Welcome to the Virtual Education Wiki ~ Open Education Wiki
Zambia: Difference between revisions
(added cat NOT) |
(CSV import all low-income countries, except Yemen done manually already) |
||
| (21 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
''by [[Paul Bacsich]] for [[Re.ViCa]]'' | |||
For | ''For entities in Zambia see [[:Category:Zambia]]'' | ||
'''Zambia is | |||
== Partners situated in Zambia == | |||
None. | |||
== Zambia in a nutshell == | |||
Sourced from http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Zambia) | |||
[[Image:Zambia.gif|right|thumb|250px|Source : http://www.cia.gov]] | |||
The Republic of ''Zambia'' is a landlocked country in [[Sub-Saharan Africa]]. The neighbouring countries are the [[Democratic Republic of the Congo]] to the north, [[Tanzania]] to the north-east, [[Malawi]] to the east, [[Mozambique]], [[Zimbabwe]], [[Botswana]], and [[Namibia]] to the south, and [[Angola]] to the west. | |||
The population of Zambia is nearly 12 million. | |||
The capital city is Lusaka, located in the southeast of the country. The population is concentrated mainly around the capital and the Copperbelt to the northwest. | |||
Zambia is divided into nine provinces, each administered by an appointed deputy minister. Each province is subdivided into several districts with a grand total of 73 districts. | |||
== Zambia education policy == | |||
== Zambia education system == | |||
(sourced from http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Zambia) | |||
Education in Zambia is provided at two levels: | |||
# basic education (years 1 to 9) | |||
# upper secondary (years 10 to 12) | |||
Some schools provide a "basic" education covering years 1 to 9, as year 9 is considered to be a decent level of education for the majority of children. However, tuition is only free up to year 7, and UNESCO estimated that 80% of children of primary school age in 2002 were enrolled. Most children drop out after year 7 when fees must be paid. | |||
Both government and private schools exist in Zambia. The private school system began largely as a result of Christian mission efforts during the late 19th and early 20th centuries. Amongst famous private schools are the International School of Lusaka, Rhodes Park School (Unofficially ranked as the best private school in Zambia), the Roman Catholic run St Mary's Seminary located in the Msupadzi area, south of Chipata, Eastern Province and Simba International School close to Ndola, Copperbelt Province. Private schools operate primarily under the British way of schooling, but also offer curricula approved by the Examinations Council of Zambia (ECZ). An example of a school that has offered a dual programme in in both the ECZ and Cambridge curriculum is Mpelembe Secondary School. | |||
Educational opportunities beyond secondary school are limited in Zambia. After secondary school, most students study at the various colleges, around the country. | |||
== Higher education == | |||
=== Universities in Zambia === | |||
There are three main universities: | |||
# [[University of Zambia]] (UNZA) - with a student population of about 6,000 | |||
# Mulungushi University (MU), - no URL known - formerly the National College of Management and Development Studies | |||
# Copperbelt University (CBU) - http://www.cbu.edu.zm - this opened in the late 1980s, taking over most of the former Zambia Institute of Technology site in Kitwe | |||
Normally they all select students on the basis of ability; competition for places is intense. | |||
The introduction of fees in the late 1990s has made university level education inaccessible for some, although the government does provide state bursaries. | |||
The page http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/List_of_universities_in_Zambia lists other universities: | |||
# [[Zambian Open University]] | |||
# Cavendish University - http://cavendishza.org | |||
# Zambia Adventist University - http://www.tagnet.org/zau/index.htm - despite not having its own URL, it has graduated students (see e.g. http://www.times.co.zm/news/viewnews.cgi?category=7&id=1189252646) | |||
# Northrise University - http://www.northriseuniversity.com - founded 2004, the first nationally recognized private university in Zambia | |||
=== Polytechnics in Zambia === | |||
Other centres of education include: | |||
# Public Administration College (NIPA) | |||
# Northern Technical College (NORTEC) # National Resources Development College (NRDC) | |||
# Evelyn Hone College of Applied Arts and Commerce - http://www.evelynhone.edu.zm/ - and note the e-learning site at http://elearning.evelynhone.edu.zm/ | |||
There are also several teacher training colleges offering two-year training programmes, whilst missionary hospitals around the country offer internationally acceptable training for nurses. | |||
Several Christian schools offer seminary-level training. | |||
== Higher education reform == | |||
=== The Bologna Process === | |||
== Administration and finance == | |||
== Quality assurance == | |||
== Zambia's HEIs in the information society == | |||
=== Towards the information society === | |||
=== Information society strategy === | |||
== Virtual Campuses in HE == | |||
=== Interesting Virtual Campus Initiatives === | |||
=== Interesting Programmes === | |||
The [[University of Zambia]] has activity. | |||
[[The Global Open University of Zambia]] has been regarded by some as suspect - see its entry. | |||
Some of the other universities and colleges are in the early stages of e-learning development but are clearly showing activity. | |||
=== Re.ViCa Case-study === | |||
None. | |||
== Lessons learnt == | |||
== References == | |||
* COL IN THE COMMONWEALTH 2006 – 2009 - http://www.col.org/SiteCollectionDocuments/COLCountryReports06-09_web.pdf - see the chapter on Zambia | |||
* FIRST eLEARNING ZAMBIA NATIONAL CONFERENCE - THEME: eLearning in National Development, March 2007, Lusaka, Zambia - http://www.assitej-international.org/media/1802/minuteslusaka.pdf | |||
* THE DEVELOPMENT AND STATE OF THE ART OF ADULT LEARNING AND EDUCATION (ALE) National report 0f ZAMBIA by MINISTRY OF EDUCATION 2008 - http://www.unesco.org/fileadmin/MULTIMEDIA/INSTITUTES/UIL/confintea/pdf/National_Reports/Africa/Africa/Zambia.pdf | |||
---- | ---- | ||
> [[Countries]] | > [[Countries]] | ||
<br> | |||
>> [[Main Page]] | |||
[[Category:Zambia| ]] | |||
[[Category:Africa]] | [[Category:Africa]] | ||
[[Category: | [[Category:Sub-Saharan Africa]] | ||
[[Category:Southern African Development Community]] | |||
[[Category:Commonwealth countries]] | |||
[[Category:Countries with Programmes]] | |||
[[Category:Tier 3]] | |||
[[Category:VISCED]] | |||
{{#set:In Commonwealth=1}} | |||
{{Countries-footer}} | |||
{{Countries-footer}} | |||
{{United Nations}} | |||
{{low-income}} | |||
Latest revision as of 16:36, 10 May 2023
by Paul Bacsich for Re.ViCa
For entities in Zambia see Category:Zambia
Partners situated in Zambia
None.
Zambia in a nutshell
Sourced from http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Zambia)
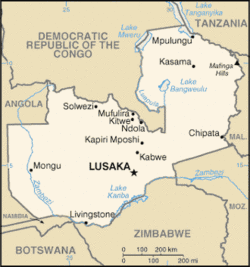
The Republic of Zambia is a landlocked country in Sub-Saharan Africa. The neighbouring countries are the Democratic Republic of the Congo to the north, Tanzania to the north-east, Malawi to the east, Mozambique, Zimbabwe, Botswana, and Namibia to the south, and Angola to the west.
The population of Zambia is nearly 12 million.
The capital city is Lusaka, located in the southeast of the country. The population is concentrated mainly around the capital and the Copperbelt to the northwest.
Zambia is divided into nine provinces, each administered by an appointed deputy minister. Each province is subdivided into several districts with a grand total of 73 districts.
Zambia education policy
Zambia education system
(sourced from http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Zambia)
Education in Zambia is provided at two levels:
- basic education (years 1 to 9)
- upper secondary (years 10 to 12)
Some schools provide a "basic" education covering years 1 to 9, as year 9 is considered to be a decent level of education for the majority of children. However, tuition is only free up to year 7, and UNESCO estimated that 80% of children of primary school age in 2002 were enrolled. Most children drop out after year 7 when fees must be paid.
Both government and private schools exist in Zambia. The private school system began largely as a result of Christian mission efforts during the late 19th and early 20th centuries. Amongst famous private schools are the International School of Lusaka, Rhodes Park School (Unofficially ranked as the best private school in Zambia), the Roman Catholic run St Mary's Seminary located in the Msupadzi area, south of Chipata, Eastern Province and Simba International School close to Ndola, Copperbelt Province. Private schools operate primarily under the British way of schooling, but also offer curricula approved by the Examinations Council of Zambia (ECZ). An example of a school that has offered a dual programme in in both the ECZ and Cambridge curriculum is Mpelembe Secondary School.
Educational opportunities beyond secondary school are limited in Zambia. After secondary school, most students study at the various colleges, around the country.
Higher education
Universities in Zambia
There are three main universities:
- University of Zambia (UNZA) - with a student population of about 6,000
- Mulungushi University (MU), - no URL known - formerly the National College of Management and Development Studies
- Copperbelt University (CBU) - http://www.cbu.edu.zm - this opened in the late 1980s, taking over most of the former Zambia Institute of Technology site in Kitwe
Normally they all select students on the basis of ability; competition for places is intense.
The introduction of fees in the late 1990s has made university level education inaccessible for some, although the government does provide state bursaries.
The page http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/List_of_universities_in_Zambia lists other universities:
- Zambian Open University
- Cavendish University - http://cavendishza.org
- Zambia Adventist University - http://www.tagnet.org/zau/index.htm - despite not having its own URL, it has graduated students (see e.g. http://www.times.co.zm/news/viewnews.cgi?category=7&id=1189252646)
- Northrise University - http://www.northriseuniversity.com - founded 2004, the first nationally recognized private university in Zambia
Polytechnics in Zambia
Other centres of education include:
- Public Administration College (NIPA)
- Northern Technical College (NORTEC) # National Resources Development College (NRDC)
- Evelyn Hone College of Applied Arts and Commerce - http://www.evelynhone.edu.zm/ - and note the e-learning site at http://elearning.evelynhone.edu.zm/
There are also several teacher training colleges offering two-year training programmes, whilst missionary hospitals around the country offer internationally acceptable training for nurses.
Several Christian schools offer seminary-level training.
Higher education reform
The Bologna Process
Administration and finance
Quality assurance
Zambia's HEIs in the information society
Towards the information society
Information society strategy
Virtual Campuses in HE
Interesting Virtual Campus Initiatives
Interesting Programmes
The University of Zambia has activity.
The Global Open University of Zambia has been regarded by some as suspect - see its entry.
Some of the other universities and colleges are in the early stages of e-learning development but are clearly showing activity.
Re.ViCa Case-study
None.
Lessons learnt
References
- COL IN THE COMMONWEALTH 2006 – 2009 - http://www.col.org/SiteCollectionDocuments/COLCountryReports06-09_web.pdf - see the chapter on Zambia
- FIRST eLEARNING ZAMBIA NATIONAL CONFERENCE - THEME: eLearning in National Development, March 2007, Lusaka, Zambia - http://www.assitej-international.org/media/1802/minuteslusaka.pdf
- THE DEVELOPMENT AND STATE OF THE ART OF ADULT LEARNING AND EDUCATION (ALE) National report 0f ZAMBIA by MINISTRY OF EDUCATION 2008 - http://www.unesco.org/fileadmin/MULTIMEDIA/INSTITUTES/UIL/confintea/pdf/National_Reports/Africa/Africa/Zambia.pdf
For OER policies and projects in Zambia see Zambia/OER
For OER policies and projects in Zambia see Zambia/OER