Welcome to the Virtual Education Wiki ~ Open Education Wiki
Czech Republic
by authorname authorsurname
Experts situated in Country
Country in a nutshell
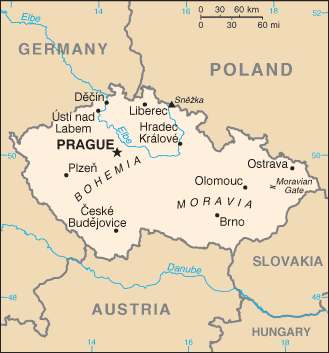
The Czech Republic is a landlocked country in Central Europe with neighbouring countries Poland to the north-east, Germany to the west, Austria to the south, and Slovakia to the east. The capital and largest city is Prague (Czech: Praha), the official language is Czech and the citizens of this country are called the Czechs. The Czech Republic is composed of the historic regions of Bohemia and Moravia, as well as parts of Silesia. The Czech Republic is a member of NATO since 1999 and the European Union since 2004. As of January 1, 2009, the Czech Republic holds the EU Presidency (2009).
The Czech Republic is a pluralist multi-party parliamentary representative democracy. President Václav Klaus is the current head of state (for the 2008-2013 term). The Prime Minister for 2008-2013 is the head of government (currently Mirek Topolánek). The Parliament has two chambers — the Chamber of Deputies] and the Senate. It is also a member of the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD), the Council of Europe (on European integration and Human Rights) and the Visegrád Group, which is a regional alliance between the Czech Republic, Hungary, Poland and Slovakia.
Since 2000, the country is divided into thirteen regions (Czech: kraje, singular kraj) and the capital city of Prague. Each region has its own elected Regional Assembly and hejtman (usually translated as hetman or president). In Prague, their powers are executed by the city council and the mayor.
- Adapted from: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Czech_Republic
Communism history
The Czech Republic is a relatively small country (an area of 78,886 km2) in Central Europe with 10.3 million inhabitants, with a population density of 131 per square km. It was formerly part of Czechoslovakia, where communists seized power in 1948 and retained almost complete control over all areas of life. In 1989 this communist regime fell and Czechoslovakia transformed from a centrally controlled country to a parliamentary democracy with the President as the head of state. This change had an impact on economy, health, life expectancy and of course also education; more information on that aspect is below.
In 1993 the Czech and Slovak Federal Republic (formerly Czechoslovakia) peacefully split into two states (one of which is now still the Czech Republic). Territorially, it is divided into 13 regions and the capital city, Prague (population over 1.3 million). The official language is Czech and the unit of currency is the Czech koruna (CZK); 1 euro is about 30 CZK.
- Adapted from: “Thematic Review of Tertiary Education - Country Background Report - Czech Republic” by Centre for Higher Education Studies, Ministry of Education, Youth and Sports, Czech Republic, 2006, PDF – 144 pages
- Documents of relevance: Czech Republic - useful information, by the Private College of Economic Studies, Ltd.
Education in Country
The nursery school (mateřská škola) offers pre-primary education to children aged from 3 to 6. It is not compulsory, but attendance is very high − almost 93 % of children of the relevant age in the last pre-school-year. Crèches (jesle) are intended for children up to the age of 3; these are not integrated into the education system but come under the responsibility of the Ministry of Health; with regard to the three-year maternity leave, the crèches are attended only by 0.5 % of a relevant age group.
Compulsory school attendance takes 9 years (6−15 years of age). Pupils (almost 80 % of the respective population) attend basic schools divided into two levels (primary level and lower secondary level). Starting with the second level there is the possibility of continuing compulsory schooling in secondary general schools (gymnázia), after the 5th year in eight-year secondary general schools, after the 7th year in six-year secondary general schools or conservatoires. After completing compulsory schooling, 96 % of the population (in relation to the age cohort of 15 to 18-year-old youths) continue studies in non-compulsory upper secondary education, namely, either in secondary general schools that, apart from the eight-year, six-year schools mentioned above, have also four-year programmes (more than 20 % of population) or in vocational and other secondary schools (48.5 % in four-year courses completed with a school-leaving examination /maturitní zkouška/, 23 % in two or three-year courses completed with an apprenticeship certificate /výuční list/, and in some other courses) or in conservatoires.
Those who have completed their upper secondary education in the fields of study requiring apprenticeship certificates can continue in ISCED 4A follow-up courses, which are completed with a school-leaving examination or they may extend their qualifications in shortened study courses.
Those who acquired education completed with a school-leaving examination (ISCED 3A or 4A), i.e. over 72 % of the population, can continue at a tertiary level, namely in tertiary professional schools (ISCED 5B), or higher education institutions (ISCED 5 and 6). Apart from that, school-leavers with the school-leaving examination (maturitní zkouška) have the possibility to extend their qualifications in post-secondary programmes of secondary schools (in shortened study courses).