Welcome to the Virtual Education Wiki ~ Open Education Wiki
Burundi: Difference between revisions
| Line 58: | Line 58: | ||
<!--(this is an important section)--> | <!--(this is an important section)--> | ||
The main university is the University of Burundi (Université du Burundi) in the capital Bujumbura. It has a web site at http://www.ub.edu.bi but internal evidence suggests that it is very out of date (e.g. the page http://www.ub.edu.bi/ub-calendrier.php displays a calendar for 2005). | |||
However there are also: | |||
# Université Espoir d’Afrique (Hope Africa University), also in Bujumbura: describing itself as a "Christian liberal arts institution" - web site at http://www.hopeafricauniversity.org/ | |||
# Université Lumière de Bujumbura (Light University of Bujumbura) - web site at http://www.ulbu.info/ with substantial information in English but some lack of information dated later than 2008 | |||
# Université de Ngozi, in Ngozi - web site at http://www.ung.bi with some headings in English but not much depth of information | |||
=== Polytechnics in Country === | === Polytechnics in Country === | ||
Revision as of 09:59, 26 April 2011
This is the page for the country of Burundi, Africa (BI).
Burundi
Education
Higher Education
author byline
Experts situated in Country
Country in a nutshell
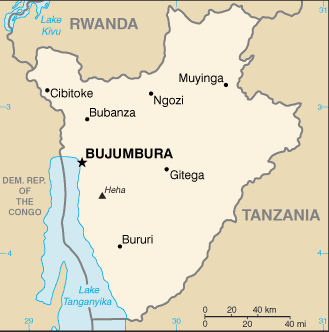
Burundi, officially the Republic of Burundi, is a country in the Great Lakes region of Eastern Africa bordered by Rwanda to the north, Tanzania to the east and south, and the Democratic Republic of the Congo to the west.
It has an estimated population of 10.2 million (CIA July 2011 est.). Its size is just under 28,000 km²
Its capital is Bujumbura.
Although the country is landlocked, much of the southwestern border is adjacent to Lake Tanganyika.
Presently, Burundi is governed as a presidential representative democratic republic. Sixty-two percent of Burundians are Roman Catholic, eight to ten percent are Muslims and the rest follow indigenous beliefs and other Christian denominations.
Burundi has a low gross domestic product, largely due to civil wars, corruption, poor access to education, and the effects of HIV/AIDS. Burundi is densely populated, with substantial emigration. Cobalt and copper are among Burundi's natural resources. Some of Burundi's main exports include coffee and sugar.
Burundi is one of the ten poorest countries in the world.
Education in Country
(There is a little information at http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Education_in_Burundi)
Education in Burundi is compulsory for six years, between the ages of 7 and 13. In 1998, the gross primary enrollment rate was 62 percent, and the net primary enrollment rate was 37 percent. Primary school attendance rates are unavailable for Burundi. While enrollment rates indicate a level of commitment to education, they do not always reflect children’s participation in school.
The government attempts to provide for most of the costs of education through grade six. An inequitable distribution of educational resources favours children in the south and central regions of the nation.There is less access of girls to education.
There are several museums in the cities, such as the Burundi Geological Museum in Bujumbura and the Burundi National Museum and the Burundi Museum of Life in Gitega.
School-level education
Further and Higher education
Universities in Country
The main university is the University of Burundi (Université du Burundi) in the capital Bujumbura. It has a web site at http://www.ub.edu.bi but internal evidence suggests that it is very out of date (e.g. the page http://www.ub.edu.bi/ub-calendrier.php displays a calendar for 2005).
However there are also:
- Université Espoir d’Afrique (Hope Africa University), also in Bujumbura: describing itself as a "Christian liberal arts institution" - web site at http://www.hopeafricauniversity.org/
- Université Lumière de Bujumbura (Light University of Bujumbura) - web site at http://www.ulbu.info/ with substantial information in English but some lack of information dated later than 2008
- Université de Ngozi, in Ngozi - web site at http://www.ung.bi with some headings in English but not much depth of information