Welcome to the Virtual Education Wiki ~ Open Education Wiki
Aland Islands: Difference between revisions
(slapped Re.ViCa version into VISCED version) |
(added {{Countries-footer}}) |
||
| (2 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
'' | ''Original minimal entry by [[Paul Bacsich]], [[Sero]]''<br> | ||
''Recent VISCED update by [[Merja Sjöblom]], [[Finnish Information Society Development Centre]]'' | |||
For entities in the Åland Islands see [[:Category:Åland Islands]] | |||
== Partners situated in Åland Islands == | |||
None, but see [[Finland]] | |||
=Åland Islands in a nutshell= | == Åland Islands in a nutshell == | ||
Mainly sourced from http://www.aland.ax/alandinbrief/index.pbs and [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/%C3%85land_Islands Wikipedia] | Mainly sourced from http://www.aland.ax/alandinbrief/index.pbs and [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/%C3%85land_Islands Wikipedia] | ||
[[Image:aland-map-boundaries.jpg|frame|right|Source: origial jpg on: http://asiapacific.anu.edu.au/blogs/reconciliationgroups/tag/tarabarov-island/]] | [[Image:aland-map-boundaries.jpg|frame|right|Source: origial jpg on: http://asiapacific.anu.edu.au/blogs/reconciliationgroups/tag/tarabarov-island/]] | ||
The Åland Islands | The ''Åland Islands'' (Finnish: '''Ahvenanmaa''') form an archipelago in the [[Baltic Sea]]. This is situated at the entrance to the Gulf of Bothnia. | ||
The archipelago forms an autonomous, demilitarized, monolingually Swedish-speaking administrative province, region and historical province of [[Finland]]. | |||
The population is some 28,000. | |||
The capital is Mariehamn. | |||
The archipelago is the smallest province of [[Finland]], comprising 0.5% of Finland's population and 0.49% of land area. | |||
[[ | Geographically, the islands consist of the main island Fasta Åland (literally "Firm Åland"), where 90% of the population resides, and an archipelago to the east that consists of over 6,500 skerries and islands. Fasta Åland is separated from the coast of [[Sweden]] by 40 kilometres (25 miles) of open water to the west. In the east, the Åland archipelago is virtually contiguous with the Finnish Archipelago Sea. Åland's only land border is located on the uninhabited skerry of Märket, which it shares with [[Sweden]]. | ||
Due to Åland's autonomous status, the powers exercised at the provincial level by representatives of the central state administration in the rest of Finland are largely exercised by the Government of Åland in Åland | |||
Politically, Åland Islands forms an autonomous, demilitarized, Swedish-speaking region and historical province of Finland. The capital is Mariehamn. The Åland Islands are governed according to the Act on the Autonomy of Åland and international treaties. These laws guarantee the islands’ autonomy from Finland, which has ultimate sovereignty over them, as well as a demilitarized status. | |||
Read more on Åland Islands from a pdf document [http://www.aland.ax/.composer/upload//alandinbrief08.pdf Åland in brief] | |||
=== The Provincial Autonomy of the Åland Islands === | |||
Diagram of the public administration from [http://www.suomi.fi/suomifi/english/state_and_municipalities/other_self-government/index.html Suomi.fi] | |||
[[Image:muu_itsehallinto_en.jpg]] | |||
=== Relations with EU === | |||
The autonomous status of the islands was affirmed by a decision made by the League of Nations in 1921 following the Åland crisis. It was reaffirmed within the treaty admitting Finland to the European Union. By law, Åland is politically neutral and entirely demilitarised, and residents are exempt from conscription to the Finnish Defence Forces. The islands were granted extensive autonomy by the Parliament of Finland in the Act on the Autonomy of Åland of 1920, which was later replaced by new legislation by the same name in 1951 and 1991. | |||
In connection with Finland's admission to the European Union, a protocol was signed concerning the Åland Islands that stipulates, among other things, that provisions of the European Community Treaty shall not force a change of the existing restrictions for foreigners (i.e., persons who do not enjoy "home region rights" (hembygdsrätt) in Åland) to acquire and hold real property or to provide certain services, implying a recognition of a separate nationality. | |||
Most inhabitants have Swedish (the sole official language) as their first language: 91.2% in 2007, and 5.0% speak Finnish. | |||
== Education in Åland Islands == | |||
(mainly sourced from: [http://www.norden.org/fi/sinun-pohjolasi/opiskelu-pohjoismaissa/opiskelu-ahvenanmaalla/koulutusjaerjestelmae-ahvenanmaalla Norden]) | |||
The | The Finnish Education system and policies are used also in Åland Islands. The education system consists of preschool and basic education, upper secondary and vocational schools as well as polytechnics and universities. The Finnish Education system is described in [[Finland]]. | ||
The | The language of instruction in publicly financed schools is Swedish, but an Ålandic municipality is free to provide teaching ''of'' Finnish. (In the rest of Finland, bilingual municipalities provide schooling both in Finnish and in Swedish.) | ||
Below are listed educational organizations in Åland Islands. Each organization contains a link to its website (in Swedish only): | |||
=== Upper secondary and vocational schools === | |||
* [http://www.afhs.aland.fi/ Ålands folkhögskola] | |||
* [http://www.lyceum.ax/ Ålands lyceum] | |||
* [http://www.handels.ax/ Ålands handelsläroverk] | |||
* [http://www.handels.ax/ Ålands hotell- och restaurangskola] | |||
* [http://webfronter.com/navigare/sjomansskolan/index.shtml Ålands sjömansskola] | |||
* [http://www.avi.ax/ Ålands vårdinstitut] | |||
* [http://www.ay.ax/ Ålands yrkesskola] | |||
=== Higher education === | |||
* [http://www.ahs.ax Högskolan på Åland] | |||
=== Other education === | |||
* [http://www.ha.ax/text.con?iPage=424&m=453 Öppna högskolan på Åland] | |||
* [http://www.mariehamn.ax/Medborgarinstitutet/ Medborgarinstitutet (Medis)] | |||
* [http://www.ami.ax/ Ålands musikinstitut] | |||
* [http://www.belcanto.ax/ Bel Canto r.f.] | |||
* [http://www.laroavtal.ax/ Ålands läroavtalscenter] | |||
== Relevant websites == | |||
* [http://www.asub.ax/start.con?iLan=2 Statistics Åland] | |||
* http://www.government.ax/ | |||
* [http://www.norden.org/en Official co-operation in the Nordic region] | |||
* [http://www.regeringen.ax/utbildning_kultur/ Ministry of Education and Culture in Åland] | |||
| Line 107: | Line 101: | ||
> [[Main Page]] | > [[Main Page]] | ||
[[Category:Åland Islands| ]] | |||
[[Category:Finland|-Aland Islands]] | [[Category:Finland|-Aland Islands]] | ||
[[Category:Finland - realm]] | [[Category:Finland - realm]] | ||
[[Category:Europe | [[Category:Europe]] | ||
[[Category:Nordic countries]] | [[Category:Nordic countries]] | ||
[[Category:Countries in stubs]] | [[Category:Countries in stubs]] | ||
[[Category:VISCED]] | |||
{{Countries-footer}} | |||
Latest revision as of 10:50, 10 May 2023
Original minimal entry by Paul Bacsich, Sero
Recent VISCED update by Merja Sjöblom, Finnish Information Society Development Centre
For entities in the Åland Islands see Category:Åland Islands
Partners situated in Åland Islands
None, but see Finland
Åland Islands in a nutshell
Mainly sourced from http://www.aland.ax/alandinbrief/index.pbs and Wikipedia
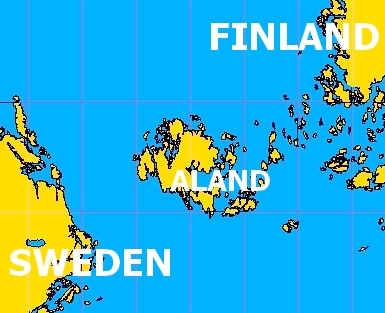
The Åland Islands (Finnish: Ahvenanmaa) form an archipelago in the Baltic Sea. This is situated at the entrance to the Gulf of Bothnia.
The archipelago forms an autonomous, demilitarized, monolingually Swedish-speaking administrative province, region and historical province of Finland.
The population is some 28,000.
The capital is Mariehamn.
The archipelago is the smallest province of Finland, comprising 0.5% of Finland's population and 0.49% of land area.
Geographically, the islands consist of the main island Fasta Åland (literally "Firm Åland"), where 90% of the population resides, and an archipelago to the east that consists of over 6,500 skerries and islands. Fasta Åland is separated from the coast of Sweden by 40 kilometres (25 miles) of open water to the west. In the east, the Åland archipelago is virtually contiguous with the Finnish Archipelago Sea. Åland's only land border is located on the uninhabited skerry of Märket, which it shares with Sweden.
Due to Åland's autonomous status, the powers exercised at the provincial level by representatives of the central state administration in the rest of Finland are largely exercised by the Government of Åland in Åland
Politically, Åland Islands forms an autonomous, demilitarized, Swedish-speaking region and historical province of Finland. The capital is Mariehamn. The Åland Islands are governed according to the Act on the Autonomy of Åland and international treaties. These laws guarantee the islands’ autonomy from Finland, which has ultimate sovereignty over them, as well as a demilitarized status.
Read more on Åland Islands from a pdf document Åland in brief
The Provincial Autonomy of the Åland Islands
Diagram of the public administration from Suomi.fi
Relations with EU
The autonomous status of the islands was affirmed by a decision made by the League of Nations in 1921 following the Åland crisis. It was reaffirmed within the treaty admitting Finland to the European Union. By law, Åland is politically neutral and entirely demilitarised, and residents are exempt from conscription to the Finnish Defence Forces. The islands were granted extensive autonomy by the Parliament of Finland in the Act on the Autonomy of Åland of 1920, which was later replaced by new legislation by the same name in 1951 and 1991.
In connection with Finland's admission to the European Union, a protocol was signed concerning the Åland Islands that stipulates, among other things, that provisions of the European Community Treaty shall not force a change of the existing restrictions for foreigners (i.e., persons who do not enjoy "home region rights" (hembygdsrätt) in Åland) to acquire and hold real property or to provide certain services, implying a recognition of a separate nationality.
Most inhabitants have Swedish (the sole official language) as their first language: 91.2% in 2007, and 5.0% speak Finnish.
Education in Åland Islands
(mainly sourced from: Norden)
The Finnish Education system and policies are used also in Åland Islands. The education system consists of preschool and basic education, upper secondary and vocational schools as well as polytechnics and universities. The Finnish Education system is described in Finland.
The language of instruction in publicly financed schools is Swedish, but an Ålandic municipality is free to provide teaching of Finnish. (In the rest of Finland, bilingual municipalities provide schooling both in Finnish and in Swedish.)
Below are listed educational organizations in Åland Islands. Each organization contains a link to its website (in Swedish only):
Upper secondary and vocational schools
- Ålands folkhögskola
- Ålands lyceum
- Ålands handelsläroverk
- Ålands hotell- och restaurangskola
- Ålands sjömansskola
- Ålands vårdinstitut
- Ålands yrkesskola
Higher education
Other education
- Öppna högskolan på Åland
- Medborgarinstitutet (Medis)
- Ålands musikinstitut
- Bel Canto r.f.
- Ålands läroavtalscenter
Relevant websites
- Statistics Åland
- http://www.government.ax/
- Official co-operation in the Nordic region
- Ministry of Education and Culture in Åland
> Finland
> Countries
> Main Page
For OER policies and projects in Aland Islands see Aland Islands/OER
