Welcome to the Virtual Education Wiki ~ Open Education Wiki
Sweden from Re.ViCa: Difference between revisions
NikkiCortoos (talk | contribs) m (added category Country Reports and changed references) |
(decategorised) |
||
| (11 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
by [[Ulla Rintala]], ''[[Aalto University]]'' | |||
For main entry on Sweden now see [[Sweden]] | |||
For entities in Sweden see [[:Category:Sweden]] | |||
==Sweden in a nutshell== | ==Sweden in a nutshell== | ||
(mainly sourced from: [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Sweden Wikipedia]) | (mainly sourced from: [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Sweden Wikipedia]) | ||
[[Image:Se-map.png|left|thumb|Source: http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/Atlas_of_Sweden]] | [[Image:Se-map.png|left|thumb|Source: http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/Atlas_of_Sweden]] | ||
Sweden, officially the '''Kingdom of Sweden''', is a Nordic country on the Scandinavian Peninsula in Northern Europe. Area-wise, it is one of the largest countries in Europe. Its population is around 9 million or on average 20 inhabitants per square kilometer. The population is very unevenly distributed: some 84 % live in urban areas, and about one third in the 3 major cities of Stockholm, Gothenburg and Malmö. | |||
Sweden is a constitutional monarchy (parliamentary democracy). It has been a member of the European Union since 1995, but it has not joined the European Monetary Union. The capital and largest city is Stockholm, with a population of around 800,000 and metropolitan area of 2 million. The official language is Swedish. | |||
Sweden has land borders with [[Norway]] to the west and [[Finland]] to the northeast, and it is connected to [[Denmark]] by the Öresund Bridge in the south. | |||
Sweden | |||
==Swedish education policy== | ==Swedish education policy== | ||
| Line 25: | Line 30: | ||
==Swedish education system== | ==Swedish education system== | ||
(mainly sourced from: ''OECD Thematic Review of Tertiary Education – Country Background Report for Sweden.'') | (mainly sourced from: ''[http://www.oecd.org/LongAbstract/0,3425,en_2649_39263238_37524408_1_1_1_1,00.html OECD Thematic Review of Tertiary Education – Country Background Report for Sweden].'') | ||
| Line 41: | Line 46: | ||
==Higher education in Sweden== | ==Higher education in Sweden== | ||
(mainly sourced from: [http://www.studyinsweden.se/Home/ Study in Sweden], ''OECD Thematic Review of Tertiary Education – Country Background Report for Sweden | (mainly sourced from: [http://www.studyinsweden.se/Home/ Study in Sweden], ''[http://www.oecd.org/LongAbstract/0,3425,en_2649_39263238_37524408_1_1_1_1,00.html OECD Thematic Review of Tertiary Education – Country Background Report for Sweden]'' and ''[http://www.oecd.org/LongAbstract/0,3425,en_2649_33735_43925757_1_1_1_1,00.html Education at a Glance – OECD Briefing Note for Sweden]'') | ||
See also the following OECD report for more information about the Swedish higher education | See also the following OECD report for more information about the Swedish higher education: [http://www.oecd.org/document/16/0,3343,en_2649_39263238_35580240_1_1_1_1,00.html Thematic Review of Tertiary Education - Country Background Reports]. | ||
:[http://www.oecd.org/document/16/0,3343,en_2649_39263238_35580240_1_1_1_1,00.html Thematic Review of Tertiary Education - Country Background Reports]. | |||
| Line 57: | Line 61: | ||
In academic year 2007 – 2008, the Swedish HEIs adopted a new degree structure that conforms to the Bologna Process. The new degree structure creates three levels of higher education – a first level, second level, and third level – each with minimum requirements for entry (see picture 4). Degrees awarded at each level are defined in terms of the expected results and abilities of students. Sweden has also introduced a new credit system, which is compatible with the European Credit Transfer and Accumulation System (ECTS). Under the new system, one academic year of full-time studies is equivalent to 60 higher education credits. | In academic year 2007 – 2008, the Swedish HEIs adopted a new degree structure that conforms to the [[Bologna Process]]. The new degree structure creates three levels of higher education – a first level, second level, and third level – each with minimum requirements for entry (see picture 4). Degrees awarded at each level are defined in terms of the expected results and abilities of students. Sweden has also introduced a new credit system, which is compatible with the European Credit Transfer and Accumulation System ([[ECTS]]). Under the new system, one academic year of full-time studies is equivalent to 60 higher education credits. | ||
| Line 91: | Line 95: | ||
==Higher education reform== | ==Higher education reform== | ||
(mainly sourced from: [http://www.studyinsweden.se/Home/ Study in Sweden] and ''OECD Thematic Review of Tertiary Education – Country Background Report for Sweden | (mainly sourced from: [http://www.studyinsweden.se/Home/ Study in Sweden] and ''[http://www.oecd.org/LongAbstract/0,3425,en_2649_39263238_37524408_1_1_1_1,00.html OECD Thematic Review of Tertiary Education – Country Background Report for Sweden]'') | ||
| Line 98: | Line 102: | ||
==Administration and finance== | ==Administration and finance== | ||
(mainly sourced from: ''OECD Thematic Review of Tertiary Education – Country Background Report for Sweden | (mainly sourced from: ''[http://www.oecd.org/LongAbstract/0,3425,en_2649_39263238_37524408_1_1_1_1,00.html OECD Thematic Review of Tertiary Education – Country Background Report for Sweden]'') | ||
| Line 115: | Line 119: | ||
==Quality assurance== | ==Quality assurance== | ||
(mainly sourced from: ''E-learning quality. Aspects and criteria for evaluation of e-learning in higher education | (mainly sourced from: ''[http://www.hsv.se/aboutus/publications/reports/reports/2008/elearningqualityaspectsandcriteriaforevaluationofelearninginhighereducation.5.6923699711a25cb275a80003033.html E-learning quality. Aspects and criteria for evaluation of e-learning in higher education'' and ''The Swedish Higher Education System]'') | ||
| Line 132: | Line 136: | ||
===A country online=== | ===A country online=== | ||
(mainly sourced from: ''On the Move Towards Online Education in Sweden | (mainly sourced from: ''On the Move Towards Online Education in Sweden, Chapter 3 by [[Carl Holmberg]] in NKI Förlaget – [http://home.nki.no/morten/index.php/english-menu/5-english/54-online-version-of-my-book.html Online Education and Learning Management Systems] by [[Morten Flate Paulsen]].'') | ||
| Line 149: | Line 153: | ||
===The prosperous future of e-learning=== | ===The prosperous future of e-learning=== | ||
(mainly sourced from: ''On the Move Towards Online Education in Sweden | (mainly sourced from: ''On the Move Towards Online Education in Sweden, Chapter 3 by [[Carl Holmberg]] in NKI Förlaget – [http://home.nki.no/morten/index.php/english-menu/5-english/54-online-version-of-my-book.html Online Education and Learning Management Systems] by [[Morten Flate Paulsen]].'') | ||
| Line 163: | Line 168: | ||
'''Umeå University''' | '''Umeå University''' | ||
In the late 1980s, the government made a first large-scale attempt by concentrating funds and efforts on a development program at Umeå University. The overarching purpose was to contribute to rural development in the northern sparsely populated areas of the country. | In the late 1980s, the government made a first large-scale attempt by concentrating funds and efforts on a development program at [[Umeå University]]. The overarching purpose was to contribute to rural development in the northern sparsely populated areas of the country. | ||
| Line 171: | Line 176: | ||
Three main consortia emerged. The first was founded in 1993 through an agreement between the universities of Linköping, Umeå, Uppsala and Växjö, and the Royal Institute of Technology. Later in 1996, Lund University joined the consortium. The formation of this organization was a response to the ministry initiative about the need for collaboration in the development of distance education in the light of ICT development. | Three main consortia emerged. The first was founded in 1993 through an agreement between the universities of [[Linköping University|Linköping]], [[Umeå University|Umeå]], [[Uppsala University |Uppsala]] and [[Växjö University |Växjö]], and the Royal Institute of Technology. Later in 1996, Lund University joined the consortium. The formation of this organization was a response to the ministry initiative about the need for collaboration in the development of distance education in the light of ICT development. | ||
| Line 209: | Line 214: | ||
===Quality assurance and e-learning in Sweden=== | ===Quality assurance and e-learning in Sweden=== | ||
(mainly sourced from: ''E-learning quality. Aspects and criteria for evaluation of e-learning in higher education | (mainly sourced from: ''[http://www.hsv.se/aboutus/publications/reports/reports/2008/elearningqualityaspectsandcriteriaforevaluationofelearninginhighereducation.5.6923699711a25cb275a80003033.html E-learning quality. Aspects and criteria for evaluation of e-learning in higher education]'') | ||
| Line 229: | Line 234: | ||
===Swedish Net University=== | ===Swedish Net University=== | ||
(mainly sourced from: [http://www.e-uni.ee/Minerva/index.html The UNIVe Project], [http://www.nshu.se/english.html Swedish Agency for Networks and Cooperation in Higher Education], ''On the Move Towards Online Education in Sweden | (mainly sourced from: [http://www.e-uni.ee/Minerva/index.html The UNIVe Project], [http://www.nshu.se/english.html Swedish Agency for Networks and Cooperation in Higher Education], ''On the Move Towards Online Education in Sweden, Chapter 3 by [[Carl Holmberg]] in NKI Förlaget – [http://home.nki.no/morten/index.php/english-menu/5-english/54-online-version-of-my-book.html Online Education and Learning Management Systems] by [[Morten Flate Paulsen]]'') and ''[www.nshu.se/english/download/4022/nshubroschyreng2006.pdf This is NSHU – our task and mission. A presentation of the Swedish Agency for Networks and Cooperation in Higher Education (PDF)]''.) | ||
| Line 269: | Line 274: | ||
===HiG - University of Gävle=== | ===HiG - University of Gävle=== | ||
Since its established in 1977, the '''University of Gävle''' has expanded rapidly and currently comprises six departments offering some 50 degree programs and 800 elective courses. There are approximately 13,000 registered students at the university. Half of these students come from the surrounding region; the other half come from other parts of Sweden. The total number of employees is some 800, of whom over 30 are full professors and 150 senior lecturers. A high percentage of the academic staff has an international background, a fact that contributes to the university's on-going process of internationalisation. | Since its established in 1977, the [http://www.hig.se/ '''University of Gävle'''] has expanded rapidly and currently comprises six departments offering some 50 degree programs and 800 elective courses. There are approximately 13,000 registered students at the university. Half of these students come from the surrounding region; the other half come from other parts of Sweden. The total number of employees is some 800, of whom over 30 are full professors and 150 senior lecturers. A high percentage of the academic staff has an international background, a fact that contributes to the university's on-going process of internationalisation. | ||
| Line 279: | Line 284: | ||
===Mid Sweden University=== | ===Mid Sweden University=== | ||
Geographically, '''Mid Sweden University''' is located in the middle of Sweden. It is a young university, but its roots date back to as early as 1842., when the 'university' was still a teachers' education college in Härnösand. The university was established in July 1993, when the University Colleges of Sundsvall/Härnösand and Östersund were merged. In July 1995, the Sundsvall/Örnsköldsvik and Sundsvall Colleges of Health Sciences were also incorporated. Ten years later (2005), the Mid Sweden University became a full status university. | Geographically, [http://www.miun.se '''Mid Sweden University'''] is located in the middle of Sweden. It is a young university, but its roots date back to as early as 1842., when the 'university' was still a teachers' education college in Härnösand. The university was established in July 1993, when the University Colleges of Sundsvall/Härnösand and Östersund were merged. In July 1995, the Sundsvall/Örnsköldsvik and Sundsvall Colleges of Health Sciences were also incorporated. Ten years later (2005), the Mid Sweden University became a full status university. | ||
| Line 289: | Line 294: | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
* [[Carl Holmberg| Holmberg Carl]] (2003): On the Move Towards Online Education in Sweden. NKI Förlaget – Online Education and Learning Management Systems by [[Morten Flate Paulsen]]. | * [[Carl Holmberg| Holmberg Carl]] (2003): On the Move Towards Online Education in Sweden. NKI Förlaget – [http://home.nki.no/morten/index.php/english-menu/5-english/54-online-version-of-my-book.html Online Education and Learning Management Systems] by [[Morten Flate Paulsen]].'') | ||
* [[OECD| Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development]] (2007): Education at a Glance – OECD Briefing Note for Sweden. | * [[OECD| Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development]] (2007): [http://www.oecd.org/LongAbstract/0,3425,en_2649_33735_43925757_1_1_1_1,00.html Education at a Glance – OECD Briefing Note for Sweden]. | ||
* Swedish Agency for Networks and Cooperation in Higher Education (2006): This is NSHU – our task and mission. A presentation of the Swedish Agency for Networks and Cooperation in Higher Education | * Swedish Agency for Networks and Cooperation in Higher Education (2006): [www.nshu.se/english/download/4022/nshubroschyreng2006.pdf This is NSHU – our task and mission. A presentation of the Swedish Agency for Networks and Cooperation in Higher Education (PDF)] | ||
* Swedish National Agency for Higher Education (2006): OECD Thematic Review of Tertiary Education – Country Background Report for Sweden | * Swedish National Agency for Higher Education (2006): [http://www.oecd.org/LongAbstract/0,3425,en_2649_39263238_37524408_1_1_1_1,00.html OECD Thematic Review of Tertiary Education – Country Background Report for Sweden] | ||
* Swedish National Agency for Higher Education (2008:11R):E-learning quality. Aspects and criteria for evaluation of e-learning in higher education | * Swedish National Agency for Higher Education (2008:11R): [http://www.hsv.se/aboutus/publications/reports/reports/2008/elearningqualityaspectsandcriteriaforevaluationofelearninginhighereducation.5.6923699711a25cb275a80003033.html E-learning quality. Aspects and criteria for evaluation of e-learning in higher education] | ||
* Swedish National Agency for Higher Education (2008): The Swedish Higher Education System | * [http://www.hsv.se Swedish National Agency for Higher Education] (2008): The Swedish Higher Education System | ||
| Line 310: | Line 315: | ||
* [http://www.hig.se//ufk/is/introduction.html University of Gävle] | * [http://www.hig.se//ufk/is/introduction.html University of Gävle] | ||
* [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Main_Page Wikipedia] | * [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Main_Page Wikipedia] | ||
* [http://www.hsv.se/ | * [http://www.hsv.se/aboutus/publications/reports/reports/2008/elearningqualityaspectsandcriteriaforevaluationofelearninginhighereducation.5.6923699711a25cb275a80003033.html Report E-learning quality, 2008:11R] | ||
| Line 318: | Line 323: | ||
> [[Sweden]] | |||
---- | ---- | ||
> [[Countries]] | > [[Countries]] | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
>> [[Main Page]] | >> [[Main Page]] | ||
[[Category:Sweden| ]] | [[Category:Sweden| ]] | ||
[[Category: | [[Category:VISCED]] | ||
Latest revision as of 10:30, 30 October 2011
by Ulla Rintala, Aalto University
For main entry on Sweden now see Sweden
For entities in Sweden see Category:Sweden
Sweden in a nutshell
(mainly sourced from: Wikipedia)
Sweden, officially the Kingdom of Sweden, is a Nordic country on the Scandinavian Peninsula in Northern Europe. Area-wise, it is one of the largest countries in Europe. Its population is around 9 million or on average 20 inhabitants per square kilometer. The population is very unevenly distributed: some 84 % live in urban areas, and about one third in the 3 major cities of Stockholm, Gothenburg and Malmö.
Sweden is a constitutional monarchy (parliamentary democracy). It has been a member of the European Union since 1995, but it has not joined the European Monetary Union. The capital and largest city is Stockholm, with a population of around 800,000 and metropolitan area of 2 million. The official language is Swedish.
Sweden has land borders with Norway to the west and Finland to the northeast, and it is connected to Denmark by the Öresund Bridge in the south.
Swedish education policy
(mainly sourced from: Nationellt Centrum för Flexibelt Lärande)
Sweden has a strong social-democratic tradition which stresses the redistributive role of state, social inclusion and equality, underpinned by high levels of taxation and public spending. The education system is an integral component of the Swedish concept of the welfare state, and the Swedish spending on education is, indeed, amongst the highest in the world.
Since last election (2006), Sweden is governed by the Alliance for Sweden, a coalition between four parties (Christian Democrats, Centre Party, Liberal Party and Moderaterna). One of the more evident traits of change is that the Alliance is stressing the decentralisation of the education systems. Thus, more power is moved to the municipalities for the basic education levels and to the universities and university colleges at tertiary level. One of the consequences of that is that some state authorities and agencies with national responsibility to e.g. support development of the education systems are closed. The new government focus heavily on advancing the compulsory school via large investments in a reformed teacher education and in-service training for teachers.
Swedish education system
(mainly sourced from: OECD Thematic Review of Tertiary Education – Country Background Report for Sweden.)
The Swedish education system consists of a compulsory comprehensive nine-year school, a three-year upper-secondary school with pre-academic as well as vocational programs, and a unitary higher education sector that includes academic, professional and vocational programs. There is also a specific sector, the folk high schools, that provides adult education at all levels, ranging from basic school qualifications to vocational programs, some of which can be described as offering an alternative to higher education.
Additionally, municipal adult education offers education at compulsory and upper-secondary school level for those lacking these qualifications as well as vocational training for adults. This is a comparably large sub system with 170,300 students in the academic year 2007/08 and close to 70,000 in language training for immigrants. After a decrease in students (17 % in 2007/08) the number of students is growing again, to a large extent due to the financial situation in the world and its consequences for Swedish labour markets.
Advanced Vocational Education is a form of vocational post-secondary education designed and carried out in close co-operation between enterprises and course providers (mostly higher education, but also upper-secondary schools, municipal adult education and companies).
Equal access to education has long been one of the pillars of the Swedish welfare state. Education from primary school to higher education is mainly tax financed and free of charge to the student. The main distinguishing feature of HE from other forms of education is that HE is based on science or art and on tested experience.
Higher education in Sweden
(mainly sourced from: Study in Sweden, OECD Thematic Review of Tertiary Education – Country Background Report for Sweden and Education at a Glance – OECD Briefing Note for Sweden)
See also the following OECD report for more information about the Swedish higher education: Thematic Review of Tertiary Education - Country Background Reports.
Swedish tertiary education is provided mainly in the higher education sector, which comprises universities and university colleges. Today, there are 14 state universities, 22 state university colleges, 3 private institutions with undergraduate as well as postgraduate education, and a number of smaller private institutions. The HEIs range from large multi-faculty institutions to specialized institutions of different sizes.
The old universities have 25,000 to 40,000 students. The policy during the 90s was that 50 % of each age group should have entered higher education before the age of 25. That goal is not so much stressed today (2009), but over the last 15 years, there has definitely been a large increase in the uptake to higher education, to some extent due to the introduction of Swedish Net University. The expansion of higher education in Sweden has contributed to the fact that by the end of the 20th century, about a half of all students in higher education were children of parents who had no higher education of their own. This is a measure of the rate of change, and shows the demand for adaptation in Swedish HEIs.
In 1977, the Swedish system was transformed from a binary system of higher education to a formally unitary one comprising academic, vocational and longer and shorter professional programs. In the later part of the 20th and early 21st century higher education has expanded significantly and new institutions have been founded throughout Sweden.
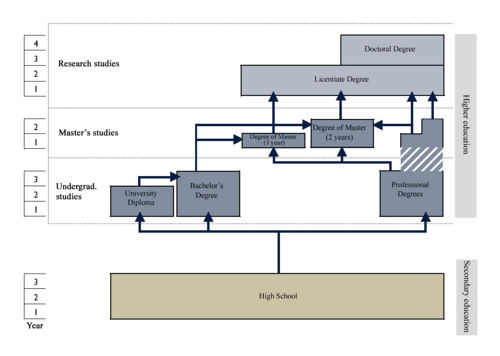
In academic year 2007 – 2008, the Swedish HEIs adopted a new degree structure that conforms to the Bologna Process. The new degree structure creates three levels of higher education – a first level, second level, and third level – each with minimum requirements for entry (see picture 4). Degrees awarded at each level are defined in terms of the expected results and abilities of students. Sweden has also introduced a new credit system, which is compatible with the European Credit Transfer and Accumulation System (ECTS). Under the new system, one academic year of full-time studies is equivalent to 60 higher education credits.
First level
At the first level of study, there are two degree options: the University Diploma, achievable after two years of study (120 ECTS), and the Bachelor's Degree, achievable after three years (180 ECTS). A prerequisite for starting higher education studies at the first level is the successful completion of an upper secondary school education. There are alternative routes to tertiary education, such as completing a study program at a folkhighschool or taking a higher education admittance test.
Second level
At the second level of study, there are also two degree options:
- There is a new two-year master’s degree - Degree of Master (Two Years) (120 ECTS). Authorization to award the Degree of Master is given to state universities and other higher education institutions that are approved for research in one or more disciplinary domains, and to private education providers that are authorized to award doctorates and licentiates in a disciplinary domain. Other higher education institutions have to apply to the Swedish National Agency for Higher Education (state education providers) or the Government (private education providers) for authorization to award the degree.
- The Degree of Master (One Year) (60 ECTS) is limited to one-year study programs only.
A prerequisite for studying at the second level is the completion of at least three years at first level at a Swedish higher education institution, or the international equivalent – such as a three-year bachelor’s degree (180 higher education credits). Specialized knowledge may also suffice.
Third level
At the third level of study, students are eligible for a Licentiate Degree after two years of research (120 ECTS), and a Doctoral Degree (PhD) after four years of research (240 ECTS). A prerequisite for studies at the third level is possession of a second-level degree – a Degree of Master (Two Years) or a Degree of Master (One Year) – or the completion of four years of full-time studies – three at the first level and at least one year at the second level. Comparable international degrees are also admissible, and specialized knowledge may suffice as well.
Sweden has seen an impressive growth in tertiary qualification over the past generations. Among the younger population (25-34 -year-olds), 37 % hold a university degree in comparison with 25 % among the 55-64 -year-olds. Graduation from traditional universities stands at 37.7 %. Sweden is also one of the European countries, of which graduation rate from advanced research programs (PhD or equivalent) exceeds 2.0 % (Sweden: 2.2%).
The share of international education market is relatively modest for Sweden which receives 1.4 % of all foreign students enrolled in tertiary education. However, Sweden still places itself well ahead of its Nordic neighbors. In 2005, international students comprised 4.4 % of all tertiary enrolment (76 %) in Sweden.
Higher education reform
(mainly sourced from: Study in Sweden and OECD Thematic Review of Tertiary Education – Country Background Report for Sweden)
Tertiary education in Sweden has expanded substantially, not least in terms of students, and gone through many transformations since 1990. Among the most important changes are the introduction of a decentralized system of governance for higher education and a stringent quality evaluation system, reformed research funding, and the establishment of a new form of tertiary education outside the HE system (advanced vocational training).
Administration and finance
(mainly sourced from: OECD Thematic Review of Tertiary Education – Country Background Report for Sweden)
Like all other public administration sectors in Sweden, also higher education is subject to management by objectives and results. State higher education institutions in Sweden are formally
Government agencies, subject to the same general body of legislation as other agencies, but with a complementary set of sector-specific laws and regulations designed, among other things, to safeguard academic freedom.
Decision making in HE is decentralized, with a relatively high degree of powers and responsibilities having been delegated to the institutions. The Government decides on objectives and specifies the required results, while it is the responsibility of the institutions to ensure that the activities are carried out in the best possible way. There is a substantial amount of freedom for the institutions to decide on the use of their resources and organization of their activities as well as their educational profile. The institutions are required to report back to the Government in various ways. Also within the institutions, the degree of decentralization is high. Thus, a lot of power is exercised by the departments.
Higher education and research in Sweden, as a whole, is financed predominantly by public funds, mainly via direct allocations from the state to the institutions. However, the proportion allocated directly in relation to other funding sources differs for undergraduate and graduate studies on the one hand and for research and doctoral studies on the other. In total, over 85 % of the revenues for higher education, excluding research and doctoral studies, consist of direct state allocations. The proportion of funding received by the HEI’s for research and doctoral studies from direct state allocations is substantially lower.
Importantly, the amount of resources received by an institution is related to the number of students attracted to study at the specific institution as well as the number of graduates. That quantity oriented system has called for a well developed organization of scrutiny in the ways teachers, subject areas, programs, departments and institutions are performing.
Quality assurance
(mainly sourced from: E-learning quality. Aspects and criteria for evaluation of e-learning in higher education and The Swedish Higher Education System)
The Swedish National Agency for Higher Education is responsible for the quality evaluation. A national quality assurance system was developed in 2001, when the national agency was commissioned by the Swedish Government to evaluate all academic subjects and vocational programs at all higher education institutions over a six-year period of 2001 – 2007. The Swedish National Agency for Higher Education has completed two rounds of quality audits of higher education institutions.
A new quality assurance system was launched in 2007. The new system is made up of five different components. These are:
- Audits of the quality assurance mechanisms of higher education institutions,
- Evaluations of subjects and programs,
- Appraisals of the entitlement to award degrees,
- Thematic evaluations and thematic studies,
- Identification of centers of educational excellence.
Swedish HEIs in the information society
A country online
(mainly sourced from: On the Move Towards Online Education in Sweden, Chapter 3 by Carl Holmberg in NKI Förlaget – Online Education and Learning Management Systems by Morten Flate Paulsen.)
As in other countries, investments in information technology have been relatively high over the decades. The use of radio, television, video, and computers in education and training has been investigated and discussed by state commissions one after another. The decades of development work and various committees have, indeed, had its effect: common awareness and investments in technology infrastructure have been increased. A large variety of technical equipment and fast communication networks have also been successively installed. A turning point came in the mid 1990s, and some of the main factors behind it were:
- very strong demonstration of official policy on the introduction of IT;
- setting-up of agents for change supporting development of education systems;
- pushes and pulls – more space for local initiatives.
In February 1994, the Swedish Prime Minister Carl Bildt gave a speech about setting a new political agenda for the transformation of Sweden into a nation drawing upon the resources of information technology. He formed an IT Commission where he himself was a chair and many of the other ministers of his government were delegates. Included in the commission were also researchers and representatives of business and industry. The idea was to initiate, promote and get IT-related transformations in all sectors of society, and the main task for the commission was to highlight the possibilities of IT, to identify limitations and pave the way for the introduction of it. Also an IT policy was developed.
From 1994 onwards, the idea was to invest approximately one billion Swedish crowns (€ 110 million) per year in research and development work. Up till 2003, that most probably also was the case. Altogether development programs, foundations, research schemes, national agencies and authorities, and municipalities some years spent more than that. All in all, the fact that the government itself tried to demonstrate good practice, to be a spearhead in the introduction of IT, was of high importance.
The prosperous future of e-learning
(mainly sourced from: On the Move Towards Online Education in Sweden, Chapter 3 by Carl Holmberg in NKI Förlaget – Online Education and Learning Management Systems by Morten Flate Paulsen.)
When in many other countries open universities were created, Sweden chose not to build a single-mode institution for distance education. Instead an extremely decentralized system was set up for the tertiary level. The responsibility for carrying out distance education rested with the individual university departments, which at the same time organized traditional forms of university education. Thus, a dual-mode system was created.
At the beginning of 1990s, about 800 distance education courses were arranged. A majority of those courses, however, had either no distance education at all or were courses with just a few distance education elements. Even though small changes over the years were shown, the state-of-the-art was not at all up to the standards expected by the authorities. On the other hand, the number of students following distance education courses in the academic year 1994 – 1995 was 25,800, which was an increase of 60 % over a couple of years and about 10 % of the student population.
During the 70s, 80s and 90s, the ambitions of the government were to increase the extent of distance education. In the light of history, the actions taken for improving that field can be described as four steps (Umeå University, The University Consortia, Dukom and Distum, Nätuniversitetet), each of which was a trial of alternative strategies.
Umeå University
In the late 1980s, the government made a first large-scale attempt by concentrating funds and efforts on a development program at Umeå University. The overarching purpose was to contribute to rural development in the northern sparsely populated areas of the country.
The University Consortia
The second step was taken by the government through making resources available to stimulate co-operation between universities. By gathering expertise from different institutional bodies and bringing a diversity of stakeholder perspectives together, new and more potent organizers of distance education could grow. This brought about the establishment of a number of university consortia with the purpose of developing distance education in joint projects.
Three main consortia emerged. The first was founded in 1993 through an agreement between the universities of Linköping, Umeå, Uppsala and Växjö, and the Royal Institute of Technology. Later in 1996, Lund University joined the consortium. The formation of this organization was a response to the ministry initiative about the need for collaboration in the development of distance education in the light of ICT development.
Another consortium that was founded in the mid-90s was 'Svenska distanshögskolan' which was a co-operation between higher education institutions in Gävle, Blekinge and Örebro, Mid Sweden University, a study organisation TBV and the national educational TV-channel, UR. A third consortium was founded by Göteborg University together with the nearby university colleges in Borås, Trollhättan, Uddevalla, Skövde and the University of Karlstad.
The three consortia had somewhat similar agendas. The size of their total activities by the turn of the century was in the proximity of 6,000 students studying 40 – 50 courses equivalent to about 7 to 15 ECTS each. The majority of students were adults who were in the work force, i.e. employed people. By the end of year 2000 one of the consortia suggested that a virtual university should be formed in a joint venture by the three consortia. This proposal, however, did not receive funds from the government. Basically this meant that no more funds was allocated directly to the operations of the consortia. Some activities, however, continued e.g. collaboration and cooperation in developing and delivering education in forms, which are better described as thematic networks.
The political agenda guiding the development of higher education in Sweden at the time dealt with the accessibility of education also for people. Taking into account their social life and possibilities to have full time work. The concept Lifelong Learning came once again into use. Other considerations were the access to higher education by different socio-economic, gender and ethnic strata of the population.
Additionally, there were economical reasons on the political agenda for higher education at the time. The concept of Lifelong Learning became the primary argument for opening up Swedish higher education for a widened target group. The governmental proposition for the parliament in fall 2001 included many aspects of the openness of higher education and the forming of Swedish net university.
Dukom and Distum
The third step was taken through forming the Commission on Distance Methods within Education. The Minister of Education appointed the Commission during 1995 with the assignment to outline strategies for distance education policy. A national web site with tools for Distance Teaching and Distance Studies was to be organized. Additionally, research in the field of distance education was to be informed about.
In July 1999, the Swedish Agency for Distance Education (Distum) commenced its operations in Härnösand in the north of Sweden. The agency promoted the development and application of distance education based on information and communication technologies (ICT-based distance education). The operations encompassed universities/colleges and popular public education throughout the country. In March 2002, however, the Ministry of Education and Science decided to close the agency.
Swedish Net University
The fourth route towards a more pluralistic way of teaching and learning at the universities was tested 2002 until the end of 2008. The Swedish government decided to set up the Swedish Net University. It was based upon the distance (netbased) courses and programs already given by the universities and university colleges. Participation in the framework the Net University gave was voluntary. In order to support the project, the Swedish Net University Agency was set up. The primary task of the agency was to co-ordinate the different courses given by various Swedish universities and for that purpose run a web site exposing the courses. The agency also supported improvements in skills and competence among distance education teachers and other personnel and identified topics and areas that would benefit from more distance education.
Thus, the initiatives in this fourth step of promoting distance education and its followers moved back to the institutional level. That together with seed money was the driving forces in this case. During the first years of existence, each student taking courses via the Net University gave a much higher return to the university than students following on campus courses. For the first two years, 371 million SEK (€ 41 million) was spent on this purpose.
Moving out of central initiatives
When new policy was developed after the election 2006 the core theme was to underline the decentralisation in the Swedish education systems. The idea of national agencies guiding the developments was abandoned and the institutions of higher education should themselves find ways of organisations for distance education and flexible learning. Thus, the Swedish Net University Agency was closed in 2008. The Swedish Net University still exists but as an initiative run by the individual universities.
Quality assurance and e-learning in Sweden
(mainly sourced from: E-learning quality. Aspects and criteria for evaluation of e-learning in higher education)
In Sweden, the same universities and university colleges that organize campus based education also offer e-learning courses and programs. This system is commonly called dual mode. The policy in Sweden is that the same fundamental quality requirements should apply to e-learning as to campus based higher education. However, there is also a consensus that there are significant differences between e-learning and campus based education. To address these differences, adjustments in the methods of evaluating higher education are required. Traditional quality criteria and evaluation methods do not identify and assess the new aspects of higher education introduced by e-learning.
In 2002 – 2003, a report on the quality of IT-supported distance education was compiled under the auspices of the Swedish Net University Agency. The report focused on quality audits and defined four main quality processes:
- Accessibility
- Widening participation
- Transfer of credits
- Educational development
In 2008 the National quality assessing organisation published a survey on e-learning quality (the Swedish National Agency for Higher Education 2008:11R)). The main aim of the survey was to provide a synthesis based on international research and practice in quality and quality assessment of e-learning. It was meant to form a basis for strategic development of the HSV quality assurance system. The central issues were “what constitute quality in e-learning in higher education” and what challenges does that put on the Universities and on the assessing bodies.
Virtual initiatives in HE
Swedish Net University
(mainly sourced from: The UNIVe Project, Swedish Agency for Networks and Cooperation in Higher Education, On the Move Towards Online Education in Sweden, Chapter 3 by Carl Holmberg in NKI Förlaget – Online Education and Learning Management Systems by Morten Flate Paulsen) and [www.nshu.se/english/download/4022/nshubroschyreng2006.pdf This is NSHU – our task and mission. A presentation of the Swedish Agency for Networks and Cooperation in Higher Education (PDF)].)
The Swedish Net University (NU) was founded in March 2002. The aim of NU is to widen the distance education market in Sweden. This is being done through two main lines of activities. One is the provision of a portal for all courses which are delivered over the Internet by any Swedish institution of higher education. The other line of activities was the support of development of methods within distance education. Extra funds have been given to the institutions according to their contribution of courses to the NU. The annual budget of the NU amounts to about € 3.9 million per year (2004). Most of the fundings where allocated to support networks between the Universities. The network worked with joint-programmes as well as collaboration around study guidance councelling and pedagogical development in the context of distance education (see also: The Swedish Net University in Facts and Figures 2002 - 2006).
In order to support the NU project, the Swedish Net University Agency was also set up. The primary task of the agency was to co-ordinate the different courses given by various Swedish universities and for that purpose run a web site exposing the courses. The agency also supported improvements in skills and competence among distance education teachers and other personnel and identified topics and areas that would benefit from more distance education.
Since 2006, the Swedish Net University Agency has been known as the Swedish Agency for Networks and Cooperation in Higher Education (NSHU). So the Swedish Net University and its student portal have remained, but the Agency now has two additional main tasks – educational development and widening participation. Moreover, they are to promote the new structure of Swedish higher education and degrees (Bologna Process), as well as the collaboration between Swedish universities and university colleges and, together with them, support further development.
In 2008, the Swedish Government decided to give NSHU notice of closure. So the agency was shut down at the end of year 2008. However, the closure did not concern the Swedish Net University. Today, all IT-supported distance education is available at studera.nu instead. In five years, the number of distance students has also increased from 55,000 students in 2003 to over 100 000 students in 2007. Additionally, the number of completely web-based courses and programs has increased from about 30 % in 2003 to as much as 54 % in 2007.
KHiS - Municipalities and Universities in Collaboration
The tradition of distance education in Swedish universities has mainly followed the dual mode and small-scale lines of development. Many universities in Sweden established themselves in the distance education during the 1980s and 1990s. At that time, also municipal learning centers for higher education, where students could meet, form study groups and use technical facilities for their university studies, were developed. The learning centers, in turn, organized themselves in networks such as NITUS, Academi Norr and KHiS - Municipalities and Universities in Collaboration.
KHiS - Municipalities and Universities in Collaboration (Kommuner och Högskolor i Samverkan) is a collaborative organization formed by 54 municipalities and 5 universities in Northern Sweden. The universities include Luleå University of Technology, Umeå University, SLU - Swedish University of Agricultural Sciences in Umeå, Mid Sweden University and University of Gävle.
The purpose of KHiS is to collaborate and create increased accessibility to higher education and competency development in the northern region, taking into account the local competency needs. This is mainly achieved through the development of flexible education programs delivered at a distance, and also by prioritizing the usage of information and communication technologies (ICT) and associated teaching techniques. Information about the learning centers is spread trough universities.
Lärcentra.se is a service, developed by KHiS with other suchlike networks, to offer more information about the learning centers in Sweden.
Gotland University
Gotland University, established in 1998, is among the youngest universities in Sweden. It is located in the World Heritage city of Visby. The university offers quality programs and courses in English both on campus and online.
In 2005, the number of registered students was 5,127 and the number of full-time students: 2,335 (63 % of whom were 25 years or older). Some 42 % were registered at a masters program and 58 % at courses. A 'typical' student at Gotland University studied single courses from a distance. In 2005, the total number of full-time students in distance education was 1,120 (whereas on campus, the equivalent figure was 1,092). The number of employees (2005) was 207 and the number of teachers 108 (of whom 51 had a PhD). The number of professors was 10. The total income (2005) was approximately 153,000,000 SEK.
The internet based courses offered by Gotland University cannot be studied on campus. The communication between teachers and students is entirely based on e-mail, discussion boards and the chat in virtual class room. In the virtual class room, teachers also provide their guidance and students can find their course material, hand-ins and exams, among other things.
HiG - University of Gävle
Since its established in 1977, the University of Gävle has expanded rapidly and currently comprises six departments offering some 50 degree programs and 800 elective courses. There are approximately 13,000 registered students at the university. Half of these students come from the surrounding region; the other half come from other parts of Sweden. The total number of employees is some 800, of whom over 30 are full professors and 150 senior lecturers. A high percentage of the academic staff has an international background, a fact that contributes to the university's on-going process of internationalisation.
The most common form of distance education at HiG is the combination of Internet and video conferences, but also e-mail and telephone are commonly used. In some courses, there may even be one or more meetings at the university. Certain courses are, however, completely web-based and have no obligatory meetings at the university or any other place. Students and teachers communicate via e-mail, computer conferences, or so-called virtual classrooms. In order to take online courses at HiG, one only needs access to a personal computer with Internet connection.
A learning center is the central support funtion for distance education and flexible learning at HiG. The learning center also closely cooperates with the study centers in the region.
Mid Sweden University
Geographically, Mid Sweden University is located in the middle of Sweden. It is a young university, but its roots date back to as early as 1842., when the 'university' was still a teachers' education college in Härnösand. The university was established in July 1993, when the University Colleges of Sundsvall/Härnösand and Östersund were merged. In July 1995, the Sundsvall/Örnsköldsvik and Sundsvall Colleges of Health Sciences were also incorporated. Ten years later (2005), the Mid Sweden University became a full status university.
Today, Mid Sweden University has three campuses in Härnösand, Sundsvall and Östersund, with approximately 15,000 students. Around 60 % are campus students, while the rest engage in distance tuition via net based courses and programs. Every year students from all over the world come to study at Mid Sweden University, which offers courses for international students at all three campuses.
The work of Mid Sweden University is based on undergraduate courses, research and co-operation with regional actors. There are some 700 independent courses, 50 study programs and 30 master programs offer at the university. The number of employees is around 900 (54 professors).
References
- Holmberg Carl (2003): On the Move Towards Online Education in Sweden. NKI Förlaget – Online Education and Learning Management Systems by Morten Flate Paulsen.)
- Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development (2007): Education at a Glance – OECD Briefing Note for Sweden.
- Swedish Agency for Networks and Cooperation in Higher Education (2006): [www.nshu.se/english/download/4022/nshubroschyreng2006.pdf This is NSHU – our task and mission. A presentation of the Swedish Agency for Networks and Cooperation in Higher Education (PDF)]
- Swedish National Agency for Higher Education (2006): OECD Thematic Review of Tertiary Education – Country Background Report for Sweden
- Swedish National Agency for Higher Education (2008:11R): E-learning quality. Aspects and criteria for evaluation of e-learning in higher education
- Swedish National Agency for Higher Education (2008): The Swedish Higher Education System
Relevant websites
- BOLDIC - The Baltic-Nordic Network for Exchange of Experience in ODL
- Gotland University
- Government Offices of Sweden
- MegaTrends in E-Learning Provision
- Mid Sweden University
- Study in Sweden
- Swedish Agency for Networks and Cooperation in Higher Education
- Swedish Net University
- The UNIVe Project
- University of Gävle
- Wikipedia
- Report E-learning quality, 2008:11R
Relevant reports
> Sweden