Welcome to the Virtual Education Wiki ~ Open Education Wiki
Hong Kong: Difference between revisions
(→References: added cat Chinese) |
(CSV import high-income countries, all but Andorra which was done manually earlier) |
||
| (7 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
''by [[Paul Bacsich]] for [[Re.ViCa]]'' | |||
''For entities in Hong Kong see [[:Category:Hong Kong]]'' | |||
== Partners situated in Hong Kong == | == Partners situated in Hong Kong == | ||
| Line 4: | Line 10: | ||
== Hong Kong in a nutshell == | == Hong Kong in a nutshell == | ||
( | ''Hong Kong'' (Chinese: 香港), officially the '''Hong Kong Special Administrative Region''', is a territory located in Southern [[China]] in East Asia, bordering the province of Guangdong to the north and facing the South China Sea to the east, west and south. | ||
[[Image:Hongkong.gif|right|thumb|400px|Source : http://www.cia.gov]] | |||
It has a population of 7 million people but only 1,108 km2 (428 sq mi) of land, making it one of the most densely populated areas in the world. | |||
Beginning as a trading port, Hong Kong became a dependent territory of the United Kingdom in 1842, and remained so until transfer of sovereignty of Hong Kong to the People's Republic of China in 1997. Along with [[Macao]], Hong Kong is one of the two special administrative regions under the "one country, two systems" policy. As a result, Hong Kong is largely self-governing, has its own currency, legal and political systems, a high degree of autonomy in all areas except foreign affairs and defence and is generally not considered part of mainland China. | |||
Renowned for its expansive skyline and natural setting, Hong Kong is one of the world's leading financial capitals, a major business and cultural hub, and maintains a highly developed capitalist economy. Its identity as a cosmopolitan centre where east meets west is reflected in its cuisine, cinema, music and traditions, and although the population is predominantly Chinese, residents and expatriates of other ethnicities form a small but significant segment of society. | |||
| Line 10: | Line 23: | ||
== Hong Kong education system | == Schools in Hong Kong == | ||
Hong Kong's education system roughly follows the system in England (in the [[UK]]), although at the higher education levels, both English and American systems exist. The medium of instruction is mainly spoken Cantonese, written Chinese and English, but Mandarin language education has been increasing. PISA, the Programme for International Student Assessment, has ranked Hong Kong's education system as the second best in the world. | |||
Hong Kong's public schools are operated by the Education Bureau. The system features a non-compulsory three-year kindergarten, followed by a compulsory six-year primary education, a three-year junior secondary education, a non-compulsory two-year senior secondary education leading to the Hong Kong Certificate of Education Examinations, and a two-year matriculation course leading to the Hong Kong Advanced Level Examinations. Most comprehensive schools in Hong Kong fall under three categories: the rarer public schools; the more common subsidised schools, including government aids and grant schools; and private schools, often run by Christian organisations and having admissions based on academic merit rather than on financial resources. Outside this system are the schools under the Direct Subsidy Scheme and private international schools. | |||
== Higher education == | == Higher education == | ||
There are nine public universities in Hong Kong, and a number of private higher institutions, offering various bachelor's, master's, and doctoral degrees, other higher diplomas and associate degree courses. | |||
=== Universities in Hong Kong === | === Universities in Hong Kong === | ||
( | The [[University of Hong Kong]], the oldest institution of tertiary education in territory, was referred by Quacquarelli Symonds as a "world-class comprehensive research university" and was ranked 26th on the 2008 THES - QS World University Rankings [78] , making it 3rd in Asia (after only to University of Tokyo and Kyoto University). The Hong Kong University of Science & Technology and Chinese University of Hong Kong are ranked 39 and 42 respectively, making them ranked 5th and 6th respectively in Asia. | ||
=== Polytechnics in Hong Kong === | === Polytechnics in Hong Kong === | ||
== | == Education reform == | ||
=== The Bologna Process === | === The Bologna Process === | ||
| Line 36: | Line 55: | ||
== | == Information society == | ||
=== Towards the information society === | === Towards the information society === | ||
| Line 43: | Line 62: | ||
== Virtual | == Virtual initiatives == | ||
=== Interesting Virtual Campus Initiatives === | === Interesting Virtual Campus Initiatives === | ||
| Line 66: | Line 85: | ||
== References == | == References == | ||
---- | ---- | ||
See also [[Macao]] and [[China]]. | |||
> [[Countries]] | > [[Countries]] | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
| Line 76: | Line 98: | ||
[[Category:Hong Kong| ]] | [[Category:Hong Kong| ]] | ||
[[Category:Asia]] | [[Category:Asia]] | ||
[[Category:East Asia]] | |||
[[Category:Chinese-speaking countries and territories]] | [[Category:Chinese-speaking countries and territories]] | ||
[[Category:Countries with Programmes]] | |||
[[Category:Tier 3]] | |||
[[Category:VISCED]] | |||
{{Countries-footer}} | |||
{{high-income}} | |||
Latest revision as of 20:28, 10 May 2023
by Paul Bacsich for Re.ViCa
For entities in Hong Kong see Category:Hong Kong
Partners situated in Hong Kong
Hong Kong in a nutshell
Hong Kong (Chinese: 香港), officially the Hong Kong Special Administrative Region, is a territory located in Southern China in East Asia, bordering the province of Guangdong to the north and facing the South China Sea to the east, west and south.
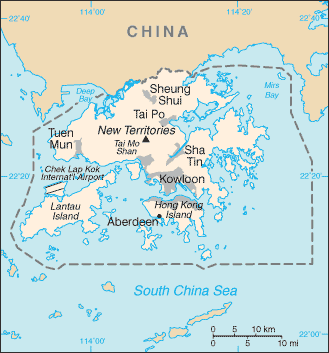
It has a population of 7 million people but only 1,108 km2 (428 sq mi) of land, making it one of the most densely populated areas in the world.
Beginning as a trading port, Hong Kong became a dependent territory of the United Kingdom in 1842, and remained so until transfer of sovereignty of Hong Kong to the People's Republic of China in 1997. Along with Macao, Hong Kong is one of the two special administrative regions under the "one country, two systems" policy. As a result, Hong Kong is largely self-governing, has its own currency, legal and political systems, a high degree of autonomy in all areas except foreign affairs and defence and is generally not considered part of mainland China.
Renowned for its expansive skyline and natural setting, Hong Kong is one of the world's leading financial capitals, a major business and cultural hub, and maintains a highly developed capitalist economy. Its identity as a cosmopolitan centre where east meets west is reflected in its cuisine, cinema, music and traditions, and although the population is predominantly Chinese, residents and expatriates of other ethnicities form a small but significant segment of society.
Hong Kong education policy
Schools in Hong Kong
Hong Kong's education system roughly follows the system in England (in the UK), although at the higher education levels, both English and American systems exist. The medium of instruction is mainly spoken Cantonese, written Chinese and English, but Mandarin language education has been increasing. PISA, the Programme for International Student Assessment, has ranked Hong Kong's education system as the second best in the world.
Hong Kong's public schools are operated by the Education Bureau. The system features a non-compulsory three-year kindergarten, followed by a compulsory six-year primary education, a three-year junior secondary education, a non-compulsory two-year senior secondary education leading to the Hong Kong Certificate of Education Examinations, and a two-year matriculation course leading to the Hong Kong Advanced Level Examinations. Most comprehensive schools in Hong Kong fall under three categories: the rarer public schools; the more common subsidised schools, including government aids and grant schools; and private schools, often run by Christian organisations and having admissions based on academic merit rather than on financial resources. Outside this system are the schools under the Direct Subsidy Scheme and private international schools.
Higher education
There are nine public universities in Hong Kong, and a number of private higher institutions, offering various bachelor's, master's, and doctoral degrees, other higher diplomas and associate degree courses.
Universities in Hong Kong
The University of Hong Kong, the oldest institution of tertiary education in territory, was referred by Quacquarelli Symonds as a "world-class comprehensive research university" and was ranked 26th on the 2008 THES - QS World University Rankings [78] , making it 3rd in Asia (after only to University of Tokyo and Kyoto University). The Hong Kong University of Science & Technology and Chinese University of Hong Kong are ranked 39 and 42 respectively, making them ranked 5th and 6th respectively in Asia.
Polytechnics in Hong Kong
Education reform
The Bologna Process
(very important for European countries)
Administration and finance
Quality assurance
Information society
Towards the information society
Information society strategy
Virtual initiatives
Interesting Virtual Campus Initiatives
Most Hong Kong universities have considerable on-campus e-learning activity but say that students are reluctant to study off-campus via e-learning.
However, there is an active Open University of Hong Kong (OUHK) and a CyberU branch of one of the more commercially minded universities, Hong Kong Polytechnic University.
Moves towards distance teaching on the mainland are likely to encourage Hong Kong universities to quickly develop online capability.
Interesting Programmes
Re.ViCa Case-study
None.
Lessons learnt
References
For OER policies and projects in Hong Kong see Hong Kong/OER