Welcome to the Virtual Education Wiki ~ Open Education Wiki
Togo: Difference between revisions
| Line 75: | Line 75: | ||
====Campus Numérique Francophonie de Lome==== | ====Campus Numérique Francophonie de Lome==== | ||
Created in 1996 through the collaboration of four universities, including the University of Lome, and the Agence Universitaire de La Francophonie ([[AUF]]). The facility connects other universities from the Francophone world and allows Togolese students to pursue e-learning courses. | Created in 1996 through the collaboration of four universities, including the University of Lome, and the Agence Universitaire de La Francophonie ([[AUF]]). The facility connects other universities from the Francophone world and allows Togolese students to pursue e-learning courses. The centre offers access to the following services: querying databases, control of primary documents, web hosting, free Web navigation, training in information technology and free software (introduction to Internet content production), distance education (international environmental law, human rights, new educational technologies). [http://portal.unesco.org/culture/fr/ev.php-URL_ID=10086&URL_DO=DO_PRINTPAGE&URL_SECTION=201.html] | ||
====The University of Lome==== | ====The University of Lome==== | ||
Revision as of 09:45, 20 April 2011
author byline
Experts situated in Togo
Togo in a nutshell
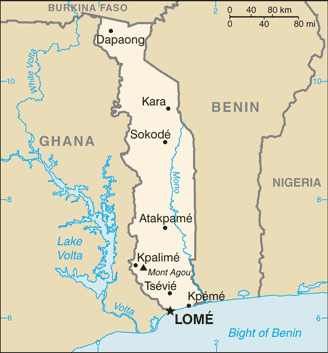
Togo (officially the Togolese Republic) is a country in West Africa bordering Ghana to the west, Benin to the east and Burkina Faso to the north. It extends south to the Gulf of Guinea, on which the capital Lomé is located.
The official language is French; however, there are many other languages spoken in Togo.
Togo's size is just less than 57,000 square kilometres (22,000 sq mi).
Togo has a population of 6.7 million people (CIA July 2011 est.).
Its capital is Lomé.
The country is dependent mainly on agriculture. The mild weather makes for good growing seasons. Togo is a tropical, sub-Saharan nation.
About a third of the population live below the international poverty line of US$1.25 a day.
Education in Togo
Two ministries in Togo are responsible for the administration of education: the National Ministry for Education and Research (MENR) and the Ministry for Vocational and Professional Training (METFP).
School-level education
http://www.ccsenet.org/journal/index.php/ies/article/view/9102 http://www.spainexchange.com/guide/TG-education.htm
Pre- primary This level is not compulsory. Children enter at age two and it generally lasts for around three years.
Primary level Children enter at age five. Primary education lasts for six years and culminates in the primary certificate (CEPED) and provides access to junior secondary.
Secondary Level Secondary education is divided into two cycles. Children begin the junior level at age 12 and after four years take the graduation certificate (BEPD). This provides continuation to senior level secondary, which lasts for three years. At the completion of senior level, the school-leaving certificate part 1 is taken, providing access to 'terminal class'. Following this, the school-leaving certificate part 2 is taken, success in which provides a route to higher education.
Further and Higher education
Universities in Country
Polytechnics in Country
Colleges in Country
Education reform
Administration and finance
Quality assurance
Information society
ICT in education initiatives
Virtual initiatives in schools
Virtual initiatives in post-secondary education
Campus Numérique Francophonie de Lome
Created in 1996 through the collaboration of four universities, including the University of Lome, and the Agence Universitaire de La Francophonie (AUF). The facility connects other universities from the Francophone world and allows Togolese students to pursue e-learning courses. The centre offers access to the following services: querying databases, control of primary documents, web hosting, free Web navigation, training in information technology and free software (introduction to Internet content production), distance education (international environmental law, human rights, new educational technologies). [1]
The University of Lome
The university has a distance learning centre.
Lessons learnt
References