Welcome to the Virtual Education Wiki ~ Open Education Wiki
Tonga: Difference between revisions
(added key cats) |
(initial material) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
== Partners situated in Tonga == | == Partners situated in Tonga == | ||
None. | |||
== Tonga in a nutshell == | == Tonga in a nutshell == | ||
''Tonga'', officially the '''Kingdom of Tonga''' (Tongan: '''Pule'anga Fakatu'i 'o Tonga'''), an archipelago in the South [[Pacific Ocean]], comprises 169 islands, 36 of them inhabited. The Kingdom stretches over a distance of about 800 kilometres (500 miles) in a north-south line. The islands that constitute the archipelago lie south of [[Samoa]], about one-third of the way from [[New Zealand]] to [[Hawaii]]. | |||
Tonga also became known to geographers as the '''Friendly Islands''' because of the friendly reception accorded to Captain James Cook on his first visit in 1773. He happened to arrive at the time of the ʻinasi festival, the yearly donation of the first fruits to the Tuʻi Tonga, the islands' paramount chief, and received an invitation to the festivities. | |||
Tonga, the only sovereign monarchy among the island nations of the Pacific Ocean, has a unique history as the only island nation in the region to have avoided formal colonial tutelage. Tonga is poised to become a constitutional monarchy after legislations reforms, and a more fully representative election, takes place in 2010. | |||
The population of Tonga is 104,000. | |||
The capital(and largest city) is Nukuʻalofa. | |||
[[Image:Tonga.gif|right|thumb|300px|Source : http://www.cia.gov]] | |||
Over 70% of the 101,991 inhabitants of the Kingdom of Tonga live on its main island, Tongatapu. Although an increasing number of Tongans have moved into the only urban and commercial centre, Nukuʻalofa, where European and indigenous cultural and living patterns have blended, village life and kinship ties continue to be important throughout the country. Everyday life is heavily influenced by Polynesian traditions and especially by the Christian faith; for example, all commerce and entertainment activities cease from midnight Saturday until midnight Sunday, and the constitution declares the Sabbath to be sacred, forever. Some Tongans are Methodists with a significant Catholic minority and a number of members of the Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints (Mormons). | |||
The Tongan language is the official language of the islands, along with English. Tongan is a Polynesian language which is closely related to Wallisian (Uvean), Niuean, Hawaiian, and Samoan. | |||
== Tonga education policy == | == Tonga education policy == | ||
| Line 28: | Line 44: | ||
=== The Bologna Process === | === The Bologna Process === | ||
| Line 48: | Line 64: | ||
=== Interesting Virtual Campus Initiatives === | === Interesting Virtual Campus Initiatives === | ||
=== Interesting Programmes === | === Interesting Programmes === | ||
| Line 57: | Line 73: | ||
== Lessons learnt == | == Lessons learnt == | ||
None so far. | |||
== References == | == References == | ||
---- | ---- | ||
Revision as of 20:37, 27 January 2010
Partners situated in Tonga
None.
Tonga in a nutshell
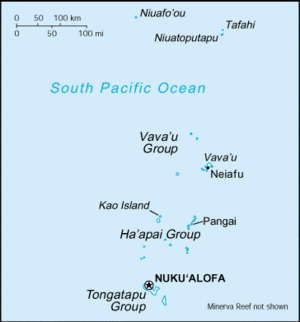
Tonga, officially the Kingdom of Tonga (Tongan: Pule'anga Fakatu'i 'o Tonga), an archipelago in the South Pacific Ocean, comprises 169 islands, 36 of them inhabited. The Kingdom stretches over a distance of about 800 kilometres (500 miles) in a north-south line. The islands that constitute the archipelago lie south of Samoa, about one-third of the way from New Zealand to Hawaii.
Tonga also became known to geographers as the Friendly Islands because of the friendly reception accorded to Captain James Cook on his first visit in 1773. He happened to arrive at the time of the ʻinasi festival, the yearly donation of the first fruits to the Tuʻi Tonga, the islands' paramount chief, and received an invitation to the festivities.
Tonga, the only sovereign monarchy among the island nations of the Pacific Ocean, has a unique history as the only island nation in the region to have avoided formal colonial tutelage. Tonga is poised to become a constitutional monarchy after legislations reforms, and a more fully representative election, takes place in 2010.
The population of Tonga is 104,000.
The capital(and largest city) is Nukuʻalofa.
Over 70% of the 101,991 inhabitants of the Kingdom of Tonga live on its main island, Tongatapu. Although an increasing number of Tongans have moved into the only urban and commercial centre, Nukuʻalofa, where European and indigenous cultural and living patterns have blended, village life and kinship ties continue to be important throughout the country. Everyday life is heavily influenced by Polynesian traditions and especially by the Christian faith; for example, all commerce and entertainment activities cease from midnight Saturday until midnight Sunday, and the constitution declares the Sabbath to be sacred, forever. Some Tongans are Methodists with a significant Catholic minority and a number of members of the Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints (Mormons).
The Tongan language is the official language of the islands, along with English. Tongan is a Polynesian language which is closely related to Wallisian (Uvean), Niuean, Hawaiian, and Samoan.
Tonga education policy
Tonga education system
Higher education
Universities in Tonga
Polytechnics in Tonga
Higher education reform
The Bologna Process
Administration and finance
Quality assurance
Tonga HEIs in the information society
Towards the information society
Information society strategy
Virtual Campuses in HE
Interesting Virtual Campus Initiatives
Interesting Programmes
Re.ViCa Case-study
Lessons learnt
None so far.