Welcome to the Virtual Education Wiki ~ Open Education Wiki
Thailand: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
(tidy) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
'''''This report uses the new [[POERUP]]-compatible version of the [[VISCED]] templat''e''' | |||
''By [[Paul Bacsich]] and [[Thomas Salmon]]'' | ''By [[Paul Bacsich]] and [[Thomas Salmon]]'' | ||
| Line 390: | Line 393: | ||
> [[Countries]] <br> >> [[Main Page]] | > [[Countries]] <br> >> [[Main Page]] | ||
[[Category:Thailand]] [[Category:Association_of_Southeast_Asian_Nations]] [[Category:Asia]] [[Category:Countries_with_Programmes]] [[Category:VISCED]] [[Category:POERUP]] | [[Category:Thailand| ]] | ||
[[Category:Association_of_Southeast_Asian_Nations]] | |||
[[Category:Asia]] | |||
[[Category:Countries_with_Programmes]] | |||
[[Category:VISCED]] | |||
[[Category:POERUP]] | |||
Revision as of 13:44, 8 February 2013
This report uses the new POERUP-compatible version of the VISCED template
By Paul Bacsich and Thomas Salmon
For entities in Thailand see Category:Thailand
Partners and experts in Thailand
None.
Thailand in a nutshell
(sourced from http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Thailand)
Thailand, in full the Kingdom of Thailand (Thai: ราชอาณาจักรไทย - Ratcha Anachak Thai) is an independent country that lies in the heart of Southeast Asia.
- The country's official name was Siam (Thai: สยาม RTGS: Sayam) until 1939 when it was changed to Thailand. It was renamed Siam from 1945 to 1949, after which it was again renamed Thailand. Also spelled Siem, Syâm or Syâma, it has been identified with the Sanskrit Śyâma (श्याम, meaning "dark" or "brown"). But the names Shan and A-hom seem to be variants of the same word, and Śyâma is possibly not its origin but a learned and artificial distortion.
Thailand is bordered to the north by Laos and Burma, to the east by Laos and Cambodia, to the south by the Gulf of Thailand and Malaysia, and to the west by the Andaman Sea and Burma. Its maritime boundaries include Vietnam in the Gulf of Thailand to the southeast and Indonesia and India in the Andaman Sea to the southwest.
Thailand is the world's 50th largest country in terms of total area (slightly smaller than Yemen and slightly larger than Spain), with a surface area of approximately 513,000 km2 (198,000 sq mi), and the 21st most-populous country, with approximately 63 million people.
The capital and largest city of Thailand is Bangkok. It is also the country's centre of political, commercial, industrial and cultural activities.
About 75% of the population is ethnically Thai, 14% is of Chinese origin, and 3% is ethnically Malay; the rest belong to minority groups including Mons, Khmers and various hill tribes. There are an estimated 2.2 million legal and illegal migrants in Thailand.[4] Thailand has also attracted a small number of expatriates from developed countries in the West. The country's official language is Thai.
Thailand is one of the most devoutly Buddhist countries in the world. The national religion is Theravada Buddhism which is practiced by more than 94.7% of all Thais. Muslims make up 4.6% of the population and 0.7% belong to other religions.[6] Culture and traditions in Thailand are significantly influenced by India, as are Burma, Laos and Cambodia.
Thailand is a constitutional monarchy with King Bhumibol Adulyadej, the ninth king of the House of Chakri, as the ruling monarch. The King has reigned for more than sixty-three years, making him the longest reigning Thai monarch and the longest reigning current monarch in the world. The King is recognized as the Head of State, the Head of the Armed Forces, the Upholder of the Buddhist religion, and Defender of the Faith. Thailand is the only country in Southeast Asia that has never been colonized by a European power.
Thailand experienced rapid economic growth between 1985 and 1995 and today is a newly-industrialized country with an emphasis in exports and a flourishing tourism industry, thanks to various world-famous tourist destinations such as Pattaya, Bangkok, and Phuket.
Thailand is divided into 75 provinces (จังหวัด, changwat) , which are gathered into 5 groups of provinces by location. There are also 2 special governed districts: the capital Bangkok (Krung Thep Maha Nakhon) and Pattaya, of which Bangkok is at provincial level and thus often counted as a 76th province.
Each province is divided into districts and the districts are further divided into sub-districts (tambons). As of 2006 there are 877 districts (อำเภอ, amphoe) and the 50 districts of Bangkok (เขต, khet). Some parts of the provinces bordering Bangkok are also referred to as Greater Bangkok (ปริมณฑล, pari monthon). These provinces include Nonthaburi, Pathum Thani, Samut Prakan, Nakhon Pathom and Samut Sakhon. The name of each province's capital city (เมือง, mueang) is the same as that of the province: for example, the capital of Chiang Mai province (changwat Chiang Mai) is Mueang Chiang Mai or Chiang Mai.
Education in Thailand
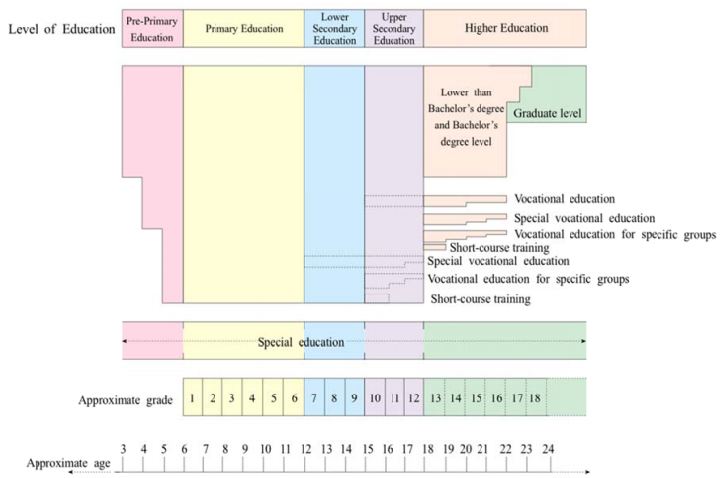
Basic education in Thailand consists of six years of primary education, three years of lower secondary, and three years of upper secondary education.. Students can choose vocational tracks in upper secondary schools and sometimes also in lower secondary schools. Primary education is close to universal in Thailand. Education is compulsory up to and including Grade 9, and the government provides free education through to Grade 12.
Schools in Thailand
Structure of Thai Education System (UNESCO 2011)
Thailand enjoys a high level of literacy, and education is provided by a well organized school system of kindergartens, primary, lower secondary and upper secondary schools, numerous vocational colleges, and universities. The private sector of education is well developed and significantly contributes to the overall provision of education which the government would not be able to meet through the public establishments. Thailand has never been colonized, and its teaching relies heavily on rote rather than on student centred methodology. Education in a modern sense is therefore relatively recent and still needs to overcome some major cultural hurdles in order to ensure further development and improvement to its standards.
The establishment of reliable and coherent curricula for its primary and secondary schools is subject to such rapid changes that schools and their teachers are not always sure what they are supposed to be teaching, and authors and publishers of textbooks are unable to write and print new editions quickly enough to keep up with the volatile situation.
The school structure is divided into four key stages: the first three years in elementary school, Prathom 1 - 3, are for age groups 6 to 8, the second level, Prathom 4 through 6 are for age groups 9 to 11, the third level, Matthayom 1 - 3, is for age groups 12 to 14. The upper secondary level of schooling consists of Matthayom 4 - 6, for age groups 15 to 17 and is divided into academic and vocational streams. There are also academic upper secondary schools, vocational upper secondary schools and comprehensive schools offering both academic and vocational tracks. Students who choose the academic stream usually intend to enter a university. Vocational schools offer programs that prepare students for employment or further studies.
Admission to an upper secondary school is through an entrance exam. On the completion of each level, students need to pass the NET (National Educational Test) to graduate. Children are required only to attend six years of elementary school and at least the first three years of high school. Those who graduate from the sixth year of high school are candidates for two decisive tests: O-NET (Ordinary National Educational Test) and A-NET (Advanced National Educational Test).
Public schools are administered by the government, and the private sector comprises schools run for profit and fee-paying non-profit schools which are often run by charitable organisations - especially by Catholic diocesan and religious orders that operate over 300 large primary/secondary schools throughout the country. Village and sub-district schools usually provide pre-school kindergarten (anuban) and elementary classes, while in the district towns, schools will serve their areas with comprehensive schools with all the classes from kindergarten to age 14, and separate secondary schools for ages 11 through 17.
Due to budgetary limitations, rural schools are generally less well equipped than the schools in the cities and the standard of instruction, particularly for the English language, is much lower, and many high school students will commute 60 - 80 kilometres to schools in the nearest city.
The school year in Thailand is divided into two semesters, and for primary and secondary schools generally begins on or around 15 May, to end in March, and from June to March for higher education. It has a two or three week break between the two terms in September. The long summer break coincides with the hottest part of the year and Songkran, the traditional Thai new year celebrations. Schools enjoy all public and Buddhist religious holidays and Christian and international schools usually close for the Christmas-New Year break.
The issue concerning university entrance has therefore also been in constant upheaval for a number of years. Nevertheless, education has seen its greatest progress in the years since 2001; most of the present generation of pupils and students are computer literate, and knowledge of English is on the increase at least in quantity if not in quality.
Vocational Education
Currently 412 colleges are governed by the Vocational Education Commission (VEC), of the Ministry of Education with more than a million students following the programs In 2004. Additionally, approximately 380,000 students were studying in 401 private vocational schools and colleges.
Technical and vocational education (TVE) begins at the senior high school grade where students are divided into either general or vocational education. At present, around 60 per cent of students follow the general education programmes. However, the government is endeavouring to achieve an equal balance between general and vocational education.
Three levels of TVE are offered: the Certificate in Vocational Education (Bor Wor Saw) which is taken during the upper secondary period; the Technical Diploma (Bor Wor Chor), taken after school-leaving age, and the Higher Diploma on which admission to university for a Bachelor degree programme may be granted. Vocational education is also provided by private institutions.
Dual Vocational Training (DVT)
Essential to DVT is the active participation of the private sector. In 1995, based primarily on the German model,[8] the Department of Vocational Education launched the initiative to introduce dual vocational training programmes which involve the students in hand-on training in suitably selected organisations in the private sector.
DVT is a regular element of the DoVE "Certificate" and "Diploma" program. The training is for a period of three years with more than half of the time devoted to practical training on-the-job, spread over two days a week, or for longer periods depending on the distance, throughout the semesters.
Two levels of DVT are offered: the three-year Certificate level for skilled workers where students and trainees are admitted at the age of 15 after completing Matthayom 3 (Grade 9); and the two-year Diploma technician level for students who have graduated with the Certificate of Vocational Education after 12 years of formal education.
In the scheme, vocational, unlike regular internships, where students may be assigned to work on unpaid irrelevant jobs, the cooperative education programme enables the students of the vocational schools to do field work while benefiting from an allowance to cover living expenses or free accommodation, and compensation for their contributions made towards the company's income and profits as temporary employees.
Schools collaborate directly with the private sector in drafting action plans and setting goals for students to meet. Generally, the company will offer permanent employment to the trainees on graduation and successful completion of the programme. Conversely, companies that recruit trainees from among young people who have completed a minimum of nine years at school may enroll their employees with a Technical or Vocational College where they are taught vocational subjects as the theoretical background to the occupational field in which they are being trained.
Further and Higher Education
Universities in Thailand
The established public and private universities and colleges of higher education are under the jurisdiction of the Ministry of University Affairs in both the government and private sectors. These offer excellent programmes especially in the fields of Medicine, the Arts, Humanities, and Information Technology, although many students prefer to pursue studies of law and business in Western faculties abroad or in those which have created local facilities in Thailand.
During the first years of the 21st century, the number of universities increased dramatically on a controversial move by the Thaksin government to rename many public institutes as universities.
For a full list see http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/List_of_universities_in_Thailand
In the Times Higher Education Supplement World University Rankings 2004, Chulalongkorn University was ranked 46th in the world for social sciences and 60th for biomedicine. In September 2006, three universities in Thailand were ranked "Excellent" in both academic and research areas by Commission on Higher Education. Those universities are:
- Chiang Mai University
- Chulalongkorn University
- Mahidol University
In 2012 King Mongkut's University of Technology Thonburi (KMUTT), one of Thailand's leading science and technology institutions and one of nine research universities in the country was the only Thai educational institution to figure among the top 400 universities overall in the world university rankings for that year.
Polytechnics in Thailand
Over half of the provinces have a government Rajabhat University, formerly Rajabhat Institute, traditionally a Teacher Training College.
Colleges in Thailand
Education reform
Schools
Despite successes in increasing participation and expansion at all levels of education in Thailand educational issues of quality across all levels of education are seen to affect the competitiveness of Thai labour force. Key reform initiatives for example seek to address the quality of education in primary and secondary schools in rural areas and in tertiary institutions in urban areas.
Approximately 50 % of children are reported to have achieved Level 1 or below out of six learning levels of PISA 2009 in all three subjects, Reading, Mathematics and Science. It is believed that the main reason of poor outcomes for Thai students is due to the lack of quality educators. Attracting the highest quality individuals to the teaching field and improving teacher training are key issues. Key reform initiatives also aim to introduce a more student-centered learning approach at all levels of education
Post-secondary
Higher education in Thailand has changed dramatically over the past four decades, reflecting the three major global trends of massification, privatization, and internationalization. In 2010 the country had a total of 150 higher education institutions and 19 community colleges with approximately 2 million students.
In the long term reform priorities reflect the needs of an ageing population supported by a declining population in the workforce and a critical need within industry for highly-skilled technical workers. According to the 15-year Long Range Plan on Higher Education (2008-2022) it is projected that demographic changes will result in a decrease of participation in higher education, shifting the main focus of higher education reform towards quality issues.
Current programmes such as the “One District, One Scholarship” in fact seek to increase the access of disadvantaged group of students to higher education. However, reform priorities also focus on the improvement of quality, performance-based funding and increasing collaboration between the universities and the private sector. This is reflected in plans to increase the ratio of vocational to general academic track at the secondary education level from the current proportion of 40:60 to 60:40 in the next 10 years so as to produce sufficient numbers of graduates from TVET with technical skills and knowledge.
Administration and finance
Schools
The Ministry of Education (MoE) has overall responsibility for the regulation of Thai education.The Thai government’s general commitment to decentralization is reflected in the Local Administrative Bodies Act (Decentralization Act of 1999) which requires that 35% of the national budget be delegated to although Local Administration Organizations (LAOs) and gives local authorities the power to levy local taxes.
The MoE shares responsibilities for the regulation of the TVET sector with the Ministry of Labour (MoL), which oversees the National Skill Standards and Testing System and the evaluation of workplace learning. The Office of the Private Education Commission, (OPEC) which is part of the MoE, has administrative responsibilities in relation to private institutions of higher education, as well as the oversight of private schools
Post-secondary
Public higher education in Thailand falls under the Office of the Higher Education Commission (OHEC), which is part of the Ministry of Education (MoE). OHEC is directly responsible for the administration of all public higher education institutions, as well as overseeing the performance of private institutions.
Quality assurance, inspection and accreditation
Schools
The Office for National Education Standards and Quality Assessment (ONESQA) is responsible for assessing all Thai educational institutions, both public and private and all levels of education from pre-school to graduate education, with the aim to assist educational to improving their performance and standards.
Post-secondary
In 1999, the Ministry of Education set up a quality assurance and accreditation system covering both internal and external quality assurance in Higher Education. It has removed quality assurance from OHEC’s mandate, instead making ONESQA responsible for all external quality assurance.
Although internal quality assurance is the responsibility of each individual education institution, all institutions are required to submit to external assessment by ONESQA as part of a five-year cycle. Two previous five year cycles (2001–2005 and 2006–2010) have been completed, and the third cycle for 2011–2015 has begun. The MoE in 2003 also proposed a set of regulations for setting up internet-based programmes in universities
Information society
Internet in Thailand
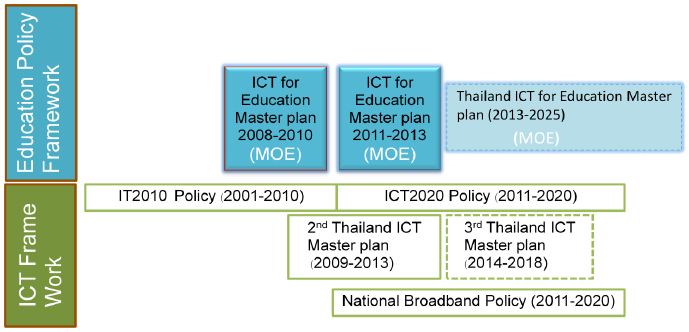
Thailand’s Second Information and Communication Technology Master Plan (2009-2013) ensures continuity within the policy framework of IT 2010 and the First ICT Master Plan by continuing to emphasize the development and application of ICT for e-Commerce, e-Industry, e-Education, e-Society and e-Government. It focuses on infrastructure and knowledge building to bridge the digital divide and to facilitate a shift towards a knowledge-based economy. Initiatives seek to promote the creation of online creative communities and a learning society, creating web portals, diverse electronic content, and social groupings that are robust. For example learning networks have been set up among educational institutions, temples, libraries and community learning centers in order to facilitate access to useful learning and information resources.
Thailand’s National Broadband Policy aims to bring 80% of Thai people to access broadband within the year 2015 and 95% within the year 2020. The current ICT 2020 policy also focuses on e-Government, broadband for SMEs, schools, e-health. disaster warning via broadband services, and energy saving and green ICT.
In terms of infrastructure progress has been made by The Ministry of Information and Communication Technology (MICT) on grid computing, next-generation Internet Protocol (IPv6) development, broadband wireless, computer security, and Web 2.0 and Web services. In 2013 mobile users in Thailand will be able to experience much faster data transfer speeds and improved access to multimedia services with the expansion of 3G mobile service deployment.
Educational internets in Thailand
SchoolNet
In the first year of its implementation in 1995, SchoolNet successfully achieved the target of getting 20 schools connected. Later on in 1999, this number gradually increased to 1,500, which was the maximum capacity of the access infrastructure in the first phase. By 2002, 4,600 schools were connected to SchoolNet.
UniNet
Thailand Education and Research Network (UniNet) initiated in 1996 linking 24 universitiies and 25 IT campuses. Renamed as EdNET in 2001, it was expanded to include Rajabhat Universities and polytechnics.
NEDNet
From 2010 SchoolNet merged with Ednet. In 2012 it became NEDNet, integrating UniNet with all education networks including MoE Net (primary & secondary) and VEC Net (vocation education). NEDNet also hosts the Thai Library Integrated System (ThaiLIS). This is a database conecting the central university library system, regional libraries and records, with a reference database of theses and a digital collection of e-books. Academic and government institutions are connected through networks for research in education (ThaiREN) along with the Thai Social / Scientific Academic and Research Network (ThaiSARN).
Thai Telecenters
Thai telecentres and community ICT learning centres constitute a wide informal learning network. They run information literacy projects and have expanded from 20 centers in 2007 to 2,500 Centers in 2012. The main purpose is to provide ICT skills and knowledge to marginalised groups, such as women, ethnic minorities and people living with HIV/AIDS.
Examples of organisations supporting telecentres for different objectives include the Community Information Centre (supported by Healthcare Management College, Chulalongkorn University), Thai Rural Community Development Network (supported by the Student Telecentre Organisation).
One Laptop Per Child (OLPC)
In 2013 Thailand will be completing shipment of the world’s largest education tablet distribution deal to date with the Chinese firm Shenzhen Scope, aiming to provide over 1.5 milllion tablets to 6 and 12 year old students. Current test projects such as the pilot ‘Braincloud solution’ involve cloud computing using tablet devices to access learning resources and courseware using virtual fibre technology. In this pilot project ‘Brain Tower’ stations will act as servers and provide a learning management system (LMS).
Copyright law in Thailand
ICT in education initiatives
Virtual initiatives in schools
Distance learning support by TV for school students
Established in 1996, DLTV currently broadcasts a total of 15 educational channels from the Wang Klaikangwon Palace School, Hua-Hin. It combines primary and secondary curriculum from grade 1 to grade 12 and also includes vocational training, community education and university education. It provides educational benefits and equal opportunities to Thai students nationwide especially in the remote and far-reaching areas of the country where the lack of teachers is still a major challenge to the educational system. It broadcasts via the Ku-band beam on the THAICOM 5 satellite to more than 17,000 schools across the country and also to other viewers who subscribe to satellite providers of commercial television. In December 2008, the Thaicom Public Company Limited, Asia's leading commercial satellite operator and the operator of the IPSTAR satellite broadband system, announced it has renewed a 10-year contract with the Distance Learning Education via Satellite Foundation of Thailand (DLF) for three-quarters of one Ku-band transponder on the Thaicom 5 satellite to broadcast DLTV channels,
The launch of the third phase of this project, the DLF eLearning network took place on 2 May 2002. It has more recently served as a model for distance learning systems in Papua New Guinea and its transmission is used in the nearby countries of Vietnam, Lao, Myanmar, Cambodia and China.
Thai Teachers TV:
Burapha University's Faculty of Education is the main agency tasked with preparing content for Thai Teachers TV under a project sponsored by the Office of the Higher Education Commission. Since it began in April 2010 it has expanded to a membership of 172,433 teachers in all 77 provinces, with 71 universities using Teachers TV along with 9 model universities in 9 regions. In 2012 approximately 30% of its content was developed by local teachers in Thailand while the rest was taken from the United Kingdom's Teachers TV.
OER initiatives in schools
Virtual initiatives in post-secondary education
See the following principal initiatives:
- Thai Open University (STOU)
- Ramkhamhaeng University (public)
- Assumption University (private).
ASEAN Virtual Institute of Science and Technology (AVIST)
AVIST is a virtual learning network for continuing professional development and advanced studies in science and technology, offering opportunities for real practical experience at participating universities. It was set up in 2005 and is hosted at the Asian Institute of Technology (AIT) in Bangkok.
AVIST is also intended to be a virtual institute without a physical campus, based on the pilot site created in 2002. At the initial stages each ASEAN country offered some courses which are appropriate for sharing among insitutions. Steps towards joint accreditation and joint curricula are being developed. Courses are developed using VClass, an open source e-learning platform designed for delivering online courses through virtual classroom learning
OER initiatives in post-secondary education
Thailand Cyber University (TCU) consortium
The TCU government initiative seeks to encourage the sharing of educational resources within the Thai university sector under the Commission on Higher Education. Its mission includes expanding access, establishing a knowledge center to encourage life-long learning, improving and developing the quality of higher education, creating knowledge management and the sharing of educational resources among educational institutions efficiently and effectively.
The project acts as a body to initiate, cooperate, and support e-Learning management in higher educational institutes in order to create high quality standards for e-learning and shareable courseware to develop a national infrastructure for the delivery of blended and distance learning. Thailand Cyber University has successfully delivered a range of certificate level online courses in subjects related to the development of online courseware. Currently formal education, informal courses and study guides as well as short certificated courses are available. It hosted the 4th Asia Regional OpenCourseWare and Open Education Conference (AROOC) in January 2013.
At present the Thailand Cyber University Open Courseware site contains two courses available in OCW format: Accessible Courseware Development and e-Learning Thai Language.
Chulalongkorn University (CU)
The Faculty of Engineering at Chulalongkorn University is a partner of Thailand Cyber University and is tasked with the responsibility to produce e-learning materials for the Software Development Degree Program, which is a 100% distance learning program. It also hosts Chula Open Courseware (OCW) which is a twin project of MIT OCW. In addition to translating MIT materials and distributing them online, the Faculty of Engineering develops class materials and provides them free-of-charge on the web through Chula OCW.
Chulalongkorn University also is part of a wider distance learning network in conjunction with the World Bank Global Distance Learning Network (GDLN). CU-GDLN was established as part of the Center of Academic Resources network (CARNET) at CU.
E-learning systems used in Thai Higher Education and Government Institutions
| Type of LMS | Institution | URL |
| Moodle | Chiangmai University | http://cmuonline.cm.edu |
| Yonok University | http://class.yonok.ac.th/ | |
| Khon Kaen University | http://learning.kku.ac.th/ | |
| Ubon Ratchathani University | http://csit.sci.ubu.ac.th/moodle/ | |
| Suranaree University of Technology | http://sutonline.sut.ac.th/ | |
| Rangsit University | http://elearning.rsu.ac.th/ | |
| Mahidol University | http://www.sc.mahidol.ac.th/e_learning/moodle.htm | |
| King Mongkut’s University of Technology North Bangkok | http://www.ssru.ac.th/kmutnb/panita/moodle/ | |
| North Bangkok College | http://e-learning2.northbkk.ac.th/nbc/ | |
| Burapha University | http://course.buu.ac.th/moodle/index.php | |
| Prince of Songkhla University | http://lms.psu.ac.th/ | |
| Thaksin University | http://tsl.tsu.ac.th/ | |
| Walailak University | http://mlearning.wu.ac.th/ | |
| ATutor | Naresuan University | http://learning.nu.ac.th/ |
| Sukkothai Thammathirat University | http://www.stou.ac.th/elearning/home/ | |
| Srinakharinwirot University | http://sot.swu.ac.th/ | |
| King Mongkut’s University of Technology Ladkrabang | http://lcms.kmitl.ac.th/login.php | |
| Claroline | Thammasat University | http://e-learning.tu.ac.th/ |
| Thai LMS | Thailand Cyber University / Ministry of Education | http://www.thaicyberu.go.th/ |
| National Science and Technology Development Agency | http://www.thai2learn.com/index.php | |
| Nation Electronic and Computer Technology Center (NECTEC) | http://www.learnsquare.com/ | |
| Chulalongkorn University | http://www.chulaonline.com/ | |
| Kasetsart University | http://course.kps.ku.ac.th/course/login/ilogins.php | |
| Ramkhamhaeng University | http://eu.ram.edu/elearning/index.php | |
| Silpakorn University | http://elearning.su.ac.th/elearning/index.php | |
| Bangkok University | http://elearning.bu.ac.th/index2.html | |
| Assumption University | http://www.elearning.au.edu/ | |
| Asian Institute of Technology | http://www.vclass.net/ |
Lessons learnt
References
1. ICDE (2012). Country Profile Thailand. Retrieved 20/01/ 2013, from http://www.icde.org/projects/regulatory_frameworks_for_distance_education/country_profiles/thailand/
2. Akhtar, S., & Arinto, P. (Eds.). (2010). Digital Reveiw of Asia Pacific 2009-2010 (Vol. Thailand): Sage Publications Pvt. Limited. Retrieved 20/01/ 2013, from http://www.digital-review.org/uploads/files/pdf/2009-2010/chap-40_thailand.pdf
3. UNESCO. (2011). UNESCO National Education Support Strategy (UNESS) Thailand. Retrieved 20/01/ 2013, from http://doc.iiep.unesco.org/cgi-bin/wwwi32.exe/%5Bin=epidoc1.in%5D/?t2000=032294/(100)
4. UNESCO (2012). Thailand Education System Profile. Retrieved 20/01/ 2013, from http://www.unescobkk.org/education/resources/country-profiles/thailand/
5. Khaopa, W. (September 26, 2011). Teachers TV Making it work for Thailand. The Nation. Retrieved 20/01/2013, from http://www.nationmultimedia.com/2011/09/26/national/Teachers-TV-making-it-work-for-Thailand-30166121.html.
6. Vajarodaya, K. (2007). Twelfth Anniversary of the Distance Learning Foundation: Free and Open Low-Cost Distance Education via Satellite and Internet, Wang Klaikangwon Model Paper presented at the 4th International Conference on eLearning for Knowledge-Based Society, Muang Thong Thani. Retrieved 20/01/2013, from http://www.elearningap.com/eLAP2007/Proceedings/P03eLearningAP_TwelfthAnniversary.pdf
7. Garun, N. (2012). Thailand signs the world’s largest educational tablet distribution deal. Retrieved 20/01/2013, from http://www.digitaltrends.com/international/thailand-signs-the-worlds-largest-educational-tablet-distribution-deal/#ixzz2IiwApeVy
8. Rueangprathum, A., Philuek, W., & Fung, C. C. (2009). e-Learning in Thailand – a survey of current situation and trend. Murdoch University & Suratthani Rajabhat University. Retrieved 25/01/2013, from http://www.academia.edu/936956/e-Learning_in_Thailand_-_a_survey_of_current_situation_and_trend
9. Baggaley, J., Belawati, T., & Malik, N. (2006). Building collaborative ODL research: the PANdora projects. Paper presented at the Information and Communication Technology for Social Development: An International Symposium, Jakarta.