Welcome to the Virtual Education Wiki ~ Open Education Wiki
Pakistan: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
(CSV import United Nations members - Albania was done manually) |
||
| (14 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
''' | == Partners situated in Pakistan == | ||
None. | |||
== Pakistan in a nutshell == | |||
[[Image:Pakistan.gif|right|thumb|400px|Source : http://www.cia.gov]] | |||
Pakistan (Urdu: پاکستان '''Pākistān'''), officially the '''Islamic Republic of Pakistan''', is a South Asian country located in the mountainous region adjoining Central Asia and the Middle East. It has a 1,046 kilometre (650 mile) coastline along the Arabian Sea and Gulf of Oman in the south, and is bordered by [[Afghanistan]] and [[Iran]] in the west, the Republic of [[India]] in the east and the People's Republic of [[China]] in the far northeast. [[Tajikistan]] also lies adjacent to Pakistan but is separated by the narrow Wakhan Corridor. In recent times, Pakistan has been called part of the "New Middle East". | |||
With the adoption of its constitution in 1956, Pakistan became an Islamic republic. | |||
Pakistan is the sixth most populous country in the world and has the second largest Muslim population in the world after [[Indonesia]]. The country is listed among the "Next Eleven" economies. | |||
Pakistan is a founding member of the Organisation of the Islamic Conference, South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation, Developing 8 Countries, G20 developing nations, Asia Cooperation Dialogue and the Economic Cooperation Organisation. It is also a member of the United Nations, Commonwealth of Nations, World Trade Organisation, Shanghai Cooperation Organisation, G33 developing countries, Group of 77 developing nations, major non-NATO ally of the United States and is a nuclear state. | |||
The population of Pakistan is around 166 million. | |||
Its capital is Islamabad. | |||
Official languages are Urdu and English. | |||
== Pakistan education policy == | |||
== Pakistan education system == | |||
Education in Pakistan is divided into five levels: primary (grades one through five); middle (grades six through eight); high (grades nine and ten, leading to the Secondary School Certificate); intermediate (grades eleven and twelve, leading to a Higher Secondary School Certificate); and university programmes leading to graduate and advanced degrees. | |||
Pakistan also has a parallel secondary school education system in private schools, which is based upon the curriculum set by the University of Cambridge. Some students choose to take the O level and A level exams, which are administered by the British Council, in place of government exams. | |||
There are currently 730 technical & vocational institutions in Pakistan. The minimum qualifications to enter male vocational institutions, is the completion of grade 8. The programmes are generally two to three years in length. The minimum qualifications to enter female vocational institutions, is the completion of grade 5. | |||
All academic education institutions are the responsibility of the provincial governments. The federal government mostly assists in curriculum development, accreditation and some financing of research. | |||
English medium education is to be extended, on a phased basis, to all schools across the country. Through various educational reforms, by the year 2015, the ministry of education expects to attain 100% enrolment levels amongst primary school aged children, and a literacy rate of 86% amongst people aged over 10. | |||
Pakistan also has madrassahs that provide free education and also offer free boarding and lodging to students who come mainly from the poorer strata of society. After criticism, efforts have been made to regulate them by including modern disciplines such as English, science, mathematics, economics, and computer science. | |||
== Higher education == | |||
=== Universities in Pakistan === | |||
(sourced from http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/List_of_universities_in_Pakistan) | |||
According to Higher Education Commission of Pakistan there are 124 Universities in Pakistan of which 68 are public universities and 56 are private universities. | |||
At the federal level there are the following universities: | |||
'''Public universities''' | |||
# National Defence University, Islamabad | |||
# [[Pakistan Virtual University]], Lahore | |||
# National University of Science and Technology, Rawalpindi | |||
# Quaid-e-Azam University, Islamabad | |||
# Pakistan Institute of Development Economics, Islamabad | |||
# Pakistan Institute of Engineering & Applied Sciences, Islamabad | |||
# National University of Modern Languages, Islamabad | |||
# International Islamic University, Islamabad | |||
# Institute of Space Technology (IST), Islamabad | |||
# Federal Urdu University of Arts, Science and Technology, Islamabad and Karachi | |||
# COMSATS Institute of Information Technology, Islamabad | |||
# Bahria University, Islamabad | |||
# [[Allama Iqbal Open University]], Islamabad | |||
# Air University, Islamabad (established by the Pakistan Air Force in 2002) | |||
'''Private universities''' | |||
# Riphah International University, Islamabad | |||
# National University of Computer and Emerging Sciences, Islamabad | |||
# Foundation University, Rawalpindi | |||
There are also many universities, public and private, at the states level. | |||
=== Polytechnics in Pakistan === | |||
There are over 100. | |||
== Higher education reform == | |||
=== The Bologna Process === | |||
== Administration and finance == | |||
== Quality assurance == | |||
== Pakistan's HEIs in the information society == | |||
=== Towards the information society === | |||
=== Information society strategy === | |||
== Virtual Campuses in HE == | |||
=== Interesting Virtual Campus Initiatives === | |||
These include: | |||
* [[Allama Iqbal Open University]] | * [[Allama Iqbal Open University]] | ||
* [[Pakistan Virtual University]] | * [[Pakistan Virtual University]] | ||
The [[Habib University Foundation]] is doing some interesting analytic work on learning spaces. | |||
=== Interesting Programmes === | |||
=== Re.ViCa Case-study === | |||
None. | |||
== Lessons learnt == | |||
== References == | |||
---- | ---- | ||
> [[Countries]] | > [[Countries]] | ||
<br> | |||
>> [[Main Page]] | |||
[[Category:Pakistan| ]] | |||
[[Category:Asia]] | [[Category:Asia]] | ||
[[Category: | [[Category:Commonwealth countries]] | ||
[[Category: | |||
[[Category:Countries with Programmes]] | |||
[[Category:VISCED]] | |||
{{#set:In Commonwealth=1}} | |||
{{Countries-footer}} | |||
{{United Nations}} | |||
Latest revision as of 14:28, 10 May 2023
Partners situated in Pakistan
None.
Pakistan in a nutshell
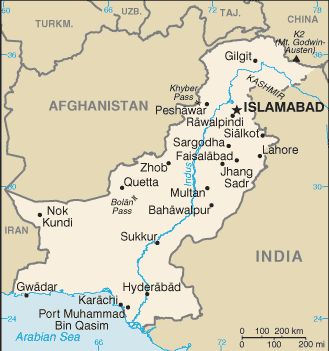
Pakistan (Urdu: پاکستان Pākistān), officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan, is a South Asian country located in the mountainous region adjoining Central Asia and the Middle East. It has a 1,046 kilometre (650 mile) coastline along the Arabian Sea and Gulf of Oman in the south, and is bordered by Afghanistan and Iran in the west, the Republic of India in the east and the People's Republic of China in the far northeast. Tajikistan also lies adjacent to Pakistan but is separated by the narrow Wakhan Corridor. In recent times, Pakistan has been called part of the "New Middle East".
With the adoption of its constitution in 1956, Pakistan became an Islamic republic.
Pakistan is the sixth most populous country in the world and has the second largest Muslim population in the world after Indonesia. The country is listed among the "Next Eleven" economies.
Pakistan is a founding member of the Organisation of the Islamic Conference, South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation, Developing 8 Countries, G20 developing nations, Asia Cooperation Dialogue and the Economic Cooperation Organisation. It is also a member of the United Nations, Commonwealth of Nations, World Trade Organisation, Shanghai Cooperation Organisation, G33 developing countries, Group of 77 developing nations, major non-NATO ally of the United States and is a nuclear state.
The population of Pakistan is around 166 million.
Its capital is Islamabad.
Official languages are Urdu and English.
Pakistan education policy
Pakistan education system
Education in Pakistan is divided into five levels: primary (grades one through five); middle (grades six through eight); high (grades nine and ten, leading to the Secondary School Certificate); intermediate (grades eleven and twelve, leading to a Higher Secondary School Certificate); and university programmes leading to graduate and advanced degrees.
Pakistan also has a parallel secondary school education system in private schools, which is based upon the curriculum set by the University of Cambridge. Some students choose to take the O level and A level exams, which are administered by the British Council, in place of government exams.
There are currently 730 technical & vocational institutions in Pakistan. The minimum qualifications to enter male vocational institutions, is the completion of grade 8. The programmes are generally two to three years in length. The minimum qualifications to enter female vocational institutions, is the completion of grade 5.
All academic education institutions are the responsibility of the provincial governments. The federal government mostly assists in curriculum development, accreditation and some financing of research.
English medium education is to be extended, on a phased basis, to all schools across the country. Through various educational reforms, by the year 2015, the ministry of education expects to attain 100% enrolment levels amongst primary school aged children, and a literacy rate of 86% amongst people aged over 10.
Pakistan also has madrassahs that provide free education and also offer free boarding and lodging to students who come mainly from the poorer strata of society. After criticism, efforts have been made to regulate them by including modern disciplines such as English, science, mathematics, economics, and computer science.
Higher education
Universities in Pakistan
(sourced from http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/List_of_universities_in_Pakistan)
According to Higher Education Commission of Pakistan there are 124 Universities in Pakistan of which 68 are public universities and 56 are private universities.
At the federal level there are the following universities:
Public universities
- National Defence University, Islamabad
- Pakistan Virtual University, Lahore
- National University of Science and Technology, Rawalpindi
- Quaid-e-Azam University, Islamabad
- Pakistan Institute of Development Economics, Islamabad
- Pakistan Institute of Engineering & Applied Sciences, Islamabad
- National University of Modern Languages, Islamabad
- International Islamic University, Islamabad
- Institute of Space Technology (IST), Islamabad
- Federal Urdu University of Arts, Science and Technology, Islamabad and Karachi
- COMSATS Institute of Information Technology, Islamabad
- Bahria University, Islamabad
- Allama Iqbal Open University, Islamabad
- Air University, Islamabad (established by the Pakistan Air Force in 2002)
Private universities
- Riphah International University, Islamabad
- National University of Computer and Emerging Sciences, Islamabad
- Foundation University, Rawalpindi
There are also many universities, public and private, at the states level.
Polytechnics in Pakistan
There are over 100.
Higher education reform
The Bologna Process
Administration and finance
Quality assurance
Pakistan's HEIs in the information society
Towards the information society
Information society strategy
Virtual Campuses in HE
Interesting Virtual Campus Initiatives
These include:
The Habib University Foundation is doing some interesting analytic work on learning spaces.
Interesting Programmes
Re.ViCa Case-study
None.
Lessons learnt
References
For OER policies and projects in Pakistan see Pakistan/OER