Welcome to the Virtual Education Wiki ~ Open Education Wiki
Morocco
Partners situated in Morocco
None.
Morocco in a nutshell
(sourced from http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Morocco)
Morocco, officially the Kingdom of Morocco, is a country located in Northern Africa. The full Arabic name al-Mamlaka al-Maġribiyya translates to "The Western Kingdom". Al-Maġrib (meaning "The West") is commonly used.
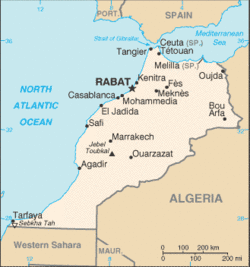
It has a coast on the Atlantic Ocean that reaches past the Strait of Gibraltar into the Mediterranean Sea. It is bordered by Algeria to the east, Spain to the north (a water border through the Strait and land borders with three small Spanish enclaves, Ceuta, Melilla, and Peñón de Vélez de la Gomera), and Mauritania to the south via the Western Sahara territories (which have unclear legal status).
It has a population of nearly 32 million and an area just under 447,000 square kilometres (173,000 sq mi).
Morocco is the only country in Africa that is not currently a member of the African Union and it has shown no interest in joining. However, it is a member of the Arab League, Arab Maghreb Union, Francophonie, Organisation of the Islamic Conference, Mediterranean Dialogue group, and Group of 77. It is also a major non-NATO ally of the United States.
Morocco is a de jure constitutional monarchy with an elected parliament. The King of Morocco, with vast executive powers, can dissolve government and deploy the military, among other prerogatives. Opposition political parties are legal, and several have been formed in recent years
Morocco is divided into 16 regions and subdivided into 62 prefectures and provinces. As part of a 1997 decentralization/regionalization law passed by the legislature, sixteen new regions were created.
Morocco is a constitutional monarchy with an elected parliament. The King of Morocco holds vast executive powers, including dissolving parliament at will. Executive power is exercised by the government but more importantly by the king himself. Legislative power is vested in both the government and the two chambers of parliament, the Assembly of Representatives and the Assembly of Councillors. The king can also issue decrees called dahirs which have the force of law. Parliamentary elections were held in Morocco on 7 September 2007, and were considered by some neutral observers to be mostly free and fair; although voter turnout was estimated to be 37%, the lowest in decades. The political capital is Rabat, and the largest city is Casablanca; other large cities include Marrakesh, Tetouan, Tangier, Salé, Fes, Agadir, Meknes and Oujda.
Every Moroccan speaks at least one of the two languages Berber and Moroccan Arabic, as a mother tongue. Both languages have regional dialects and accents. Most Moroccans practice Sunni Islam and are of Arabized Berber and Berber stock. Arab-Berber comprise about 99.1% of the Moroccan population.
Morocco education policy
Education in Morocco is free and compulsory through primary school (age 15). Nevertheless, many children – particularly girls in rural areas – still do not attend school. The country's illiteracy rate has been stuck at around 50% for some years, but reaches as high as 90% among girls in rural regions.
Morocco allocates approximately one-fifth of its budget to education. Much of this is spent on building schools to accommodate the rapidly growing population. Education is mandatory for children between the ages of 7 and 13 years. In urban areas the majority of children in this age group attend school, though on a national scale the level of participation drops significantly. About three-fourths of school-age males attend school, but only about half of school-age girls; these proportions drop markedly in rural areas. Slightly more than half of the children go on to secondary education, including trade and technical schools. Of these, few seek higher education. Poor school attendance, particularly in rural areas, has meant a low rate of literacy, which is about two-fifths of the population.
Morocco gained independence from the French in 1956 and since then the Government of Morocco has embarked to implement comprehensive reforms in education and technical vocational training. Despite facing economic challenges in the 1990s and early 2000, the government continued concerted efforts to improve overall educational landscape. In 2006 the expenditure on education as a percentage of GDP was 5.5 percent, higher than the education expenditure as a percent of GDP for Arab countries, such as, Oman, Kuwait and Egypt.
Since early 2000s the gross enrollment rates have been rising steadily for all levels of education. Completion rates at the primary level have increased from 57.8 in 2004 to 61.7 percent in 2006. Despite this improvement, Morocco’s education system needs to tackle gender disparity at all levels, high dropout and repetition rates especially at primary and secondary levels, and increased pressure on the higher education to absorb the rising number of secondary graduates. Throughout Morocco, female illiteracy rate is higher than men's. They reach 83 percent in rural areas, even 90 percent in some communities. Morocco is ranked 130th in Human Development Index (HDI). It has an adult literacy rate of 52 percent in 2004. Although education completion and enrollment rates have improved, the possibility of achieving the MDGs for Morocco is uncertain.
Morocco education system
In Morocco the education system offers the following three tracks:
- The Modern track, which is the continuation of the French system
- Original track, which is the Koranic teachings
- The technical track, to have skilled workforce.
School-level education
Pre-primary level Pre-primary education is compulsory and available from ages four to six. Private kindergarten institutions are found mainly in the cities and towns, while Koranic preschool is more widespread, teaching reading and writing skills.
Primary level Beginning age seven, primary education lasts for five years until age 12, and is compulsory. Progression to secondary school is dependant on passing the Certificate d'Etudes Primaries.
Secondary Level Secondary education is divided into two sections, starting with the premier cycle d'education secondaire, lasting four years. Those successfully completing the primary cycle advance to either the three-year secondary cycle, deuxième cycle secondaire, or to technical or vocational schools.
Further and Higher education
Morocco has more than 48 universities, institutes of higher learning, and polytechnics dispersed at urban centres throughout the country. There are 14 public universities and many private institutions.
Universities in Morocco
Morocco has about 230,000 students enrolled in 14 public universities. Four are of particular note.
- The Mohammed V University in Rabat - the country’s largest university, with branches in Casablanca and Fès
- Al-Akhawayn, a private university founded in 1993 by King Hassan II and King Fahd of Saudi Arabia, is an English-language American-style university comprising about 1,000 students.
- The University of Al Karaouine, in Fez, is considered the oldest continuously operating university in the world and has been a center of learning for more than 1,000 years.
- The Veterinary Institute in Rabat, which conducts leading social science research in addition to its agricultural specialties
The page http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/List_of_universities_in_Morocco gives a longer list:
- Abdelmalek Essaâdi University, Tétouan - Tanger
- Al Akhawayn University, Ifrane
- Cadi Ayyad University, Marrakech
- Chouaib Doukkali University , El Jadida
- Hassan II Ain Chok University , Casablanca
- Hassan II Mohammedia University , Mohammedia
- Hassan Premier University , Settat
- Ibn Tofail University , Kenitra
- Ibnou Zohr University , Agadir
- Mohamed Premier University , Oujda
- Mohammed V University, Rabat
- Mohammed V University at Agdal, Rabat
- Mohammed V University at Souissi, Rabat
- Moulay Ismail University , Meknès
- Sidi Mohamed Benabdellah University , Fez
- University of Al Karaouine, Fes
- Université Moulay Slimane (formerly called Cadi Ayyad University until late 2007), Beni Mellal
A number of universities have started providing software and hardware engineering courses as well; annually the academic sector produces 2,000 graduates in the field of information and communication technologies.
Moroccan institutions have also established partnerships with institutes in Europe and Canada and offer joint degree programs in various fields from well-known universities.
Polytechnics in Morocco
Colleges in Morocco
Education reform
Administration and finance
Quality assurance
Also to increase public accountability, Moroccan universities are evaluated since 2000, with the intention of making the results public to all stakeholders, including parents and students.
Information society
ICT in education initiatives
Virtual initiatives in schools
Virtual initiatives in post-secondary education
The Moroccan Virtual Campus
The Moroccan Virtual Campus launched in 2002 aiming to link the various e-learning projects within Moroccan universities, enabling students to choose their study location and time, and to create greater knowledge access. [1] [2]
==
The report Development of the E-Learning in Morocco gives some useful pointers:
Despite numerous technical and publishing challenges, distance learning ((involving some e-learning)) is gaining momentum in Morocco in both the public and private sectors. Short-term forecasts show that 15% of private companies\’ training budgets will soon be dedicated to distance learning programmes.
The increased availability and functionality of information technology (IT) has brought new teaching tools to the Moroccan market, including mobile phones, video-conferencing, e-mail, discussion forums, chat software and document sharing.
Open and/or remote learning (formation ouverte et/ou à distance, or FOAD), provides flexible training opportunities to individuals, businesses, and government bodies. Training packages can be tailored according to individual or collective needs and electronic resources can be accessed from anywhere. Because classrooms are virtual, students can study at their own pace and teachers can instruct and assess on a flexible schedule.
An increase in the number of government-sponsored FOAD projects suggests a general shift towards the greater use of IT in the training sector. Morocco's finance ministry recently decided to integrate a dedicated distance learning service into its organisational structure. The Ministry of National Education has begun work on an interactive television system (TVI) which aims to provide remote training for teachers across the Kingdom.
Since 2006, Abdelfadil Bennani, President of Ibn Zohr University, has led a particularly ambitious project to create a Virtual Moroccan Campus. The campus aims to pool the resources of e-learning programmes throughout the university system, with the ultimate goal of developing full remotely-provided courses of study at the vocational, undergraduate, and graduate degree levels.
Despite the growing popularity of e-learning in Morocco, it is still in its infancy. For Radouane Mrabet, a teacher and researcher at the National School of Information Technology and Systems Analysis (ENSIAS), FOAD’s slow progress in the country can be explained by the exorbitant costs of developing training platforms and modules. "Even when these two major stumbling blocks are overcome, organisers must be prepared to bear the cost of tutors to provide support and remote supervision to trainees," he added.
So far, the private sector is best equipped to handle those costs. "Businesses are starting to fund distance learning for their employees," remarked Said Tahrir, Managing Director of the Moroccan subsidiary of business-training firm Formademos. Many large international corporations have already begun to provide their employees with virtual training modules that complement conventional training already in place.
Training centres have not been blind to these developments, and many have made a marketing push to capture the e-learning market. Formademos has launched two Masters programmes aimed at university graduates with at least one year of work experience. One programme offers a degree in "education and employment systems technology", and the other program offers a degree in business administration.
Lessons learnt
References
- The Road Not Traveled: Education Reform in the Middle East and North Africa, 2008, http://siteresources.worldbank.org/INTMENA/Resources/EDU_Flagship_Full_ENG.pdf
- Development of the E-learning in Morocco, 2007, http://www.medibtikar.eu/+Development-of-the-E-learning-in+.html