Welcome to the Virtual Education Wiki ~ Open Education Wiki
Australia: Difference between revisions
Grego lucas (talk | contribs) |
Grego lucas (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 55: | Line 55: | ||
Pre-schools are usually run by local councils, community groups or private organizations except in the Northern Territory and Queensland where they are run by the Territory and State Governments respectively. Pre-school is offered to three- to five-year-olds, although attendance numbers vary widely (from 50% in New South Wales to 93% in Victoria). The year before a child is due to attend primary school is the main year for pre-school education. This year is far more commonly attended, and usually takes the form of a few hours of activity five days a week. | Pre-schools are usually run by local councils, community groups or private organizations except in the Northern Territory and Queensland where they are run by the Territory and State Governments respectively. Pre-school is offered to three- to five-year-olds, although attendance numbers vary widely (from 50% in New South Wales to 93% in Victoria). The year before a child is due to attend primary school is the main year for pre-school education. This year is far more commonly attended, and usually takes the form of a few hours of activity five days a week. | ||
''Schools in Australia can be classified according to sources of funding and administrative structures. There are three such categories in Australia: Public Schools (also known as 'Government' schools or 'State' schools), Independent Schools (informally known as 'private' schools) and Catholic schools.'' | |||
Revision as of 09:24, 18 December 2008
Partners situated in Australia
None. However, a member of the International Advisory Committee is based in Australia.
Australia in a nutshell
Australia is a country occupying a whole continent in the southern hemisphere of considerable relevance to European policy in education.
Australia has a population of 20 million according to the CIA Factbook. It is a Commonwealth country with many links to the UK - many people and ideas in education flow to and fro between the countries, and this is true also in e-learning.
It could be argued that the relevance of Australia is mainly to the larger nations of the European Union, yet since it has a states structure as well the relevance is wider, in fact to all nations large and small.
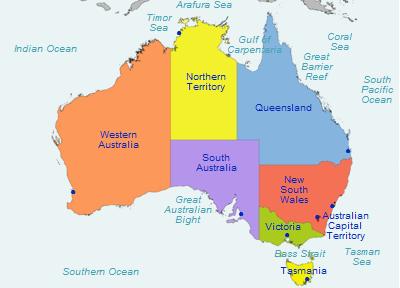
Australia has six states, plus two major mainland territories and several minor territories including islands. The states are New South Wales, Queensland, South Australia, Tasmania, Victoria, and Western Australia. The two major mainland territories are the Northern Territory and the Australian Capital Territory (ACT).
The population of the four largest states is as follows:
- New South Wales: 6,927 million
- Victoria: 5.2 million
- Queensland: 4.2 million
- South Australia: 1.5 million
- Western Australia: 2.1 million
All other states and territories have populations each well under .5 million, and so are relevant only to microstates - with Tasmania as perhaps the most relevant due to its island situation.
Australia education policy
Education in Australia is primarily the responsibility of states and territories.
A real ICT policy and organisational framework exists for the use of Information and Communication Technologies in Australian Education Training. A Joint Ministerial Statement on Information and Communications Technologies in Australian Education and Training: 2008-2011 was endorsed by MCEETYA and MCVTE in June 2008.
(To follow.)
Australia education system
Generally, education in Australia follows the three-tier model which includes primary education (primary schools), followed by secondary education (secondary schools/high schools) and tertiary education (universities and/or TAFE (Technical and Further Education Colleges)).
Education is compulsory up to an age specified by legislation; this age varies from state to state but is generally 15-17, that is prior to completing secondary education. Post-compulsory education is regulated within the Australian Qualifications Framework, a unified system of national qualifications in schools, vocational education and training (TAFE) and the higher education sector (university).
The academic year in Australia varies between states and institutions, but generally runs from late January until mid-December for primary and secondary schools and TAFE colleges, and from late February until mid-November for universities.
Pre-school
Pre-school in Australia is relatively unregulated, and is not compulsory. The first exposure many Australian children have to learn with others outside of traditional parenting is day care or a parent-run playgroup. This sort of activity is not generally considered schooling. Pre-school education is separate from primary school in all states and territories except Western Australia and Queensland, where pre-school education is taught as part of the primary school system.
Pre-schools are usually run by local councils, community groups or private organizations except in the Northern Territory and Queensland where they are run by the Territory and State Governments respectively. Pre-school is offered to three- to five-year-olds, although attendance numbers vary widely (from 50% in New South Wales to 93% in Victoria). The year before a child is due to attend primary school is the main year for pre-school education. This year is far more commonly attended, and usually takes the form of a few hours of activity five days a week.
Schools in Australia can be classified according to sources of funding and administrative structures. There are three such categories in Australia: Public Schools (also known as 'Government' schools or 'State' schools), Independent Schools (informally known as 'private' schools) and Catholic schools.
School
School is compulsory in Australia between the ages of six and fifteen, depending on the state and date of birth, with, in recent years, over three quarters of students staying on until they are eighteen. Government schools educate about two thirds of Australian students, with the other third in independent schools, a proportion which is rising in many parts of Australia.
Government schools are free, while independent schools, both religious and secular, charge fees. Regardless of whether a school is government or independent, they are required to adhere to the same curriculum frameworks. Most school students, be they in government or independent school, usually wear uniforms, although there are varying expectations and some Australian schools do not require uniforms.
Government (or state) schools
Government or state schools are run by the local state or territory government. They do not charge compulsory fees, with the majority of their costs met by the relevant government, and the rest by voluntary levies and fundraising.
They can be divided into two categories: open and selective. The open schools accept all students from their government defined catchment areas. Selective government schools mostly cater for academically gifted students (the top 5 percent), although there are performing arts and sports schools. Almost all selective schools are in New South Wales,[citation needed] though a few exist in other areas.
Selective schools are more prestigious than open government schools, and generally achieve better results in the school-leaving exams than independent or open government schools. Entrance to selective schools is often highly competitive and they cater to a large geographical area.
Other schools
Most Catholic schools are either run by their local parish and/or by each state's Catholic Education Department.
Non-Catholic non-government schools (often called "Independent" schools) enroll about 14% of students. These include schools operated by religious groups and secular educational philosophies such as Montessori.
Some independent schools charge high fees. Government funding for independent schools often comes under criticism from the Australian Education Union and the Australian Labor Party.
Higher education
Universities in Australia
Australia has 38 universities that are members of Universities Australia, the Australian analogue of Universities UK.
Most Australian universities developed substantial capability in distance learning in the 1980s and several have now migrated this to e-learning.
Perhaps the best known is the University of Southern Queensland.
There is a service provider called NextEd who operates globally and in particular supported the GUA.
Polytechnics in Australia
(To follow. TAFE?)
Higher education reform
Administration and finance
Quality assurance
The Australian Universities Quality Agency (AUQA) is an independent, not-for-profit national agency that will promote, audit, and report on quality assurance in Australian higher education.
AUQA was formally established by the Ministerial Council on Education, Training and Youth Affairs (MCEETYA) in March 2000. It operates independently of governments and the higher education sector under the direction of a Board of Directors. AUQA is owned by and receives core, operational funding from the Commonwealth, State and Territory Ministers for higher education who are members of MCEETYA. The AUQA Constitution is available for download.
Internal quality assurance is supervised by the Open Universities Australia Academic Programs Committee.
Australia's HEIs in the information society
Towards the information society
Information society strategy
In Australia 14% of students (95 000) are doing distance education.
Benchmarking e-learning
Australia is one of the few countries where benchmarking e-learning has been taken seriously. Others include UK and New Zealand.
There has been interest in benchmarking in Australia on two fronts:
- a long strand of development and piloting of the ACODE scheme
- an impending pilot of eMM by around six institutions
Although the ACODE scheme is a distinct scheme, it has several similarities with the Pick&Mix style of benchmarking which has been used for some analytic purposes in Re.ViCa - and in fact Paul Bacsich was the external advisor to the ACODE scheme. There are interesting differences, including a stronger focus in ACODE on IT.
Major e-learning initiatives
Open Universities Australia, formerly Open Learning Australia, Australia’s national specialist distance tertiary education agency, was established by the Australian Government to ensure that the highest quality tertiary education was open to all Australians. There are no education prerequisites for entry to most undergraduate courses, no limits on numbers and in most cases no requirements to attend on-campus or residential seminars. Learners can study in any or all of the four study periods each year, commencing March, June, September or December.
Open Universities Australia is owned and operated by a consortium of seven Australian Universities.
- Curtin University of Technology
- Griffith University
- Macquarie University
- Monash University
- RMIT University
- Swinburne University of Technology
- University of South Australia (UNISA)
TAFE Open Learning or Open Learning Institute of TAFE Queensland (OLI)
Open Learning Institute of TAFE, Australia is an accredited public provider of training courses using distance and internet delivery. The Institute's four stream courses areas are: Business Services, Engineering & Environment Technologies, Education & Training, Community, Health & Personal Services.
TAFE Open Learning helps deliver quality vocational and lifestyle programs to some 25,000 people each year.
TAFE Open Learning is nationally recognised for providing opportunity to enrol into innovative TAFE programs that are tailored for transition into employment and for updating current industry required skills.
TAFE virtual campus Online Learning and Information Portal for the Victorian TAFE System.
The TAFE VC is an established state funded virtual learning platform offering a range of e-learning products and services to a diverse group of students and organisations including TAFE, ACE, registered training organisations, industry and enterprise, schools and Government agencies.
Open Training and Education Network
The Open Training and Education Network (OTEN) in Sydney is the specialist distance education and open learning institute of TAFE NSW, part of the NSW Department of Education and Training. As part of TAFE NSW - Western Sydney Institute, OTEN is the largest provider of distance education and flexibly-delivered programs in Australia. It offers world-class distance education services and products and enrols more than 37,000 students in over 250 TAFE NSW courses. Most courses give graduates nationally recognised qualifications through the AQF (Australian Qualifications Framework). Other specific-purpose courses are recognised by all of TAFE NSW.
University of Phoenix
The University of Phoenix provides Australian and international students with degree programs in some of the fastest growing fields including: Business, Global Management, Technology Management, Information Systems, Education, and Healthcare. All supported by a state-of-the-art virtual learning platform containing some of the best academic resources and professional tools in the world. Our no-nonsense approach to higher education has made us the largest private, accredited university in the United States, and a premier educational provider for working professionals throughout the world. Currently serving students in more than 130 countries.
ECAR Case study 4, 2003], (PDF)
University of Southern Queensland
Distance Education Australia - Online University Courses
University of Southern Queensland Distance Education Centre (DEC) is the first distance education facility in the world to receive international quality accreditation to ISO9001standard. USQ is ALSO accredited with the Distance Education Training Council (DETC), an American public service organisation dedicated to identifying quality distance learning institutions. More than 300 undergraduate and postgraduate award programs of study (eg degree, diploma, certificate) are currently offered by USQ.
Case study in UNESCO "The Virtual University"
University of Queensland e-learning site
Edith Cowan University
Global University Alliance
University of New England UNEOnline
USQonline
References
Web sites :
- Government Educational Portal
- Study in Australia : is the official Australian Government site for studying in Australia
- Wikipedia