Welcome to the Virtual Education Wiki ~ Open Education Wiki
Croatia: Difference between revisions
(added links to Yugosphere and country cat - and added author name) |
(CSV import high-income countries, all but Andorra which was done manually earlier) |
||
| (5 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 94: | Line 94: | ||
[[Category:Croatia| ]] | [[Category:Croatia| ]] | ||
[[Category:European Union]] | |||
[[Category:Europe]] | [[Category:Europe]] | ||
[[Category:Western Balkans]] | [[Category:Western Balkans]] | ||
[[Category:Yugosphere]] | [[Category:Yugosphere]] | ||
| Line 102: | Line 102: | ||
[[Category:VISCED]] | [[Category:VISCED]] | ||
{{#set:In European Union=1}} | |||
{{Countries-footer}} | |||
{{United Nations}} | |||
{{NATO}} | |||
{{high-income}} | |||
Latest revision as of 20:28, 10 May 2023
For a general discussion of virtual education in this country see Yugosphere
Original Re.ViCa entry by Gertjan of ATiT
For entities in Croatia see Category:Croatia
Partners situated in Croatia
Croatia in a nutshell
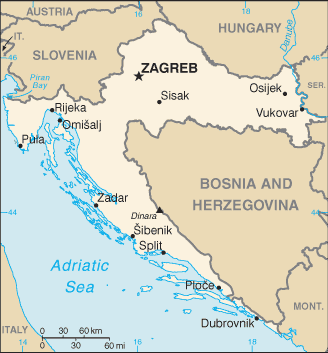
Croatia, officially the Republic of Croatia, is a country in Southeast Europe, at the crossroads of the Pannonian Plain, the Balkans, and the Mediterranean Sea. Its capital (and largest city) is Zagreb. Croatia borders Slovenia and Hungary to the north, Bosnia and Herzegovina to the southeast, Serbia and Montenegro to the east, and it has a sea border with Italy to the northwest.
The Croats arrived in the early seventh century in what is Croatia today. They organized the state into two dukedoms. The first king, Tomislav I was crowned in AD 925 and Croatia was elevated into a kingdom. The Kingdom of Croatia retained its sovereignty for almost two centuries, reaching its peak during the rule of Kings Petar Krešimir IV and Zvonimir. Via "Pacta conventa", Croatia entered a personal union with Hungary in 1102. In 1526, the Croatian Parliament elected Ferdinand from the House of Habsburg to the Croatian throne. In 1918, Croatia declared independence from Austria–Hungary and co-founded the Kingdom of Yugoslavia. During World War II, Nazis invaded Yugoslavia and with the aid of the Ustaše, created the Independent State of Croatia. After the war, Croatia became a founding member of Second Yugoslavia. On 25 June 1991, Croatia declared independence and became a sovereign state.
Croatia is a high-income country as well as member of the United Nations, the Council of Europe, the Organization for Security and Co-operation in Europe, NATO, the World Trade Organization, CEFTA, and is an elected member of the UN Security Council for the 2008–09 term. The country is also a candidate for membership of the European Union, and a founding member of the Union for the Mediterranean upon its establishment in 2008.
Croatia education policy
Croatia education system
Higher education
Universities in Croatia
- University Josip Juraj Strossmayer, Osijek
- University of Dubrovnik
- Rochester Institute of Technology-American College of Management and Technology
- University of Pula
- Dubrovnik International University
- University of Rijeka
- University of Split
- University of Zadar
- University of Zagreb
Polytechnics in Croatia
Higher education reform
The Bologna Process
Administration and finance
Quality assurance
Croatia HEIs in the information society
Towards the information society
Information society strategy
Virtual Campuses in HE
Interesting Virtual Campus Initiatives
Interesting Programmes
Re.ViCa Case-study
Lessons learnt
References
For OER policies and projects in Croatia see Croatia/OER