Welcome to the Virtual Education Wiki ~ Open Education Wiki
Djibouti: Difference between revisions
| Line 84: | Line 84: | ||
> [[Countries]] | > [[Countries]] | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
| Line 95: | Line 95: | ||
[[Category:Country reports]] | [[Category:Country reports]] | ||
[[Category:Countries with Programmes]] | [[Category:Countries with Programmes]] | ||
[[Category:VISCED]] | |||
Revision as of 21:38, 20 June 2011
Experts situated in Djibouti
Djibouti in a nutshell
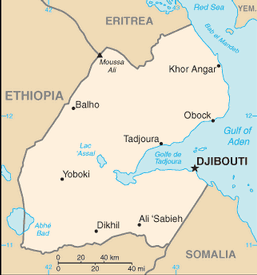
Djibouti (Arabic: جيبوتي Jībūtī, Somali: Jabuuti), officially the Republic of Djibouti, is a country in the Horn of Africa. It is bordered by Eritrea in the north, Ethiopia in the west and south, and Somalia in the southeast. The remainder of the border is formed by the Red Sea and the Gulf of Aden. On the other side of the Red Sea, on the Arabian Peninsula, 20 kilometres (12 mi) from the coast of Djibouti, is Yemen.
Djibouti's size is just over 23,000 square kilometres (8,900 sq mi) with an estimated population of over 757,074 (CIA July 2011 est.).
Its capital is the city of Djibouti.
About a fifth of the population of the country live below the international poverty line of US$1.25 a day.
Education in Djibouti
School-level education
School level education is compulsory between the ages 6 and 16, but is not free. The school year runs from September to June and the language of instruction is French in public and Catholic schools and Arabic in Koranic schools.
Pre-primary education is two years, but only a tiny percentage of the population can afford it.
Primary level education lasts for five years.
Middle school lasts for four years and culminates in the Certificate of Fundamental Education.
Secondary education is open to those who have gained the certificate at the end of the nine years of compulsory education, and lasts for three years.
Further and Higher education
Universities in Djibouti
- University of Djibouti - established 2006[1]