Welcome to the Virtual Education Wiki ~ Open Education Wiki
Cyprus: Difference between revisions
| Line 10: | Line 10: | ||
Cyprus is the Mediterranean's third largest island. A former British colony, it became an independent republic in 1960 and a member of the [[Commonwealth]] in 1961. The Republic of Cyprus is one of the advanced economies in the region, and has been a member of the [[European Union]] since 1 May 2004. | Cyprus is the Mediterranean's third largest island. A former British colony, it became an independent republic in 1960 and a member of the [[Commonwealth]] in 1961. The Republic of Cyprus is one of the advanced economies in the region, and has been a member of the [[European Union]] since 1 May 2004. | ||
In 1974, following 11 years of intercommunal violence (1963–1974) between the Greek Cypriots and Turkish Cypriots, and an attempted coup d'état by Greek Cypriot nationalists who aimed at annexing the island to Greece and were backed by the Greek military junta then in power in Athens, Turkey invaded and occupied the northern portion of the island. This led to the displacement of thousands of Cypriots and the establishment of a separate Turkish Cypriot political entity in the north. This event and its resulting political situation are matters of ongoing dispute. | In 1974, following 11 years of intercommunal violence (1963–1974) between the Greek Cypriots and Turkish Cypriots, and an attempted coup d'état by Greek Cypriot nationalists who aimed at annexing the island to Greece and were backed by the Greek military junta then in power in Athens, [[Turkey]] invaded and occupied the northern portion of the island. This led to the displacement of thousands of Cypriots and the establishment of a separate Turkish Cypriot political entity in the north. This event and its resulting political situation are matters of ongoing dispute. | ||
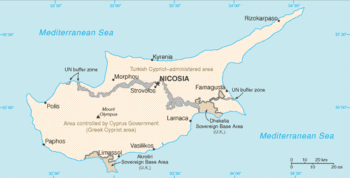
The Republic of Cyprus, the internationally recognised state, has sovereignty by law over the entire island of Cyprus and its surrounding waters except small portions that are allocated by treaty to the United Kingdom as sovereign military bases. The island is de facto partitioned into four main parts: | The Republic of Cyprus, the internationally recognised state, has sovereignty by law over the entire island of Cyprus and its surrounding waters except small portions that are allocated by treaty to the United Kingdom as sovereign military bases. The island is de facto partitioned into four main parts: | ||
Revision as of 09:33, 3 September 2009
Partners situated in Cyprus
None.
Cyprus in a nutshell
Cyprus, officially the Republic of Cyprus, is a Eurasian island country situated in the eastern Mediterranean, south of Turkey, west of Syria, Lebanon, and Israel, east of Greece, and north of Egypt.
Cyprus is the Mediterranean's third largest island. A former British colony, it became an independent republic in 1960 and a member of the Commonwealth in 1961. The Republic of Cyprus is one of the advanced economies in the region, and has been a member of the European Union since 1 May 2004.
In 1974, following 11 years of intercommunal violence (1963–1974) between the Greek Cypriots and Turkish Cypriots, and an attempted coup d'état by Greek Cypriot nationalists who aimed at annexing the island to Greece and were backed by the Greek military junta then in power in Athens, Turkey invaded and occupied the northern portion of the island. This led to the displacement of thousands of Cypriots and the establishment of a separate Turkish Cypriot political entity in the north. This event and its resulting political situation are matters of ongoing dispute.
The Republic of Cyprus, the internationally recognised state, has sovereignty by law over the entire island of Cyprus and its surrounding waters except small portions that are allocated by treaty to the United Kingdom as sovereign military bases. The island is de facto partitioned into four main parts:
- the area under the effective control of the Republic of Cyprus, comprising about 59% of the island's area in the south;
- the Turkish-occupied area in the north, calling itself the Turkish Republic of Northern Cyprus, covering about 37% of the island's area and recognised only by Turkey;
- the United Nations-controlled Green Line, separating the two, covering about 3% of the island's area; and
- two British Sovereign Base Areas (Akrotiri and Dhekelia), covering about 3% of the island's area.
Source: Wikipedia's page about Cyprus
Cyprus education policy
Source: [ http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cyprus#Education Wikipedia's page about Cyprus > Education]
Cyprus education system
Cyprus has a highly developed system of primary and secondary education offering both public and private education. The high quality of instruction can be attributed to a large extent to the above-average competence of the teachers but also to the fact that nearly 7% of the GDP is spent on education which makes Cyprus one of the top three spenders of education in the EU along with Denmark and Sweden. State schools are generally seen as equivalent in quality of education to private-sector institutions.
Source: [ http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cyprus#Education Wikipedia's page about Cyprus > Education]
Higher education
Universities in Cyprus
- University of Cyprus
- Cyprus Academy of Art
- Cyprus University of Technology (started in 2007)
- European University - Cyprus (changed name in 2007)
- University of Nicosia (changed name in 2007)
- Frederick University
- Neapolis University
- Cyprus Institute
- Open University of Cyprus
A complete list can be found on Wikipedia: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/List_of_colleges_and_universities_in_Cyprus
Polytechnics in Cyprus
Higher education reform
The Bologna Process
Administration and finance
Quality assurance
Cyprus's HEIs in the information society
Towards the information society
Information society strategy
Virtual Campuses in HE
Interesting Virtual Campus Initiatives
The Open University of Cyprus (OUC) is the only University in Cyprus dedicated to distance learning.
Interesting Programmes
Re.ViCa Case-study
None.