Welcome to the Virtual Education Wiki ~ Open Education Wiki
France from Re.ViCa: Difference between revisions
Grego lucas (talk | contribs) |
(tidied authors and links and decategorised) |
||
| (42 intermediate revisions by 7 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
''by [[Gregory Lucas]] and [[Widad Benhabiles]]. with additional contributions by other members of [[Re.ViCa]]'' | |||
[[ | For the main entry on this country see [[France]] | ||
For entities in France see [[:Category:France]] | |||
== Partners situated in France == | |||
* [[Université Louis Pasteur]] | |||
[[Image:France map ULP.JPG|thumb|left|250px|(map cf: Eugris)]] | |||
==France in a nutshell == | |||
France is a country whose metropolitan territory is located in Western Europe and that also comprises various overseas islands and territories located in other continents. After [[Russia]], France is the largest country in Europe (643,427 km² with its overseas ''départements''). With a population of over 63 million inhabitants, France is the second most populous country in Western Europe (after [[Germany]]). Its territory is split into (administrative) regions. 22 of them are in Metropolitan France (the part of the country that is in Europe). | |||
French is the official language of France, but each region has its own unique accent; in addition to French, there are several other languages of France traditionally spoken, although use of these languages has greatly decreased over the past two hundred years. French is also an official language in 41 countries, most of which form what is called in French La Francophonie, the community of French speaking nations. | |||
== French education policy == | |||
The current priorities of the ministry responsible for national education, the [[Ministre de l'Éducation nationale]], are conveyed in a series of measures in accordance with the law of 23 April 2005. This involves, in particular: | |||
* Defining the common core | |||
* Personalised academic achievement programmes (PPRE) | |||
* Revival of priority education | |||
* Giving marks for school life | |||
* The development of apprenticeship | |||
* Improving education for disabled pupils | |||
* Teacher training | |||
For more details please see [[French education policy]] | |||
Moreover secularism is an important principle in French education. It is based on the Napoleonic concordat of 1801 and the separation law of Church and State in 1905. School must be neutral and nondenominational. For example, religion does not constitute a teaching subject, teachers do not have the right to talk of their personal beliefs and all religious propaganda is banned within the school establishment. The law 2004-228 of 15 March 2004 stipulates that "in state schools, collèges and lycées, pupils are forbidden to wear signs or clothes which conspicuously show any religious affiliation." | |||
== French education system == | |||
French educational system is highly centralized, organized, and ramified. It is divided into | French educational system is highly centralized, organized, and ramified. It is divided into four different stages: | ||
* Pre-primary education | |||
* primary education (enseignement primaire); | * primary education (enseignement primaire); | ||
* secondary education (enseignement secondaire); | * secondary education (enseignement secondaire); | ||
* higher education (enseignement supérieur). | * higher education (enseignement supérieur). | ||
Primary and secondary education are | [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Education_in_France Education in France] ''From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia'' | ||
( | |||
[[Image:French_academies.png]] | |||
[[Image:French education system.jpg]] | |||
=== Pre-primary education === | |||
France has a long tradition of ‘pre-elementary’ education. Despite the fact that it is not compulsory, all children attend the école maternelle (nursery school) from the age of 2 to 5, though provision to children aged 2 is based on availability. | |||
Public-sector ‘pre-elementary’ or ‘nursery’ schools are the responsibility of the education ministry and attendance at them is free of charge. In the private schools that cater for close to 2.4 % of children, parents pay a share of the tuition fees. Nursery schools are indeed schools in the full sense with programmes of teaching and learning activity. The main educational areas of activity contribute to the overall development of children and prepare them for ‘elementary’ school. | |||
=== Compulsory education === | |||
Education is compulsory between the ages of 6 and 16. It is divided into three stages: | |||
* Primary education (école primaire) Ages 6-11 | |||
* Lower secondary education (collège) Ages 11-15 | |||
* General and technological lycée (lycée général et technologique) or vocational lycée (lycée professionnel) Compulsory only between ages 15 and 16 | |||
The enrolment of pupils in state schooling is based on a ‘sectorial’ principle: pupils are normally registered in the primary school, ''collège'' or ''lycée'' of the geographical area in which their parents live. State education is free of charge. Private education is mostly Roman Catholic. Although the French constitution proclaims that the state is secular, a 1959 law allows private establishments to sign government contracts that procure financial support in exchange for some control. | |||
The ‘elementary’ school curriculum concentrates on the basic skills of reading, writing and arithmetic, as well as on physical education (normal motor skills, etc.) and enhancing awareness and sensitivity. The lower secondary education curriculum consists of eight or nine compulsory subjects depending on the year of study, and becomes increasingly diversified with the inclusion of optional subjects. Primary school classes have a single teacher for all subjects, whereas secondary school classes have different teachers for each subject. The education ministry determines school curricula and the aims underlying the acquisition of knowledge and skills by pupils. Teachers choose their own teaching methods and school textbooks. | |||
On completion of their ''collège'' schooling, pupils are awarded a brevet (national certificate) on the basis of their marks in the final two years and a national examination. The brevet is not a compulsory qualification and continuation of their schooling in a lycée is not dependent on their passing the examination. | |||
=== Post-compulsory education/upper secondary and post-secondary level === | |||
On completion of collège, pupils are offered three educational options: | |||
** general studies; | |||
** technological studies; | |||
** vocational training. | |||
At the ''lycée d’enseignement général et technologique'', which caters for pupils who have chosen either of the first two possibilities, provision lasts three years and leads to the general and technological baccalaureate examination that may be chosen among the three general categories (economic and social, literary, or scientific) or among the seven technological categories. The ''lycée professionnel'' prepares students in two years for the first level of vocational qualification, corresponding to the ''certificat d’aptitude professionnelle'' (CAP) or ''brevet d’études professionnelles'' (BEP). These qualifications are designed to provide direct access to employment including in-company placements or may lead to a vocational baccalaureate in one of 48 specialised fields on offer. The baccalaureate, whether general, technological or vocational, gives access to higher education. | |||
''Adapted from'' : [http://eacea.ec.europa.eu/ressources/eurydice/pdf/047DN/047_FR_EN.pdf National summary sheets on education systems in Europe and ongoing reforms-2007] | |||
=== Administration of French education system === | |||
School education comes under the minister responsible for education throughout the country. Free public-sector provision exists alongside education offered by private schools whose population has remained stable for several years, at 2 027 700 (primary and secondary education, 2006). | |||
At the beginning of the 2006/07 academic year, the school population in metropolitan France and its overseas ''départements'' (DOM) for public and private sectors stood at 12.4 million students. In order for the education system to operate, the state employs more that 1.3 million people, 850 000 of whom are public sector teachers. There are almost 2.287 million students in higher education, which employs 147 000 people, 88 000 of whom are teachers in public HEIs. The language of instruction is French. The regional languages are taught as part of the modern languages branch of studies. | |||
Notwithstanding certain decentralisation measures under which responsibility for the construction and maintenance of public-sector school buildings has been entrusted to the local area authorities, the central government has retained a decisive role in the area of educational policy. The ministry responsible for national education draws up in detail the curriculum for each subject and level of education, and provides guidelines for teaching without however obliging teachers to adopt a particular method. It administers the recruitment, training and management of teaching staff, determines the status and regulations of schools, allocating them their appropriate quota of staff. The ministry also organises examinations and awards national qualifications, in particular the baccalaureate which testifies to the satisfactory completion of secondary schooling. | |||
In order to implement this policy and the accomplishment of its numerous management tasks, France is divided into 30 such ''académies'' each headed by a rector acting directly on behalf of the minister. An ''académie'' is the administrative level enabling the regional application of education policies as defined by the government. It allows action to be taken according to local contexts in collaboration with regional groups: ''communes'' (town) for primary education, ''départements'' (district) for ''collèges'' and ''régions'' (province) for ''lycées''. | |||
The system is supervised by several inspectorates. Three general inspectorates are entrusted with very broad responsibilities for evaluation at national level in addition to two regional inspectorates, one that visits primary schools and monitor the performance of teachers, and one responsible for marking and assessing school teachers at secondary level. | |||
== Higher education in France == | |||
''Please visit this external Wikipedia page for a full [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/List_of_colleges_and_universities_in_France List of HEIs in France]'' | |||
Obtaining the baccalauréat is a pre-requisite to being admitted to an institution of higher education. The baccalauréat is a diploma that acknowledges the successful completion of secondary education and the first level of university studies. This is a very important feature of the French education system, one which has several consequences, particularly with regard to university studies and student orientation during the premier cycle (first cycle) at university. | |||
There are four types of programmes in the French tertiary education system: | |||
* University education, | |||
* Preparatory classes for grandes écoles, | |||
* Higher technical education sections, | |||
* Specialised schools or grandes écoles. | |||
Then, depending on the duration involved, there are two types of studies : | |||
* Shorter technical and vocational studies undertaken in university technology establishments (Instituts Universitaires de Technologies) leading to the DUT: Diplôme Universitaire de Technologie), the universities (leading to the DEUST: Diplôme d'Etudes Universitaires Scientifiques et Techniques) or higher secondary establishments (leading to the BTS: Brevet de Technicien Supérieur). Entry into these channels is based on a selection process and account is taken of pupils' record of achievement during their secondary schooling. | * Shorter technical and vocational studies undertaken in university technology establishments (Instituts Universitaires de Technologies) leading to the DUT: Diplôme Universitaire de Technologie), the universities (leading to the DEUST: Diplôme d'Etudes Universitaires Scientifiques et Techniques) or higher secondary establishments (leading to the BTS: Brevet de Technicien Supérieur). Entry into these channels is based on a selection process and account is taken of pupils' record of achievement during their secondary schooling. | ||
* Lengthier studies undertaken at a university or one of the "Grandes Ecoles" (to which entry is after two years of preparation in the Classes Préparatoires aux Grandes Ecoles (CPGE). After admission into these schools, the studies themselves generally last three years and lead to the "diplômes d'écoles". There is no selection for entry into university. Universities issue generic qualifications and also vocational qualifications. Teacher training is also undertaken at university. | * Lengthier studies undertaken at a university or one of the "Grandes Ecoles" (to which entry is after two years of preparation in the Classes Préparatoires aux Grandes Ecoles (CPGE). After admission into these schools, the studies themselves generally last three years and lead to the "diplômes d'écoles". There is no selection for entry into university. Universities issue generic qualifications and also vocational qualifications. Teacher training is also undertaken at university. | ||
Higher education in France also has specialised schools, recruitment being based on the baccalaureate, competitions or dossiers. They concern the paramedical sector (nursing schools, physiotherapists, etc.), the social sector (schools for specialised educators, social assistants, etc.), the arts sector or architecture. Studies vary in duration and lead to state-recognised diplomas or specific school diplomas. | |||
These categories can also be broken down further into: | |||
* those which can be accessed directly with a baccalauréat or an equivalent diploma, involving no pre-entry selection process: university programmes, with the exception of university institutes of technology; | |||
* those which are accessed through a pre-entry selection process: preparatory classes for grandes écoles (CPGE), higher technical education sections (STS), Instituts Universitaires de Technologie (IUT or University institutes of technology) and specialised schools. Selections are made based on an admissions application. The type of baccalauréat earned and the marks obtained by the pupil in the last two years of lycée are determining factors; | |||
* those for which the selection process occurs after the student has obtained a licence. This is the case for IUFM (university teacher training institutes) programmes, Grandes écoles recruiting by competitive examination following two or three years of preparatory classes (CPGE mostly). | |||
''Adapted from'' : [http://eacea.ec.europa.eu/ressources/eurydice/eurybase/pdf/0_integral/FR_EN.pdfEurybase, the Information Database on Education Systems in Europe; The Education System in France 2007/08] | |||
Teacher training is provided at Instituts universitaires de formation des maîtres (IUFM) after 3 years of post-baccalauréat studies. Access to the profession for all levels of education takes place by means of a competitive examination, followed by a practical placement which must be validated by a certificate of competency or successful performance in a professional qualification examination. Those who are successful in competitive examinations for permanent posts are offered teaching positions in an académie. | |||
Two categories of teachers exist at the level of higher education: | |||
1) research teachers: lecturers and university professors who have the dual task of ensuring the development of basic and applied research and of conveying the resulting knowledge to students. They are permanent state employees; | |||
2) other higher education teaching staff: associate or guest professors; second-degree teaching staff in higher education; professors who teach classes préparatoires (CPGE); assistant teachers (which is disappearing); temporary teaching and research assistants; foreign language teachers and lecturers; part-time lecturers and part-time staff. | |||
''Adapted from'' : [http://eacea.ec.europa.eu/ressources/eurydice/pdf/047DN/047_FR_EN.pdf National summary sheets on education systems in Europe and ongoing reforms-2007] | |||
[[Image:French higher education.JPG]] | |||
The amount of the enrolment fees is set each year jointly by the ministry in charge of higher education and the ministry in charge of finance. In the context of the organisation of the European higher education programme, ( LMD) tuition fees have been revised and standardised in order to facilitate student orientation. A single fee has been introduced for each course of study: 165 euros for a licenceprogramme, 215 euros for a master’s programme and 326 euros for a doctoral programme (rates valid for the 2007/2008 academic year). Engineering and paramedical programmes maintain their own registration fees. For engineering degrees, the annual tuition rate for public institutions of higher education under the authority of the Ministry of Higher Education has been set at 512 euros. | |||
Some establishments require additional payments (special fees), which are set by its board of administration. These usually range from 10 €-30 €, but can go as high as 100 € for some services, such as unlimited computer access. Additional fees cover preventive medical costs, athletic and cultural activities, photocopies, and, in some universities, student reception services. A breakdown of fees paid is listed on the student’s university card. | |||
The cost of certain special programmes, like the diplôme d’université(DU), is almost entirely paid for by the student, ranging from 80 € to 650 € (rounded figures valid for the 2005/2006 school year) depending on the course of study. These costs are either mandatory or optional depending on the school. Some universities do not charge them. | |||
Universities have no legal right to increase the national registration fees through additional charges. French law gives schools the possibility of requesting additional fees, but specifies that the request must be clearly indicated as optional. | |||
In France, students benefit from several types of financial aid: scholarships, accommodation and food aid and other financial aids. Since 2001, the proportion of scholarship students in higher education has remained stable at 30%. In 2005, 522,000 students benefited from national education grants (i.e. 1.3% more than in 2004) for a total amount of 1.3 billion Euros. Students benefiting from scholarships based on social criteria represent 95% of supported students. | |||
In September 2007, the minister in charge of higher education presented a "new structure for the funding of student life". This new system, established as part of the "students’ living conditions" project, aims at correcting the injustices and insufficiencies of the current system and recognising students’ merit and international mobility. | |||
=== Universities in France === | |||
French universities are organized by academy because this is how the French educational system is organized. France is divided into thirty-five academies, of which thirty-one host the principal administrative seats of universities. Although the rectors or vice-rectors who head the academies do not have administrative control over the universities, the division into academies is nonetheless important because it governs admissions. Students in France have the right to be admitted to a university in the academy in which they passed the baccalauréat, and in some cases to a university in another specified academy. | |||
''From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia'' [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/List_of_public_universities_in_France List of public universities in France] | |||
Scientific, cultural and professional institutions (EPCSCP): since the enactment of the 1984 Savary law, there are a total of 82 EPCSCPs, thee of which are national polytechnical institutes (INP) in Grenoble, Nancy and Toulouse. | |||
Since 1984, they have been organised into training and research units (UFR). They also include internal institutes and schools such as university institutes of technology (IUT), created in 1966, and professional university institutes (IUP), created in 1994. | |||
=== Polytechnics in France === | |||
[http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/National_Polytechnic_Institutes_(France) The National Polytechnic Institutes] or ''Instituts Nationaux Polytechniques'' (INPs) in France are three consortiums of grandes écoles that offer engineering degrees. They were established in 1970. They are classed together with French universities although they are quite different from the public universities, both in their organization and in the fact that they have competitive admissions. | |||
The three institutions are: | |||
* The National Polytechnic Institute of Toulouse (Institut National Polytechnique de Toulouse or INP Toulouse) | |||
* The Grenoble Institute of Technology (Institut National Polytechnique de Grenoble or INP Grenoble) | |||
* The National Polytechnic Institute of Lorraine (Institut National Polytechnique de Lorraine) | |||
=== Universités de Technologie === | |||
[http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Universities_of_Technology_(France) Universities of Technology] are public institutions awarding degrees and diplomas that are accredited by the French Ministry of Higher Education and Research. Although called "universities", the universities of technology are in fact non-university institutes (''écoles extérieures aux universities'') established since 1972. | |||
They possess the advantage of combining all the assets of the engineering ''Grandes Ecoles'' and those of universities as they develop simultaneously and coherently three missions: education, research and transfer of technology. | |||
They maintain close links with the industrial world both on national and international levels and they are reputed for their ability to innovate, adapt and provide an education that matches the ever changing demands of industry. | |||
This network includes three institutions: | |||
* The University of Technology of Belfort-Montbéliard (Université de Technologie de Belfort-Montbéliard or UTBM) | |||
* The University of Technology of Compiègne (Université de Technologie de Compiègne or UTC) | |||
* The University of Technology of Troyes (Université de Technologie de Troyes or UTT) | |||
=== Grandes Ecoles === | |||
In France [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Grandes_%C3%A9coles Grandes écoles] or Graduate schools (literally in French "Grand Schools" or "Elite Schools") are higher education establishments outside the mainstream framework of the public universities system. Unlike French public universities which have an obligation to accept all candidates of the same region who hold a Baccalauréat, the selection criteria of Grandes écoles rests mainly on competitive written and oral exams, undertaken by students of dedicated preparatory classes. They do not have a large student body (3,000 at the largest establishment; most have a few hundred students each year) and are generally focused on a single subject area, mainly engineering, business or humanities. They have traditionally produced most of France's high ranking civil servants, politicians and executives as well as many scientists and philosophers. | |||
== Higher education reform == | |||
In May 2006, the Commission issued a [http://ec.europa.eu/education/policies/2010/doc/comuniv2006_en.pdf communication] making detailed recommendations on how to modernise higher education in Europe. In its most contested suggestion, the report urged member states to give universities more autonomy and accountability and encouraged governments to "open up universities to the business community". | |||
A French Universities' Freedoms and Responsibilities law to implement EU recommendations on reforming higher education was presented on 24 May 2007 and adopted by the French Parliament in August 2007. The law, set to be implemented over the next five years, will: | |||
* give French universities more autonomy to decide upon their budget and staff (by creating foundations to collect money and devise their own recruitment processes), and; | |||
* enable universities to open their administration to external staff, allowing representatives of the business world to take part in university governance. | |||
While the reform is now under way and has broad support of university presidents, opposition remains among some members of the university community. Lecturers' and students' representatives fear 'privatisation' of the university sector and that the state will stop financing courses it regards as not cost-effective. (…) All students, university staff and the French association of researchers fear that state disengagement could lead to excessive private-sector influence over higher education curricula and unequal development of universities. | |||
The majority students' union Unef claimed law could lead to selection, higher fees, domination by business and increased inequality between universities, and called on its supporters to take action this month. | |||
''Adapted from'' : [http://www.euractiv.com/en/education/french-university-funding-reform-faces-renewed-opposition/article-173586 EurActiv.com] | |||
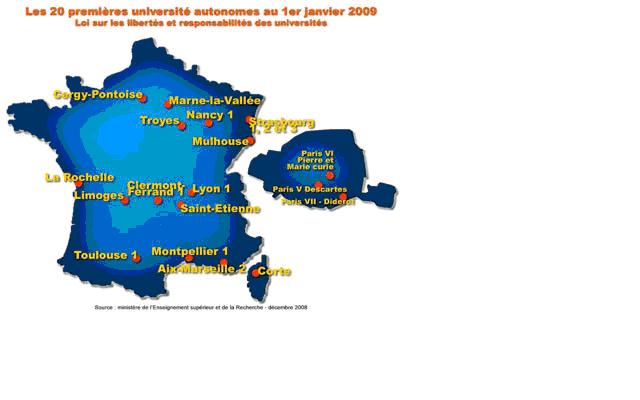
[[Image:French autonomous HEIs.JPG]] | |||
In addition, the reforms of French higher education in 1968-1971 broke apart several public universities into numerous autonomous successor universities. For example, the University of Paris was split into thirteen universities, Paris I through Paris XIII. These universities have subsequently formed groupings in order to pool resources and better advance their joint activities. Some of these groupings, which typically take the legal form of a groupement d'interêt public, or GIP, are themselves called universities or university centers. In addition to universities, they may include other institutions of higher education and research as well as municipal and regional governments. The process has accelerated with the law of 18 April 2006 on the reform of research in France. This has permitted the creation of tighter groupings called pôles de recherche et d'enseignement supérieur, or PRES. In addition, there are a number of consortia of engineering schools, such as the Grenoble Institute of Technology, that the Ministry of Higher Education and Research lists as if they were universities. | |||
''From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia'' [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/List_of_public_university_systems_and_consortiums_in_France List of public university systems and consortiums in France] | |||
=== The Bologna Process === | |||
Initiated in 1999, adjustments to the higher education system in accordance with the principles of the Bologna Process have been accompanied by a series of regulations published since April 2002 to adapt the French higher education system to the development of the EHEA (European Higher Education Area) for the purpose of implementing the LMD reform (Licence-Master-Doctorat or Bachelor-Master-Doctorate) and promoting the widespread use of ECTS and the Diploma Supplement. | |||
Institutions have begun an overhaul of programmes offered in ECTS credits since 2002, and of the organisation of modular programmes allowing more flexibility and better gradual study guidance of students. ECTS is already used for transfer and accumulation and will be fully implemented by 2007/08 for all programmes related to the LMD system. | |||
Within the framework of the LMD reform, the Diploma Supplement (DS) is being implemented progressively by all HEIs. By 2008, it will be issued automatically by all institutions free of charge, in French and in another language chosen by the institution. | |||
The ''Répertoire national des certifications professionnelles'' (RNCP, or National Repertory for Qualifications), representing the National Framework for Qualifications (diplomas, degrees and certificates), was also introduced in 2002. | |||
In the meantime, the market-oriented Bachelor’s degree, in accordance with the agreed on principle of employability especially for first-level studies, was introduced in 1999. The (market-oriented or research-oriented) Master’s degree was introduced in the 2002/03 academic year and requires 120 ECTS credits after the Bachelor’s degree, i.e. 300 credits after the baccalauréat. | |||
The LMD reform will involve all higher-education institutions (HEIs). Its implementation has been effective since the beginning of the 2006 academic year for all universities. By 2010, it should apply to all HEIs and most of their programmes. Some branches, mostly in the field of medicine and engineering, are still based on the long-cycle structure although architecture studies were reformed in 2005. Moreover a Bachelor’s/Master’s structure does not exist yet at specialised schools that are usually organised as single-cycle studies lasting two years (or up to four years for paramedical studies), plus a second cycle lasting one year (leading to a market-oriented Bachelor’s degree) that is offered for technology studies. | |||
Therefore, the implementation of the LMD reform, which gears the structure of French higher education to the European system by offering three levels of studies (licence/master/doctorat), brings with it a new degree structure for higher education in France: | |||
• Degrees obtained after 2 years of post-baccalauréat studies, corresponding to 120 ECTS: technological university degree (DUT), scientific and technical university degree (DEUST), higher technician's diploma(BTS), or general university degree (DEUG); | |||
• Degrees obtained after 3 years of post-baccalauréat studies, corresponding to 180 ECTS credits: national specialised technology diploma (DNTS), vocational licence and licence; | |||
• Intermediate degree, obtained after 4 years of post-baccalauréat studies, corresponding to 240 ECTS: master's degree; | |||
• Degrees obtained after 5 years of post-baccalauréat studies, corresponding to 300 ECTS credits: master's degree, diplôme d’études approfondies (DEA, or advanced studies degree), diplôme d’études supérieures spécialisées (DESS, or specialised higher studies degree); | |||
• Degrees obtained after post-master's studies, corresponding to 480 ECTS credits: doctorate. | |||
Doctoral studies were also restructured in April 2002 and August 2006. Organized in doctoral schools, they are accessible after graduation with a master degree or by special authorisation to students who have completed the equivalent level of studies abroad or who benefit from the recognition of prior learning. As a general rule, after three years, these studies lead to a PhD’s degree after a thesis defence. The possibility to prepare a PhD within the framework of ‘joint international thesis supervision’ has been widened since 2005. | |||
''Adapted from'' : [http://eacea.ec.europa.eu/ressources/eurydice/pdf/047DN/047_FR_EN.pdf National summary sheets on education systems in Europe and ongoing reforms-2007] | |||
== Administration and finance == | |||
French university funding system has often been criticised for its opacity and complexity. The reform proposes to introduce a more market-oriented approach basing university funding more on universities' performance rather than on the number of registered students. Indeed, the current system pushes universities to enrol more first-year students than they can handle to ensure cash flow. To evaluate performance, several criteria were proposed like to evaluate the amount of outside funding attracted by university research laboratories, namely business sources, or employment and salary levels of students graduated from different universities at intervals of six months and three years, as well as to allocate university funding on the basis of the number of students actually taking exams rather than the number of registered ones. The union argues that cutting funding for those most in need will not help resolve huge rates of failure among students. On the contrary, UNEF argues that the funds for universities recording huge failure rates need to be increased to help them implement more ambitious policies. | |||
''Adapted from'' : [http://eacea.ec.europa.eu/ressources/eurydice/pdf/047DN/047_FR_EN.pdf National summary sheets on education systems in Europe and ongoing reforms-2007] | |||
Funding priorities of Valérie Pécresse, Minister for Higher Education and Research, are: | |||
* Making careers in university teaching and in research more attractive, including improved pay, administrative structures and pensions. | |||
* Encouraging student success, with the aim of halving the first-year failure rate within five years and achieving the objective of 50% of young people attaining licence (bachelor's equivalent) level. State spending per student will rise by EUR 450 to EUR 8,530, including increased grants, loans and emergency financial aid for students; more student accommodation, restaurants and access for disabled students. Licence reform will be introduced (see[http://www.universityworldnews.com/article.php?story=20080117161421945 Plan to halve student failure rate]). | |||
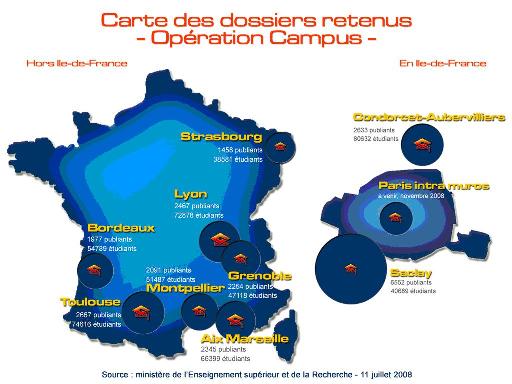
* Transition of universities to autonomy, renovating and updating buildings and facilities (see [http://www.universityworldnews.com/article.php?story=20080731155128679 First wave of autonomous universities]). The 10 successful projects selected under Operation Campus, the government scheme to create internationally competitive, top-ranking centres of higher education and research, will share an additional EUR5 billion (see [http://www.universityworldnews.com/article.php?story=20080717164201410 More super-campuses announced]). For the others, EUR 800 million will be made available during the period 2009-2011 for them to enter private partnerships. | |||
* Promoting public research "in a strategy of excellence", including increased spending on environmental research in the areas of agricultural and biodiversity, health and environment, climate change and transversal programmes. | |||
* Developing private research, with more generous tax breaks for private companies engaging in R&D, and public-private research | |||
[[Image:French-super-campuses.JPG]] | |||
- | |||
- | |||
Twenty of France's 80-plus universities assumed new powers of autonomy on 1 January under the government's Universities' Freedoms and Responsibilities law. The legislation gives the universities control over their budgets, staff recruitment and salaries, and other areas that were previously the responsibility of the state. All universities must adopt the reform by 2012, though academics and students continue to express their opposition. (…) | |||
The autonomous institutions will have total control of their budgets, instead of only a quarter of their spending. To ensure a smooth transition, each university will receive grants totalling EUR 250,000 (US$335,000) to meet expenses such as staff training and recruitment of consultants and specialists. | |||
' | The law also enables universities to create foundations and seek sponsorship from individuals and businesses to fund teaching and research projects such as professorships, mobility grants and laboratories. They may also apply to become owners of their university's buildings. | ||
Higher education and research are the government's chief priority in the 2009 budget which totals more than EUR 24 billion (US$30 billion), an increase of 6.5% compared with 2008, plus the introduction of 'Operation Campus', a project to create 10 top-ranking centres of higher education and research with extra funds of up to EUR5 billion. The EUR1.8 billion increase is due to be matched by the same amount annually, resulting in an extra EUR9 billion for higher education, research and innovation by 2012. | |||
The | The extra resources are in line with promises made by President Nicolas Sarkozy during his election campaign last year to promote higher education and research, and increase funding to French universities to be internationally competitive and arm France for the "worldwide battle for intelligence" (see [http://www.universityworldnews.com/article.php?story=20071206163217917 Adapting to the global battle of intelligence]. Sarkozy has undertaken to increase finance for higher education by EUR5 billion, and for research and innovation by EUR4 billion, during the five years up to 2012. | ||
However the sector has not escaped 900 job cuts although these are proportionally less severe than those imposed on other ministries. Current government policy is non-replacement of one in two public sector employees leaving to take retirement. But higher education and research have fared relatively lightly: the total of 900 axed posts represents only one in 12 departing workers, and tenured teaching and research posts will not be cut at all, according to the ministry. | |||
''Adapted from'' : Jane Marshall's articles in [http://www.universityworldnews.com/advancedsearch.php?mode=search&country=75 UniversityWorldNews.com] | |||
== Quality assurance == | |||
With regard to quality assessment, the general principle established by regulations in 2002 is that of regular internal and external assessments of HEIs as well as programmes and qualification award measures. The regulation is based on periodic assessment, and no decisions (recognition, labelling, funding) are taken by the Ministry without such an external evaluation. | |||
- | The results of the external evaluation of all activities – scientific, educational and management – are considered during negotiation of the four-year contract between a university or HEI and the state. They are also taken into account when the state, which guarantees the quality of degrees, takes decisions regarding the habilitation (a kind of accreditation) to award them. Engineering, business and management programmes must be assessed by specific national committees in order for institutions to receive the habilitation to award national degrees. | ||
In terms of internal evaluations, the methods for evaluating the training and teaching provided by universities are set by the administrative board upon proposal from the board for curricular and student life, boards on which elected student representatives sit. In accordance with the principles of the Bologna Process, the contractual agreement with universities and other HEIs has emphasised the reinforcement of internal evaluation systems as a priority. | |||
''Adapted from'' : [http://eacea.ec.europa.eu/ressources/eurydice/pdf/085DN/085_FR_EN.pdf Focus on the Structure of Higher Education in Europe 2006/07 National Trends in the Bologna Process] | |||
From 2007, the new French Agency for the Evaluation of Research and Higher Education, AERES (Agence d’évaluation de la recherche et de l’enseignement supérieur) covers all external evaluation activities. It took over the activities of the three former evaluation bodies: the ''Comité national d’évaluation'', CNE (for evaluation of HEIs and research institutions), the ''Comité national d’évaluation de la recherche'', CNER, (for the evaluation of national research organisations), and the ''Mission scientifique, technique et pédagogique'' , MSTP (for the evaluation of research teams, study programmes and degrees). | |||
The agency is therefore responsible for assessing strategy, research and teaching in all state-run higher education and research establishments: universities, grandes écoles, engineering and business schools and research organisations as well as inspecting all national higher education and research establishments | |||
State funding and accreditation of university courses and research projects are carried out by the Ministry for Higher Education and Research on the basis of the agency's findings. Organisations operate through four-year contracts with the ministry, and AERES will assess each research unit in situ during that period. | |||
Evaluations cover the development of internal quality assurance mechanisms, consistency and relevance of evaluation procedures, feedback on evaluation programmes and training of specialists and staff. Reflecting increased internationalisation, at least a fifth of the members are from abroad. | |||
In line with France's commitment to European Union higher education and research programmes, AERES will itself be reviewed for the European Quality Assurance Register in 2009. The agencies or bodies responsible for quality assurance at the national level are not subject to peer review. | |||
In | |||
''Adapted from'' : Jane Marshall's articles in [http://www.universityworldnews.com/advancedsearch.php?mode=search&country=75 UniversityWorldNews.com] | |||
== French HEIs in the information society == | |||
'''Information society strategy''' | |||
On 20 October 2008, the State Secretary in charge of digital economy development presented the main features of the '''DIGITAL FRANCE 2012 plan''' which aims at converting France in a driving force of the digital revolution. | |||
There are 154 measures that can be split in four priorities : | |||
1/ give all French people access to digital networks | |||
2/ develop the production and the offer of digital contents | |||
3/ diversify the digital uses and services | |||
4/ modernize digital services and governance | |||
'''Higher Education''' | |||
Actually there are two chapters that concern higher education and that imply the following actions : | |||
* 3.5/ Build the digital universities | |||
''Action n°94'' | |||
Develop digital services for all students, teachers, researchers and univesity staff : | |||
digital workspaces & ENTs, wireless coverage, online administrative procedures, electronic voting for students elections, multi-service cards for all by 2010, lifetime e-mail account. | |||
'''Canal U | ''Action n°95'' | ||
100 % digital educational resources for 100 % students : | |||
audio recording, automatisation, podcasting, digital documents instead of hardcopies, promote UNT's educational materials via Canal U, give free access to information media, enhance collaborative and innovative methods via blogs or wikis. | |||
''Action n°96'' | |||
Training in ICT for education : | |||
to help teachers integrate ICT in their pedagogical practices. | |||
''Action n°97'' | |||
Build a science digital library that is accessible to all users of higher education or research. | |||
''Action n°98'' | |||
Foster the development of distance courses available online. | |||
''Action n°99'' | |||
Develop a distance education offer on line especially for active workers. | |||
* 3.6/ Adapt the training offer to the needs of the digital economy | |||
''Action n°100'' | |||
Adapt initial raining to the companies' needs : | |||
include vocational modules into ICT curricula, create new courses of ICT careers. | |||
''Action N°101'' | |||
Offer young professionnals some additional university courses aimed at completing their training towards ICT jobs | |||
''Action n°102'' | |||
Implement lifelong learning university courses in order to keep professionals updated | |||
''Action n°103'' | |||
Create a framework of skills and competences for ICT careers : | |||
ensure interoperability with European portals like E-skills and E-career services, build partnership with employment platforms. | |||
== Virtual initiatives in HE== | |||
=== Virtual Campus Case-study=== | |||
[[Nancy-Université - case study]] | |||
=== Interesting Virtual Campus Initiatives === | |||
''National Virtual Campus programmes'' | |||
* [[Campus Numériques Français - Part1]] | |||
* [[Campus Numériques Français - Part 2 : ENT]] | |||
* [[Universités numériques en région]] (UNR) | |||
''National Open Educational Resources programmes'' | |||
* [[Canal U]] | |||
It is a web-TV for HE and Research. It offers a set of free channels that broadcasts university and research produced contents, especially by the Universités Numériques Thématiques. Canal-U is actually a consortium of university-web-TVs coordinated by CERIMES (Centre of Resources and Information on multimedia for Higher Education) which encompasses several organisations dealing with the broadcasting of digital materials towards HE. | |||
Launched in 2001, the CanalU website is experiencing a growing success (almost 298 000 visits by March 2006) and comes among significant references in the university audiovisual landscape by giving students free access to an impressive audiovisual collection (more than 2 000 films et 4 000 conferences on varied topics). | |||
* [[Universités Numériques Thématiques]] (UNT) | |||
The UNTs are also descripted in detail in the [http://nettskolen.nki.no/in_english/megatrends/workpackage3.html MegaTrends survey of megaproviders for France] | |||
- Université médicale virtuelle francophone (The French Medical Virtual University) | |||
- Université numérique juridique francophone (The French Digital University Law progamme) | |||
- Université numérique ingénierie et technologie (The Digital Engineering and Technology University) | |||
- [http://www.aunege.org AUNEGE], Association des universités pour l'enseignement numérique en Economie-Gestion (University Association for Digital Teaching in Economics and Management) | |||
- Université virtuelle environnement et développement durable (The Environmental and Sustainable Development Digital University programme) | |||
- Université ouverte des humanités (Humanities Open University) | |||
- Université des sciences fondamentales (Basic Sciences University) | |||
- [http://www.canege.org CANEGE] (digital campus in Economics and Management) | |||
''Main Institutions'' | |||
*[[Centre National d'Enseignement à Distance]] - [[CNED]] | |||
The National Centre for Distance Learning is the number one distance learning operator in Europe and the French-speaking world. It was established in 1939 and is now a public administrative institution under the authority of the National Education Ministry. In 1999, it celebrated its 60th anniversary with 320,000 individual enrolments. [http://www.cned.fr/institution/english/figures.htm Cned in figures] | |||
Digital Cned : on the Internet for the last ten years, Cned has integrated digital technology to aid the spread of learning and favour exchanges: virtual classrooms, online tutoring, electronic correction, student forum, online resources (Campus électronique®). | Digital Cned : on the Internet for the last ten years, Cned has integrated digital technology to aid the spread of learning and favour exchanges: virtual classrooms, online tutoring, electronic correction, student forum, online resources (Campus électronique®). | ||
''' | *[[Fédération Interuniversitaire de l'Enseignement à Distance]] - [[FIED]] ''in French only !'' | ||
The Federation of distance education universities is an association that was created in 1987 by the Ministry for National Education. It gathers now 36 universities and aims at uniting in a network all universities that develop all sorts of distance and online trainings. It also provides for an international representation for French distance education in connection with the institutional organisations (Ministry of foreign affairs, Ministry for cooperation, etc...). It is also implicated, as a partner or a project leader, in various projects on education and ICT with a view to improve quality in training and support to students. Finally, it aims to open up to all universities or institutions involved in open distance education. | |||
*[[Agence Universitaire de la Francophonie]] (AUF) | |||
''Other initiative'' | |||
The | * [[EduContact]] - The European center for higher distance education | ||
* InnoUni Learning project - 6 - Cases study in France [http://www2.spi.pt/innounilearning/documents/Interview%20Benchmark%20Process%20-%20Highlighted%208%20eLearning%20Programmes_F.pdf Interview Benchmark Process - Highlighted 8 eLearning Programmes (PDF)], | |||
=== Interesting Programmes=== | |||
[[Centre National d'Enseignement à Distance]] [[CNED]] | |||
[[Université Virtuelle en Pays de la Loire]] | |||
== | == References == | ||
EU report [http://eacea.ec.europa.eu/ressources/eurydice/pdf/085DN/085_FR_EN.pdf Focus on the Structure of Higher Education in Europe 2006/07, National Trends in the Bologna Process] | |||
EU report [http://eacea.ec.europa.eu/ressources/eurydice/pdf/047DN/047_FR_EN.pdf National summary sheets on education systems in Europe and ongoing reforms-2007] | |||
EU report [http://eacea.ec.europa.eu/ressources/eurydice/eurybase/pdf/0_integral/FR_EN.pdfEurybase, the Information Database on Education Systems in Europe; The Education System in France 2007/08] | |||
Jane Marshall's articles in [http://www.universityworldnews.com/advancedsearch.php?mode=search&country=75 UniversityWorldNews.com] | |||
Campus Numériques Français - Part1 [http://www.educnet.education.fr/chrgt/synthesefinal.pdf synthèse finale] | |||
[http://www.canal-u.tv/ Canal U] | |||
[[Universités Numériques Thématiques]] and http://www.educnet.education.fr/en/higher-educatio/tdus | |||
The | MegaTrends book on "The Provision of E-learning in the | ||
European Union" [http://nettskolen.nki.no/in_english/megatrends/Book1.pdf (PDF)] and the report on [http://nettskolen.nki.no/in_english/megatrends/UK.pdf Megatrends in e-learning provision project; Report on United Kingdom, France, Ireland, Belgium and Luxembourg (PDF)] | |||
in | |||
[[Ministère de l'Education nationale]] | |||
[[Centre National d'Enseignement à Distance]] (CNED) and http://www.cned.fr/institution/english/ | |||
Fédération Interuniversitaire de l'Enseignement à Distance (FIED) and http://www.fied-univ.fr/index.php | |||
[[Agence Universitaire de la Francophonie]] and http://www.auf.org/langues/en/the-auf-in-brief/accueil.html | |||
European Distance Universities Contact (EduContact): http://www.educontact.eu/ | |||
[[ | [[Media:CampusNumériques-Enjeux-et-Perspectives-pour-la-Formation-Ouverte-et-à-Distance.pdf| Campus Numériques: Enjeux et Perspectives pour la Formation Ouverte et à Distance (PDF - FR - 68 pages)]], by Michel Averous and Gilbert Touzot in 2002 | ||
> [[France]] | |||
---- | ---- | ||
> [[Countries]] | > [[Countries]] | ||
<br> | |||
>> [[Main Page]] | |||
[[Category:France| ]] | |||
[[Category: | [[Category:VISCED]] | ||
Latest revision as of 12:10, 30 October 2011
by Gregory Lucas and Widad Benhabiles. with additional contributions by other members of Re.ViCa
For the main entry on this country see France
For entities in France see Category:France
Partners situated in France
France in a nutshell
France is a country whose metropolitan territory is located in Western Europe and that also comprises various overseas islands and territories located in other continents. After Russia, France is the largest country in Europe (643,427 km² with its overseas départements). With a population of over 63 million inhabitants, France is the second most populous country in Western Europe (after Germany). Its territory is split into (administrative) regions. 22 of them are in Metropolitan France (the part of the country that is in Europe).
French is the official language of France, but each region has its own unique accent; in addition to French, there are several other languages of France traditionally spoken, although use of these languages has greatly decreased over the past two hundred years. French is also an official language in 41 countries, most of which form what is called in French La Francophonie, the community of French speaking nations.
French education policy
The current priorities of the ministry responsible for national education, the Ministre de l'Éducation nationale, are conveyed in a series of measures in accordance with the law of 23 April 2005. This involves, in particular:
- Defining the common core
- Personalised academic achievement programmes (PPRE)
- Revival of priority education
- Giving marks for school life
- The development of apprenticeship
- Improving education for disabled pupils
- Teacher training
For more details please see French education policy
Moreover secularism is an important principle in French education. It is based on the Napoleonic concordat of 1801 and the separation law of Church and State in 1905. School must be neutral and nondenominational. For example, religion does not constitute a teaching subject, teachers do not have the right to talk of their personal beliefs and all religious propaganda is banned within the school establishment. The law 2004-228 of 15 March 2004 stipulates that "in state schools, collèges and lycées, pupils are forbidden to wear signs or clothes which conspicuously show any religious affiliation."
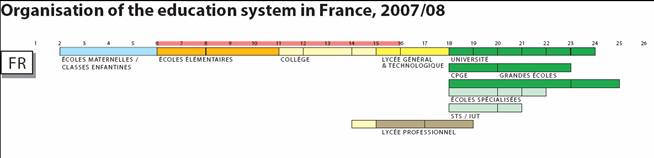
French education system
French educational system is highly centralized, organized, and ramified. It is divided into four different stages:
- Pre-primary education
- primary education (enseignement primaire);
- secondary education (enseignement secondaire);
- higher education (enseignement supérieur).
Education in France From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Pre-primary education
France has a long tradition of ‘pre-elementary’ education. Despite the fact that it is not compulsory, all children attend the école maternelle (nursery school) from the age of 2 to 5, though provision to children aged 2 is based on availability. Public-sector ‘pre-elementary’ or ‘nursery’ schools are the responsibility of the education ministry and attendance at them is free of charge. In the private schools that cater for close to 2.4 % of children, parents pay a share of the tuition fees. Nursery schools are indeed schools in the full sense with programmes of teaching and learning activity. The main educational areas of activity contribute to the overall development of children and prepare them for ‘elementary’ school.
Compulsory education
Education is compulsory between the ages of 6 and 16. It is divided into three stages:
- Primary education (école primaire) Ages 6-11
- Lower secondary education (collège) Ages 11-15
- General and technological lycée (lycée général et technologique) or vocational lycée (lycée professionnel) Compulsory only between ages 15 and 16
The enrolment of pupils in state schooling is based on a ‘sectorial’ principle: pupils are normally registered in the primary school, collège or lycée of the geographical area in which their parents live. State education is free of charge. Private education is mostly Roman Catholic. Although the French constitution proclaims that the state is secular, a 1959 law allows private establishments to sign government contracts that procure financial support in exchange for some control.
The ‘elementary’ school curriculum concentrates on the basic skills of reading, writing and arithmetic, as well as on physical education (normal motor skills, etc.) and enhancing awareness and sensitivity. The lower secondary education curriculum consists of eight or nine compulsory subjects depending on the year of study, and becomes increasingly diversified with the inclusion of optional subjects. Primary school classes have a single teacher for all subjects, whereas secondary school classes have different teachers for each subject. The education ministry determines school curricula and the aims underlying the acquisition of knowledge and skills by pupils. Teachers choose their own teaching methods and school textbooks.
On completion of their collège schooling, pupils are awarded a brevet (national certificate) on the basis of their marks in the final two years and a national examination. The brevet is not a compulsory qualification and continuation of their schooling in a lycée is not dependent on their passing the examination.
Post-compulsory education/upper secondary and post-secondary level
On completion of collège, pupils are offered three educational options:
- general studies;
- technological studies;
- vocational training.
At the lycée d’enseignement général et technologique, which caters for pupils who have chosen either of the first two possibilities, provision lasts three years and leads to the general and technological baccalaureate examination that may be chosen among the three general categories (economic and social, literary, or scientific) or among the seven technological categories. The lycée professionnel prepares students in two years for the first level of vocational qualification, corresponding to the certificat d’aptitude professionnelle (CAP) or brevet d’études professionnelles (BEP). These qualifications are designed to provide direct access to employment including in-company placements or may lead to a vocational baccalaureate in one of 48 specialised fields on offer. The baccalaureate, whether general, technological or vocational, gives access to higher education.
Adapted from : National summary sheets on education systems in Europe and ongoing reforms-2007
Administration of French education system
School education comes under the minister responsible for education throughout the country. Free public-sector provision exists alongside education offered by private schools whose population has remained stable for several years, at 2 027 700 (primary and secondary education, 2006).
At the beginning of the 2006/07 academic year, the school population in metropolitan France and its overseas départements (DOM) for public and private sectors stood at 12.4 million students. In order for the education system to operate, the state employs more that 1.3 million people, 850 000 of whom are public sector teachers. There are almost 2.287 million students in higher education, which employs 147 000 people, 88 000 of whom are teachers in public HEIs. The language of instruction is French. The regional languages are taught as part of the modern languages branch of studies.
Notwithstanding certain decentralisation measures under which responsibility for the construction and maintenance of public-sector school buildings has been entrusted to the local area authorities, the central government has retained a decisive role in the area of educational policy. The ministry responsible for national education draws up in detail the curriculum for each subject and level of education, and provides guidelines for teaching without however obliging teachers to adopt a particular method. It administers the recruitment, training and management of teaching staff, determines the status and regulations of schools, allocating them their appropriate quota of staff. The ministry also organises examinations and awards national qualifications, in particular the baccalaureate which testifies to the satisfactory completion of secondary schooling.
In order to implement this policy and the accomplishment of its numerous management tasks, France is divided into 30 such académies each headed by a rector acting directly on behalf of the minister. An académie is the administrative level enabling the regional application of education policies as defined by the government. It allows action to be taken according to local contexts in collaboration with regional groups: communes (town) for primary education, départements (district) for collèges and régions (province) for lycées.
The system is supervised by several inspectorates. Three general inspectorates are entrusted with very broad responsibilities for evaluation at national level in addition to two regional inspectorates, one that visits primary schools and monitor the performance of teachers, and one responsible for marking and assessing school teachers at secondary level.
Higher education in France
Please visit this external Wikipedia page for a full List of HEIs in France
Obtaining the baccalauréat is a pre-requisite to being admitted to an institution of higher education. The baccalauréat is a diploma that acknowledges the successful completion of secondary education and the first level of university studies. This is a very important feature of the French education system, one which has several consequences, particularly with regard to university studies and student orientation during the premier cycle (first cycle) at university.
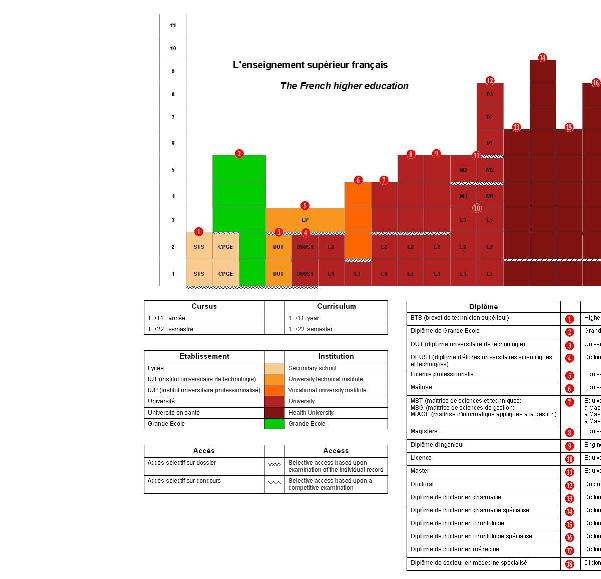
There are four types of programmes in the French tertiary education system:
- University education,
- Preparatory classes for grandes écoles,
- Higher technical education sections,
- Specialised schools or grandes écoles.
Then, depending on the duration involved, there are two types of studies :
- Shorter technical and vocational studies undertaken in university technology establishments (Instituts Universitaires de Technologies) leading to the DUT: Diplôme Universitaire de Technologie), the universities (leading to the DEUST: Diplôme d'Etudes Universitaires Scientifiques et Techniques) or higher secondary establishments (leading to the BTS: Brevet de Technicien Supérieur). Entry into these channels is based on a selection process and account is taken of pupils' record of achievement during their secondary schooling.
- Lengthier studies undertaken at a university or one of the "Grandes Ecoles" (to which entry is after two years of preparation in the Classes Préparatoires aux Grandes Ecoles (CPGE). After admission into these schools, the studies themselves generally last three years and lead to the "diplômes d'écoles". There is no selection for entry into university. Universities issue generic qualifications and also vocational qualifications. Teacher training is also undertaken at university.
Higher education in France also has specialised schools, recruitment being based on the baccalaureate, competitions or dossiers. They concern the paramedical sector (nursing schools, physiotherapists, etc.), the social sector (schools for specialised educators, social assistants, etc.), the arts sector or architecture. Studies vary in duration and lead to state-recognised diplomas or specific school diplomas.
These categories can also be broken down further into:
- those which can be accessed directly with a baccalauréat or an equivalent diploma, involving no pre-entry selection process: university programmes, with the exception of university institutes of technology;
- those which are accessed through a pre-entry selection process: preparatory classes for grandes écoles (CPGE), higher technical education sections (STS), Instituts Universitaires de Technologie (IUT or University institutes of technology) and specialised schools. Selections are made based on an admissions application. The type of baccalauréat earned and the marks obtained by the pupil in the last two years of lycée are determining factors;
- those for which the selection process occurs after the student has obtained a licence. This is the case for IUFM (university teacher training institutes) programmes, Grandes écoles recruiting by competitive examination following two or three years of preparatory classes (CPGE mostly).
Adapted from : the Information Database on Education Systems in Europe; The Education System in France 2007/08
Teacher training is provided at Instituts universitaires de formation des maîtres (IUFM) after 3 years of post-baccalauréat studies. Access to the profession for all levels of education takes place by means of a competitive examination, followed by a practical placement which must be validated by a certificate of competency or successful performance in a professional qualification examination. Those who are successful in competitive examinations for permanent posts are offered teaching positions in an académie.
Two categories of teachers exist at the level of higher education: 1) research teachers: lecturers and university professors who have the dual task of ensuring the development of basic and applied research and of conveying the resulting knowledge to students. They are permanent state employees; 2) other higher education teaching staff: associate or guest professors; second-degree teaching staff in higher education; professors who teach classes préparatoires (CPGE); assistant teachers (which is disappearing); temporary teaching and research assistants; foreign language teachers and lecturers; part-time lecturers and part-time staff.
Adapted from : National summary sheets on education systems in Europe and ongoing reforms-2007
The amount of the enrolment fees is set each year jointly by the ministry in charge of higher education and the ministry in charge of finance. In the context of the organisation of the European higher education programme, ( LMD) tuition fees have been revised and standardised in order to facilitate student orientation. A single fee has been introduced for each course of study: 165 euros for a licenceprogramme, 215 euros for a master’s programme and 326 euros for a doctoral programme (rates valid for the 2007/2008 academic year). Engineering and paramedical programmes maintain their own registration fees. For engineering degrees, the annual tuition rate for public institutions of higher education under the authority of the Ministry of Higher Education has been set at 512 euros.
Some establishments require additional payments (special fees), which are set by its board of administration. These usually range from 10 €-30 €, but can go as high as 100 € for some services, such as unlimited computer access. Additional fees cover preventive medical costs, athletic and cultural activities, photocopies, and, in some universities, student reception services. A breakdown of fees paid is listed on the student’s university card.
The cost of certain special programmes, like the diplôme d’université(DU), is almost entirely paid for by the student, ranging from 80 € to 650 € (rounded figures valid for the 2005/2006 school year) depending on the course of study. These costs are either mandatory or optional depending on the school. Some universities do not charge them.
Universities have no legal right to increase the national registration fees through additional charges. French law gives schools the possibility of requesting additional fees, but specifies that the request must be clearly indicated as optional.
In France, students benefit from several types of financial aid: scholarships, accommodation and food aid and other financial aids. Since 2001, the proportion of scholarship students in higher education has remained stable at 30%. In 2005, 522,000 students benefited from national education grants (i.e. 1.3% more than in 2004) for a total amount of 1.3 billion Euros. Students benefiting from scholarships based on social criteria represent 95% of supported students.
In September 2007, the minister in charge of higher education presented a "new structure for the funding of student life". This new system, established as part of the "students’ living conditions" project, aims at correcting the injustices and insufficiencies of the current system and recognising students’ merit and international mobility.
Universities in France
French universities are organized by academy because this is how the French educational system is organized. France is divided into thirty-five academies, of which thirty-one host the principal administrative seats of universities. Although the rectors or vice-rectors who head the academies do not have administrative control over the universities, the division into academies is nonetheless important because it governs admissions. Students in France have the right to be admitted to a university in the academy in which they passed the baccalauréat, and in some cases to a university in another specified academy.
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia List of public universities in France
Scientific, cultural and professional institutions (EPCSCP): since the enactment of the 1984 Savary law, there are a total of 82 EPCSCPs, thee of which are national polytechnical institutes (INP) in Grenoble, Nancy and Toulouse.
Since 1984, they have been organised into training and research units (UFR). They also include internal institutes and schools such as university institutes of technology (IUT), created in 1966, and professional university institutes (IUP), created in 1994.
Polytechnics in France
The National Polytechnic Institutes or Instituts Nationaux Polytechniques (INPs) in France are three consortiums of grandes écoles that offer engineering degrees. They were established in 1970. They are classed together with French universities although they are quite different from the public universities, both in their organization and in the fact that they have competitive admissions.
The three institutions are:
- The National Polytechnic Institute of Toulouse (Institut National Polytechnique de Toulouse or INP Toulouse)
- The Grenoble Institute of Technology (Institut National Polytechnique de Grenoble or INP Grenoble)
- The National Polytechnic Institute of Lorraine (Institut National Polytechnique de Lorraine)
Universités de Technologie
Universities of Technology are public institutions awarding degrees and diplomas that are accredited by the French Ministry of Higher Education and Research. Although called "universities", the universities of technology are in fact non-university institutes (écoles extérieures aux universities) established since 1972.
They possess the advantage of combining all the assets of the engineering Grandes Ecoles and those of universities as they develop simultaneously and coherently three missions: education, research and transfer of technology.
They maintain close links with the industrial world both on national and international levels and they are reputed for their ability to innovate, adapt and provide an education that matches the ever changing demands of industry.
This network includes three institutions:
- The University of Technology of Belfort-Montbéliard (Université de Technologie de Belfort-Montbéliard or UTBM)
- The University of Technology of Compiègne (Université de Technologie de Compiègne or UTC)
- The University of Technology of Troyes (Université de Technologie de Troyes or UTT)
Grandes Ecoles
In France Grandes écoles or Graduate schools (literally in French "Grand Schools" or "Elite Schools") are higher education establishments outside the mainstream framework of the public universities system. Unlike French public universities which have an obligation to accept all candidates of the same region who hold a Baccalauréat, the selection criteria of Grandes écoles rests mainly on competitive written and oral exams, undertaken by students of dedicated preparatory classes. They do not have a large student body (3,000 at the largest establishment; most have a few hundred students each year) and are generally focused on a single subject area, mainly engineering, business or humanities. They have traditionally produced most of France's high ranking civil servants, politicians and executives as well as many scientists and philosophers.
Higher education reform
In May 2006, the Commission issued a communication making detailed recommendations on how to modernise higher education in Europe. In its most contested suggestion, the report urged member states to give universities more autonomy and accountability and encouraged governments to "open up universities to the business community".
A French Universities' Freedoms and Responsibilities law to implement EU recommendations on reforming higher education was presented on 24 May 2007 and adopted by the French Parliament in August 2007. The law, set to be implemented over the next five years, will:
- give French universities more autonomy to decide upon their budget and staff (by creating foundations to collect money and devise their own recruitment processes), and;
- enable universities to open their administration to external staff, allowing representatives of the business world to take part in university governance.
While the reform is now under way and has broad support of university presidents, opposition remains among some members of the university community. Lecturers' and students' representatives fear 'privatisation' of the university sector and that the state will stop financing courses it regards as not cost-effective. (…) All students, university staff and the French association of researchers fear that state disengagement could lead to excessive private-sector influence over higher education curricula and unequal development of universities.
The majority students' union Unef claimed law could lead to selection, higher fees, domination by business and increased inequality between universities, and called on its supporters to take action this month.
Adapted from : EurActiv.com
In addition, the reforms of French higher education in 1968-1971 broke apart several public universities into numerous autonomous successor universities. For example, the University of Paris was split into thirteen universities, Paris I through Paris XIII. These universities have subsequently formed groupings in order to pool resources and better advance their joint activities. Some of these groupings, which typically take the legal form of a groupement d'interêt public, or GIP, are themselves called universities or university centers. In addition to universities, they may include other institutions of higher education and research as well as municipal and regional governments. The process has accelerated with the law of 18 April 2006 on the reform of research in France. This has permitted the creation of tighter groupings called pôles de recherche et d'enseignement supérieur, or PRES. In addition, there are a number of consortia of engineering schools, such as the Grenoble Institute of Technology, that the Ministry of Higher Education and Research lists as if they were universities.
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia List of public university systems and consortiums in France
The Bologna Process
Initiated in 1999, adjustments to the higher education system in accordance with the principles of the Bologna Process have been accompanied by a series of regulations published since April 2002 to adapt the French higher education system to the development of the EHEA (European Higher Education Area) for the purpose of implementing the LMD reform (Licence-Master-Doctorat or Bachelor-Master-Doctorate) and promoting the widespread use of ECTS and the Diploma Supplement.
Institutions have begun an overhaul of programmes offered in ECTS credits since 2002, and of the organisation of modular programmes allowing more flexibility and better gradual study guidance of students. ECTS is already used for transfer and accumulation and will be fully implemented by 2007/08 for all programmes related to the LMD system.
Within the framework of the LMD reform, the Diploma Supplement (DS) is being implemented progressively by all HEIs. By 2008, it will be issued automatically by all institutions free of charge, in French and in another language chosen by the institution.
The Répertoire national des certifications professionnelles (RNCP, or National Repertory for Qualifications), representing the National Framework for Qualifications (diplomas, degrees and certificates), was also introduced in 2002.
In the meantime, the market-oriented Bachelor’s degree, in accordance with the agreed on principle of employability especially for first-level studies, was introduced in 1999. The (market-oriented or research-oriented) Master’s degree was introduced in the 2002/03 academic year and requires 120 ECTS credits after the Bachelor’s degree, i.e. 300 credits after the baccalauréat.
The LMD reform will involve all higher-education institutions (HEIs). Its implementation has been effective since the beginning of the 2006 academic year for all universities. By 2010, it should apply to all HEIs and most of their programmes. Some branches, mostly in the field of medicine and engineering, are still based on the long-cycle structure although architecture studies were reformed in 2005. Moreover a Bachelor’s/Master’s structure does not exist yet at specialised schools that are usually organised as single-cycle studies lasting two years (or up to four years for paramedical studies), plus a second cycle lasting one year (leading to a market-oriented Bachelor’s degree) that is offered for technology studies.
Therefore, the implementation of the LMD reform, which gears the structure of French higher education to the European system by offering three levels of studies (licence/master/doctorat), brings with it a new degree structure for higher education in France:
• Degrees obtained after 2 years of post-baccalauréat studies, corresponding to 120 ECTS: technological university degree (DUT), scientific and technical university degree (DEUST), higher technician's diploma(BTS), or general university degree (DEUG);
• Degrees obtained after 3 years of post-baccalauréat studies, corresponding to 180 ECTS credits: national specialised technology diploma (DNTS), vocational licence and licence; • Intermediate degree, obtained after 4 years of post-baccalauréat studies, corresponding to 240 ECTS: master's degree;
• Degrees obtained after 5 years of post-baccalauréat studies, corresponding to 300 ECTS credits: master's degree, diplôme d’études approfondies (DEA, or advanced studies degree), diplôme d’études supérieures spécialisées (DESS, or specialised higher studies degree);
• Degrees obtained after post-master's studies, corresponding to 480 ECTS credits: doctorate.
Doctoral studies were also restructured in April 2002 and August 2006. Organized in doctoral schools, they are accessible after graduation with a master degree or by special authorisation to students who have completed the equivalent level of studies abroad or who benefit from the recognition of prior learning. As a general rule, after three years, these studies lead to a PhD’s degree after a thesis defence. The possibility to prepare a PhD within the framework of ‘joint international thesis supervision’ has been widened since 2005.
Adapted from : National summary sheets on education systems in Europe and ongoing reforms-2007
Administration and finance
French university funding system has often been criticised for its opacity and complexity. The reform proposes to introduce a more market-oriented approach basing university funding more on universities' performance rather than on the number of registered students. Indeed, the current system pushes universities to enrol more first-year students than they can handle to ensure cash flow. To evaluate performance, several criteria were proposed like to evaluate the amount of outside funding attracted by university research laboratories, namely business sources, or employment and salary levels of students graduated from different universities at intervals of six months and three years, as well as to allocate university funding on the basis of the number of students actually taking exams rather than the number of registered ones. The union argues that cutting funding for those most in need will not help resolve huge rates of failure among students. On the contrary, UNEF argues that the funds for universities recording huge failure rates need to be increased to help them implement more ambitious policies.
Adapted from : National summary sheets on education systems in Europe and ongoing reforms-2007
Funding priorities of Valérie Pécresse, Minister for Higher Education and Research, are:
- Making careers in university teaching and in research more attractive, including improved pay, administrative structures and pensions.
- Encouraging student success, with the aim of halving the first-year failure rate within five years and achieving the objective of 50% of young people attaining licence (bachelor's equivalent) level. State spending per student will rise by EUR 450 to EUR 8,530, including increased grants, loans and emergency financial aid for students; more student accommodation, restaurants and access for disabled students. Licence reform will be introduced (seePlan to halve student failure rate).
- Transition of universities to autonomy, renovating and updating buildings and facilities (see First wave of autonomous universities). The 10 successful projects selected under Operation Campus, the government scheme to create internationally competitive, top-ranking centres of higher education and research, will share an additional EUR5 billion (see More super-campuses announced). For the others, EUR 800 million will be made available during the period 2009-2011 for them to enter private partnerships.
- Promoting public research "in a strategy of excellence", including increased spending on environmental research in the areas of agricultural and biodiversity, health and environment, climate change and transversal programmes.
- Developing private research, with more generous tax breaks for private companies engaging in R&D, and public-private research
Twenty of France's 80-plus universities assumed new powers of autonomy on 1 January under the government's Universities' Freedoms and Responsibilities law. The legislation gives the universities control over their budgets, staff recruitment and salaries, and other areas that were previously the responsibility of the state. All universities must adopt the reform by 2012, though academics and students continue to express their opposition. (…)
The autonomous institutions will have total control of their budgets, instead of only a quarter of their spending. To ensure a smooth transition, each university will receive grants totalling EUR 250,000 (US$335,000) to meet expenses such as staff training and recruitment of consultants and specialists.
The law also enables universities to create foundations and seek sponsorship from individuals and businesses to fund teaching and research projects such as professorships, mobility grants and laboratories. They may also apply to become owners of their university's buildings.
Higher education and research are the government's chief priority in the 2009 budget which totals more than EUR 24 billion (US$30 billion), an increase of 6.5% compared with 2008, plus the introduction of 'Operation Campus', a project to create 10 top-ranking centres of higher education and research with extra funds of up to EUR5 billion. The EUR1.8 billion increase is due to be matched by the same amount annually, resulting in an extra EUR9 billion for higher education, research and innovation by 2012.
The extra resources are in line with promises made by President Nicolas Sarkozy during his election campaign last year to promote higher education and research, and increase funding to French universities to be internationally competitive and arm France for the "worldwide battle for intelligence" (see Adapting to the global battle of intelligence. Sarkozy has undertaken to increase finance for higher education by EUR5 billion, and for research and innovation by EUR4 billion, during the five years up to 2012.
However the sector has not escaped 900 job cuts although these are proportionally less severe than those imposed on other ministries. Current government policy is non-replacement of one in two public sector employees leaving to take retirement. But higher education and research have fared relatively lightly: the total of 900 axed posts represents only one in 12 departing workers, and tenured teaching and research posts will not be cut at all, according to the ministry.
Adapted from : Jane Marshall's articles in UniversityWorldNews.com
Quality assurance
With regard to quality assessment, the general principle established by regulations in 2002 is that of regular internal and external assessments of HEIs as well as programmes and qualification award measures. The regulation is based on periodic assessment, and no decisions (recognition, labelling, funding) are taken by the Ministry without such an external evaluation.
The results of the external evaluation of all activities – scientific, educational and management – are considered during negotiation of the four-year contract between a university or HEI and the state. They are also taken into account when the state, which guarantees the quality of degrees, takes decisions regarding the habilitation (a kind of accreditation) to award them. Engineering, business and management programmes must be assessed by specific national committees in order for institutions to receive the habilitation to award national degrees.
In terms of internal evaluations, the methods for evaluating the training and teaching provided by universities are set by the administrative board upon proposal from the board for curricular and student life, boards on which elected student representatives sit. In accordance with the principles of the Bologna Process, the contractual agreement with universities and other HEIs has emphasised the reinforcement of internal evaluation systems as a priority.
Adapted from : Focus on the Structure of Higher Education in Europe 2006/07 National Trends in the Bologna Process
From 2007, the new French Agency for the Evaluation of Research and Higher Education, AERES (Agence d’évaluation de la recherche et de l’enseignement supérieur) covers all external evaluation activities. It took over the activities of the three former evaluation bodies: the Comité national d’évaluation, CNE (for evaluation of HEIs and research institutions), the Comité national d’évaluation de la recherche, CNER, (for the evaluation of national research organisations), and the Mission scientifique, technique et pédagogique , MSTP (for the evaluation of research teams, study programmes and degrees).
The agency is therefore responsible for assessing strategy, research and teaching in all state-run higher education and research establishments: universities, grandes écoles, engineering and business schools and research organisations as well as inspecting all national higher education and research establishments
State funding and accreditation of university courses and research projects are carried out by the Ministry for Higher Education and Research on the basis of the agency's findings. Organisations operate through four-year contracts with the ministry, and AERES will assess each research unit in situ during that period.
Evaluations cover the development of internal quality assurance mechanisms, consistency and relevance of evaluation procedures, feedback on evaluation programmes and training of specialists and staff. Reflecting increased internationalisation, at least a fifth of the members are from abroad.
In line with France's commitment to European Union higher education and research programmes, AERES will itself be reviewed for the European Quality Assurance Register in 2009. The agencies or bodies responsible for quality assurance at the national level are not subject to peer review.
Adapted from : Jane Marshall's articles in UniversityWorldNews.com
French HEIs in the information society
Information society strategy
On 20 October 2008, the State Secretary in charge of digital economy development presented the main features of the DIGITAL FRANCE 2012 plan which aims at converting France in a driving force of the digital revolution.
There are 154 measures that can be split in four priorities :
1/ give all French people access to digital networks
2/ develop the production and the offer of digital contents
3/ diversify the digital uses and services
4/ modernize digital services and governance
Higher Education
Actually there are two chapters that concern higher education and that imply the following actions :
- 3.5/ Build the digital universities
Action n°94 Develop digital services for all students, teachers, researchers and univesity staff : digital workspaces & ENTs, wireless coverage, online administrative procedures, electronic voting for students elections, multi-service cards for all by 2010, lifetime e-mail account.
Action n°95 100 % digital educational resources for 100 % students : audio recording, automatisation, podcasting, digital documents instead of hardcopies, promote UNT's educational materials via Canal U, give free access to information media, enhance collaborative and innovative methods via blogs or wikis.
Action n°96 Training in ICT for education : to help teachers integrate ICT in their pedagogical practices.
Action n°97 Build a science digital library that is accessible to all users of higher education or research.
Action n°98 Foster the development of distance courses available online.
Action n°99 Develop a distance education offer on line especially for active workers.
- 3.6/ Adapt the training offer to the needs of the digital economy
Action n°100 Adapt initial raining to the companies' needs : include vocational modules into ICT curricula, create new courses of ICT careers.
Action N°101 Offer young professionnals some additional university courses aimed at completing their training towards ICT jobs
Action n°102 Implement lifelong learning university courses in order to keep professionals updated
Action n°103 Create a framework of skills and competences for ICT careers : ensure interoperability with European portals like E-skills and E-career services, build partnership with employment platforms.
Virtual initiatives in HE
Virtual Campus Case-study
Interesting Virtual Campus Initiatives
National Virtual Campus programmes
National Open Educational Resources programmes
It is a web-TV for HE and Research. It offers a set of free channels that broadcasts university and research produced contents, especially by the Universités Numériques Thématiques. Canal-U is actually a consortium of university-web-TVs coordinated by CERIMES (Centre of Resources and Information on multimedia for Higher Education) which encompasses several organisations dealing with the broadcasting of digital materials towards HE.
Launched in 2001, the CanalU website is experiencing a growing success (almost 298 000 visits by March 2006) and comes among significant references in the university audiovisual landscape by giving students free access to an impressive audiovisual collection (more than 2 000 films et 4 000 conferences on varied topics).
The UNTs are also descripted in detail in the MegaTrends survey of megaproviders for France - Université médicale virtuelle francophone (The French Medical Virtual University) - Université numérique juridique francophone (The French Digital University Law progamme) - Université numérique ingénierie et technologie (The Digital Engineering and Technology University) - AUNEGE, Association des universités pour l'enseignement numérique en Economie-Gestion (University Association for Digital Teaching in Economics and Management) - Université virtuelle environnement et développement durable (The Environmental and Sustainable Development Digital University programme) - Université ouverte des humanités (Humanities Open University) - Université des sciences fondamentales (Basic Sciences University) - CANEGE (digital campus in Economics and Management)
Main Institutions
The National Centre for Distance Learning is the number one distance learning operator in Europe and the French-speaking world. It was established in 1939 and is now a public administrative institution under the authority of the National Education Ministry. In 1999, it celebrated its 60th anniversary with 320,000 individual enrolments. Cned in figures Digital Cned : on the Internet for the last ten years, Cned has integrated digital technology to aid the spread of learning and favour exchanges: virtual classrooms, online tutoring, electronic correction, student forum, online resources (Campus électronique®).
- Fédération Interuniversitaire de l'Enseignement à Distance - FIED in French only !
The Federation of distance education universities is an association that was created in 1987 by the Ministry for National Education. It gathers now 36 universities and aims at uniting in a network all universities that develop all sorts of distance and online trainings. It also provides for an international representation for French distance education in connection with the institutional organisations (Ministry of foreign affairs, Ministry for cooperation, etc...). It is also implicated, as a partner or a project leader, in various projects on education and ICT with a view to improve quality in training and support to students. Finally, it aims to open up to all universities or institutions involved in open distance education.
Other initiative
- EduContact - The European center for higher distance education
- InnoUni Learning project - 6 - Cases study in France Interview Benchmark Process - Highlighted 8 eLearning Programmes (PDF),
Interesting Programmes
Centre National d'Enseignement à Distance CNED
Université Virtuelle en Pays de la Loire
References
EU report Focus on the Structure of Higher Education in Europe 2006/07, National Trends in the Bologna Process
EU report National summary sheets on education systems in Europe and ongoing reforms-2007
EU report the Information Database on Education Systems in Europe; The Education System in France 2007/08
Jane Marshall's articles in UniversityWorldNews.com
Campus Numériques Français - Part1 synthèse finale
Universités Numériques Thématiques and http://www.educnet.education.fr/en/higher-educatio/tdus
MegaTrends book on "The Provision of E-learning in the European Union" (PDF) and the report on Megatrends in e-learning provision project; Report on United Kingdom, France, Ireland, Belgium and Luxembourg (PDF)
Ministère de l'Education nationale
Centre National d'Enseignement à Distance (CNED) and http://www.cned.fr/institution/english/
Fédération Interuniversitaire de l'Enseignement à Distance (FIED) and http://www.fied-univ.fr/index.php
Agence Universitaire de la Francophonie and http://www.auf.org/langues/en/the-auf-in-brief/accueil.html
European Distance Universities Contact (EduContact): http://www.educontact.eu/
Campus Numériques: Enjeux et Perspectives pour la Formation Ouverte et à Distance (PDF - FR - 68 pages), by Michel Averous and Gilbert Touzot in 2002
> France