education. Students can enter a six-year program leading to the CAP, or Certificat d'Aptitude Professionelle (professional skills certification), in a variety of manual and technical fields. | |||
== Further and Higher education == | |||
=== Universities in Chad=== | |||
<!--(this is an important section)--> | |||
==== Université de N'Djaména ==== | |||
=== | The University of N'Djamena was established by government decree in 1971 and serves as the main centre of higher learning for this country. The university serves 6,000 students. It is a full member of the International University Association. It aims to become a respected centre of expertise in the field of Sustainable Development. | ||
Its national acronym is UNDJ, but UNDT and sometimes NU are also used internationally. | |||
Its web site is at http://www.univ-ndjamena.org with several pages in English. | |||
==== Other institutions ==== | |||
An old report at http://www.iusta-tchad.org/enseignement%20superieur.html lists several other universities: | |||
'''Public higher education institutions in N'Djamena:''' | |||
# ENAM : École Nationale d'Administration et de Magistrature | |||
# ISSED : Institut Supérieur des Sciences de l'Éducation | |||
'''Public higher education institutions elsewhere:''' | |||
# UNABA : Université Adam Barka d'Abéché | |||
# UDM : Université de Moundou | |||
# USTA : Université des Sciences et de la Technologie d'Ati | |||
# ESSEAB : École Supérieure des Sciences Exactes et Appliquées de Bongor | |||
# IUSAES : Institut Universitaire des Sciences Agronomiques et de l'Environnement de Sarh | |||
# IUTEM : Institut Universitaire des Techniques d'Entreprises de Moundou | |||
# IUPM : Institut Universitaire Polytechnique de Mongo | |||
# IUSTA : Institut Universitaire des Sciences et Techniques d'Abéché | |||
# IUPM : Institut Universitaire du Pétrole de Mao | |||
# ISAMB : Institut Supérieur des Arts et Métiers de Biltine | |||
'''Private higher education institutions:''' | |||
# Université Roi Fayçal de Ndjamena | |||
# and allegedly several others | |||
=== Polytechnics in Chad=== | |||
=== Colleges in Chad === | |||
== Education reform == | |||
| Line 42: | Line 96: | ||
== | == Information society == | ||
== | == ICT in education initiatives == | ||
== Virtual | === Virtual initiatives in schools === | ||
=== | === Virtual initiatives in post-secondary education === | ||
UNDJ Digital Campus | |||
See http://www.univ-ndjamena.org/digitalcampus.asp | |||
See also http://www.euclid.int and http://www.euclidconsortium.org/ | |||
== Lessons learnt == | == Lessons learnt == | ||
| Line 67: | Line 120: | ||
== References == | == References == | ||
(try to add one or two) | <!--(try to add one or two)--> | ||
---- | ---- | ||
> [[Countries]] | > [[Countries]] | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
<!--''Don't forget to change "Pangaea" to the relevant country - and also to the relevant containing continent or continental/oceanic/political (sub)region!''--> | |||
[[Category:Chad| ]] | |||
[[Category:Africa]] | [[Category:Africa]] | ||
[[Category:Sub-Saharan Africa]] | [[Category:Sub-Saharan Africa]] | ||
[[Category:Countries | [[Category:French-speaking countries]] | ||
[[Category:e-World]] | |||
[[Category:Country reports]] | |||
[[Category:Countries with Programmes]] | |||
[[Category:Tier 2]] | |||
[[Category:VISCED]] | |||
{{Countries-footer}} | |||
{{United Nations}} | |||
{{low-income}} | |||
Latest revision as of 16:36, 10 May 2023
For entities in Chad see Category:Chad
Experts situated in Chad
Chad in a nutshell
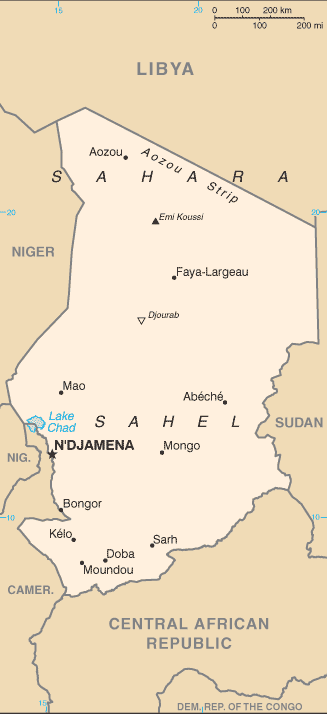
Chad (French: Tchad, Arabic: تشاد Tshād), officially known as the Republic of Chad, is a landlocked country in central Africa. It is bordered by Libya to the north, Sudan to the east, the Central African Republic to the south, Cameroon and Nigeria to the southwest, and Niger to the west. Due to its distance from the sea and its largely desert climate, the country is sometimes referred to as the "Dead Heart of Africa".
The population of Chad is just over 10.7 million (CIA July 2011 est.): 26% live in urban areas and 74% in rural ones. The country's population is young: an estimated 47% is under 15. The birth rate is estimated at 42 births per 1,000 people, the mortality rate at 16.69. The life expectancy is 47.2 years
Chad is divided into three major geographical regions: a desert zone in the north, an arid Sahelian belt in the centre and a more fertile Sudanese savanna zone in the south. Lake Chad, after which the country is named, is the largest wetland in Chad and the second largest in Africa. Chad's highest peak is the Emi Koussi in the Sahara, and N'Djamena,(formerly Fort-Lamy), the capital, is the largest city.
Politically, Chad is divided since February 2008 into 22 regions.
Chad is home to over 200 different ethnic and linguistic groups, which create diverse social structure. Arabic and French are the official languages. Islam is the most widely practiced religion.
Education in Chad
School-level education
Primary level Primary education begins age six in larger cities, and seven in more rural areas. This level is a six year curriculum and is divided into three cycles of two years each. 1st level: cours préparatoire 1 (CP1), 2nd level: cours préparatoire 2 (CP2), 3rd level: cours élémentaire 1 (CE1), 4th level: cours élémentaire 2 (CE2), 5th level: cours moyen 1(CM1), 6th level: cours moyen 2 (CM2). the CEP, or Certificat d'Etudes Primaires (primary skills certification), is administered to all children. Those who successfully pass are admitted to secondary schools, while the others are directed to vocational and technical schools.
Secondary level Secondary education is designed after the French system and comprises seven years divided into two stages. The first is four years and leads to the Brevet d'Etudes du Premier Cycle, (Junior High School Diploma) or BEPC. Students must pass this to continue to the next level. In the second stage of three years pupils enter into a stream of either humanities, economics, math, or natural sciences. These three years are usually spent in a lycée (an academic-track high school), and they end in the national Baccalauréat exam, a prerequisite for admission to the university. At the secondary level, instruction is in either French or Arabic, emphasis depending on the geographical location of the school.
Vocational or Technical Chad has a two-tier system of vocational and technical education. Students can enter a six-year program leading to the CAP, or Certificat d'Aptitude Professionelle (professional skills certification), in a variety of manual and technical fields.
Further and Higher education
Universities in Chad
Université de N'Djaména
The University of N'Djamena was established by government decree in 1971 and serves as the main centre of higher learning for this country. The university serves 6,000 students. It is a full member of the International University Association. It aims to become a respected centre of expertise in the field of Sustainable Development.
Its national acronym is UNDJ, but UNDT and sometimes NU are also used internationally.
Its web site is at http://www.univ-ndjamena.org with several pages in English.
Other institutions
An old report at http://www.iusta-tchad.org/enseignement%20superieur.html lists several other universities:
Public higher education institutions in N'Djamena:
- ENAM : École Nationale d'Administration et de Magistrature
- ISSED : Institut Supérieur des Sciences de l'Éducation
Public higher education institutions elsewhere:
- UNABA : Université Adam Barka d'Abéché
- UDM : Université de Moundou
- USTA : Université des Sciences et de la Technologie d'Ati
- ESSEAB : École Supérieure des Sciences Exactes et Appliquées de Bongor
- IUSAES : Institut Universitaire des Sciences Agronomiques et de l'Environnement de Sarh
- IUTEM : Institut Universitaire des Techniques d'Entreprises de Moundou
- IUPM : Institut Universitaire Polytechnique de Mongo
- IUSTA : Institut Universitaire des Sciences et Techniques d'Abéché
- IUPM : Institut Universitaire du Pétrole de Mao
- ISAMB : Institut Supérieur des Arts et Métiers de Biltine
Private higher education institutions:
- Université Roi Fayçal de Ndjamena
- and allegedly several others
Polytechnics in Chad
Colleges in Chad
Education reform
Administration and finance
Quality assurance
Information society
ICT in education initiatives
Virtual initiatives in schools
Virtual initiatives in post-secondary education
UNDJ Digital Campus
See http://www.univ-ndjamena.org/digitalcampus.asp
See also http://www.euclid.int and http://www.euclidconsortium.org/
Lessons learnt
References
For OER policies and projects in Chad see Chad/OER