Welcome to the Virtual Education Wiki ~ Open Education Wiki
Dominican Republic: Difference between revisions
(→Universities in Dominican Republic: more links added) |
(→References: added cat Hispaniola) |
||
| Line 154: | Line 154: | ||
[[Category:Dominican Republic| ]] | [[Category:Dominican Republic| ]] | ||
[[Category:Hispaniola]] | |||
[[Category:Caribbean]] | [[Category:Caribbean]] | ||
[[Category:Spanish-speaking countries]] | [[Category:Spanish-speaking countries]] | ||
[[Category:Countries with Programmes]] | [[Category:Countries with Programmes]] | ||
Revision as of 21:42, 15 January 2010
Not to be confused with Dominica.
Partners situated in Dominican Republic
None.
Dominican Republic in a nutshell
(sourced from http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Dominican_Republic)
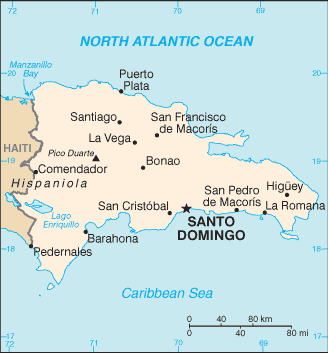
The Dominican Republic (Spanish: República Dominicana) is a nation on the island of Hispaniola, part of the Greater Antilles archipelago in the Caribbean region. The western third of the island is occupied by the nation of Haiti, making Hispaniola one of two Caribbean islands that are occupied by two countries, Saint Martin being the other.
Both by area and population, the Dominican Republic is the second largest Caribbean nation (after Cuba), with 48,442 km² and an estimated 10 million people.
The capital is Santo Domingo.
The Dominican Republic is a representative democracy, with national powers divided among independent executive, legislative, and judicial branches. The President of the Dominican Republic appoints the Cabinet, executes laws passed by the Congress, and is commander in chief of the armed forces. The president and vice president run for office on the same ticket and are elected by direct vote for 4–year terms. Legislative power is exercised by a bicameral Congress composed of the Senate (with 32 members) and the Chamber of Deputies (with 178 members).
The Dominican Republic is divided into 31 provinces. Additionally, the national capital, Distrito Nacional (National District), is contained within Santo Domingo. The provinces are divided into municipalities (municipios; singular municipio). They are the second–level political and administrative subdivisions of the country.
The population of the Dominican Republic in 2007 was estimated by the United Nations at 9,760,000, which placed it number 82 in population among the 193 nations of the world. In that year approximately 5% of the population was over 65 years of age, while 35% of the population was under 15 years of age. There were 103 males for every 100 females in the country in 2007. According to the UN, the annual population growth rate for 2006–2007 is 1.5%, with the projected population for the year 2015 at 10,121,000.
Dominican Republic education policy
http://www.seescyt.gov.do/default.aspx (Spanish)
Which is responsible to promote, regulate and manage the National System of Higher Education, Science and Technology under Law 139-01.
http://www.adru.org/ (Spanish)
It was founded on 18 August 1980 as a non-profit association composed of state and private universities Dominican recognized by existing laws, whose legal status was granted by Decree No. 2548 dated 3 July 1981.
Dominican Republic education system
Higher education
Universities in Dominican Republic
For a list of universities see http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/List_of_universities_in_the_Dominican_Republic or http://www.seescyt.gov.do/educsuperior/default.aspx (Spanish)
- Barna Business School
- Instituto Politécnico Loyola
- Instituto Superior de Agricultura
- Instituto Técnico Superior Oscus San Valero
- Instituto Tecnológico de Santo Domingo
- Instituto Tecnológico del Cibao Oriental
- Pontificia Universidad Católica Madre y Maestra
- Universidad Abierta para Adultos
- Universidad Adventista Dominicana
- Universidad APEC
- Universidad Autónoma de Santo Domingo
- Universidad Católica de Santo Domingo
- Universidad Católica Nordestana
- Universidad Católica Tecnológica del Cibao
- Universidad Central del Este
- Universidad Central Dominicana de Estudios Profesionales
- Universidad de la Tercera Edad
- Universidad del Caribe
- Universidad Dominicana Organización y Método
- Universidad Domínico - Americana
- Universidad Eugenio María de Hostos
- Universidad Experimental Félix Adam
- Universidad Federico Henríquez y Carvajal
- Universidad Iberoamericana
- Universidad Interamericana
- Universidad Nacional Evangélica
- Universidad Nacional Pedro Henríquez Ureña
- Universidad Nacional Tecnológica
- Universidad Odontológica Dominicana
- Universidad Psicología Industrial Dominicana
- Universidad Tecnológica de Santiago
Polytechnics in Dominican Republic
Higher education reform
The Bologna Process
Administration and finance
Quality assurance
Dominican Republic's HEIs in the information society
Towards the information society
Information society strategy
Virtual Campuses in HE
Interesting Virtual Campus Initiatives
Virtual Campus
Las Americas Institute of Technology (Spanish/English)
As a leading institution in the field of technology training, it makes extensive use of new technologies. For this reason we have created the Department of Educational Technology (DTE) that has several initiatives that support our strategy of distance education and educational application software.
National Judicial College (Spanish)
Training school for judges and public defenders from the Dominican Republic
The National Judicial College offers judges and public defenders virtual courses that are the academic offerings for the period October to December 2009 with seats available.
Institute of Technology of Santo Domingo(Spanish)
The Technological Institute of Santo Domingo is a private university, public service, nonprofit that started its academic activities offering postgraduate programs, short updating courses as Continuing Education, research and science communication. This situation prompted the INTEC out in the country a pioneer in that level of study. Later, in 1973 joined the undergraduate curriculum to their offer.
The virtual campus aims to develop a working methodology that serves as the basis for the INTEC to provide a training tool that comes within reach of the student community nationwide through the use of Internet technology and other means to enable the broadcasting of interactive academic content.
Distance Learning
Universidad Autónoma de Santo Domingo(Spanish) This one uses radio and TV.
http://uasd.edu.do/news/Default.aspx?article_id=1122 (Spanish) With the presence of the rector of the Universidad Autonoma de Santo Domingo (UASD), Dr. Franklin Garcia Fermin, opened the Sixth International Congress on Information Technology, Communication and Distance Education, CITIC 2009 VI CREAD CARIBBEAN.
Its purpose is to create a space for reflection and exchange that contributes to the development of Distance Learning (DL) as a mode of education and its relation to the Information Technologies and Communication Technologies (ICT).
UASD (Spanish)graduateds the first teachers in virtual learning management
Other
Dominican Institute of Telecommunications (Spanish)
Is the state agency created by the General Telecommunications Law (153-98) that regulates and oversees the development of the telecommunications market. Its mission is to "regulate and promote the provision of telecommunications services for the benefit of society, in a free, fair and effective competition” and to hear and decide the Complaint Resources (RDQ) which are submitted by users of public telecommunications services.
Distance Education Center
The Distance Learning Center is a Department of the INAP responsible for promoting educational topics using new information technologies and communication. In particular it uses semi virtual and online strategies which hold an offer of fully exhausting the opportunities of distance education. This can be an excellent channel for transmitting high-level programs offered anywhere in the world.
Interesting Programmes
See Open University for Adults.
Re.ViCa Case-study
None.