Welcome to the Virtual Education Wiki ~ Open Education Wiki
Virtual campus: Difference between revisions
(Added a note on legacy information.) |
|||
| (55 intermediate revisions by 12 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
'''(Legacy pages currently being reviewed)''' '''In a hurry? See [[Programmes]] (for online higher education, i.e. Virtual Campuses)''' | |||
---- | |||
'''''This entry covers virtual campus for universities and for colleges - but not for schools - see [[virtual school]]''.''' | |||
== Overview == | == Overview == | ||
| Line 4: | Line 11: | ||
In Re.ViCa we aim to take | == Defining “Virtual Campus” – A boundary approach== | ||
=== Overview === | |||
Although the phrase ‘virtual campus’ is an important concept in the field of education, there is no theoretical framework for it. This chapter focuses on the development of such a theoretical framework. Similar to the work Stoof, Martens, Van Merrienboer & Bastiaens (2002) did for the concept of competence, we propose the boundary approach for virtual campuses, an aid to support stakeholders in the field of e-learning in thinking about the concept ‘virtual campus’. Here the concept of the ‘virtual campus’is being explored by focusing on its dimensions. This holds the quest for one absolute definition of it is abandoned and that instead definitions are being valued against their degree of viability. | |||
The expression "virtual campus" became prominent around 1997, when various universities launched their versions of a virtual campus. It is often applied to a single university which has a virtual university “fringe” round a physical campus, but there are some totally virtual campuses, such as the Open University of Catalonia. Now there are at least 10 virtual campus operations in the UK and many more elsewhere. Increasingly a university may no longer use the phrase "virtual campus" while still in fact having one. | |||
===The boundary approach for the concept of virtual campus=== | |||
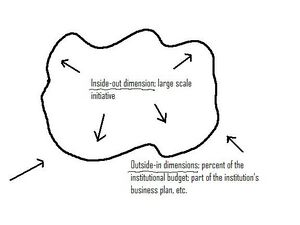
As the previous section shows there are a lot of variables involved defining the concept of the virtual campus. Depending on the context, the target group, the different goals and the technology involved a definition of ‘virtual campus’ can be formulated. The partners in the project group of the ReVica project do not want to give one single definition of the concept of the virtual campus. Since there will never be one right answer on the question what an virtual campus is,we suggest to use a conceptual representation aid as is shown in figure 1 to discuss the concept of the virtual campus. Figure 1 show the concept of a virtual campus as an amoeba-like form. The amoeba represents the virtual campus as a limited and demarcated concept, which is expressed by drawing its boundary. The boundary is being shaped by two opposing forces, being visualized as arrows (Based on the work of Stoof, Martens, Van Merriënboer & Bastiaens, 2002, p 352). From inside the figure, forces expand the boundary. This process is labeled as the ‘inside-out approach’ of the concept of the virtual campus. These are dimensions that define and construct the concept of the virtual campus. In Re.ViCa we aim to take virtual campus as synonymous with large-scale e-learning initiative. This ‘large-scale e-learning initiative’ is the inside-out dimension. | |||
[[Image:The_boundary_approach.JPG|thumb|left|Figure 1: the boundary approach to define the concept of the virtual campus]] | |||
On the other hand, the forces from outside the figure reduce the boundary. This outside-in approach focuses on the selection of terms that best express the intended meaning of the virtual campus (so it clarifies the relationships). In Re.ViCa we avoid the issue of giving distance e-learning a privileged position over campus-based e-learning but this begs the question of what is large-scale? Here we suggest some indicators, these are all outside in dimensions, which suggest large-scale - note that not all of them need to be satisfied. An e-learning initiative in a university - or consortium of universities - is major if it has many (but not necessarily all) of the following characteristics: | |||
* It requires at least one per cent of the institutional budget (this is a rule of thumb taken from Activity Based Costing theory that it is pointless to track from the top any initiatives below that level of expenditure). | |||
* It requires at least one per cent of the institutional budget (this is a rule of thumb taken from Activity Based Costing theory that it is pointless to track from the top any initiatives below that level of expenditure) | * The person responsible (as the majority proportion of his/her job) for leading that initiative has a rank and salary at least equivalent to that of a university full professor at Head of Department level, or equivalent rank of administrative or technical staff (usually an Assistant Director) - and ideally that of Dean or full Director. | ||
* The person responsible (as the majority proportion of his/her job) for leading that initiative has a rank and salary at least equivalent to that of a university full professor at Head of Department level, or equivalent rank of administrative or technical staff (usually an Assistant Director) - and ideally that of Dean or full Director | * There is a specific department to manage and deliver the iniative with a degree of autonomy from mainstream IT, library, pedagogic or quality structures. | ||
* There is a specific department to manage and deliver the iniative with a degree of autonomy from mainstream IT, library, pedagogic or quality structures | * Progress of the initiative is overseen by a Steering Group chaired by one of the most senior managers in the institution (in UK terms, a Pro-Vice Chancellor). | ||
* Progress of the initiative is overseen by a Steering Group chaired by one of the most senior managers in the institution (in UK terms, a Pro-Vice Chancellor) | * The initiative is part of the institution's business plan and is not totally dependent on any particular externally funded project | ||
* The | * There are strategy, planning and operational documents defining the initiative and regularly updated | ||
* There are strategy, planning and operational documents defining the initiative and regularly updated | |||
* The head of the institution (Vice-Chancellor, Rector, President, etc) will from time to time in senior meetings be notified of progress and problems with the initiative | * The head of the institution (Vice-Chancellor, Rector, President, etc) will from time to time in senior meetings be notified of progress and problems with the initiative | ||
* The head of the institution is able to discuss the | * The head of the institution is able to discuss the initiative in general terms with equivalent heads of other institutions - in the way that he/she would be able to discuss a new library, laboratory or similar large-scale development | ||
As said before as a project group we do not want to take the arrogant view to present one final definition of the virtual campus, Time will catch up on us when we do that and our work will become obsolete. For the time being we present a working definition, that involves large scale initiatives (an inside out dimension) which are recognizable on the list of characteristics above. The boundary approach makes it easier to change the definition in the future and discuss new opinions. | |||
== Virtual campus definition of the European Commission== | == Virtual campus definition of the European Commission== | ||
Cooperation between higher education institutions in the field of e-learning, regarding: design of joint curricula development by several universities, including agreements for the evaluation, validation and recognition of acquired competences, subject to national procedures; large–scale experiments of virtual mobility in addition to physical mobility and development of innovative dual mode curricula, based on both traditional and on-line learning methods. This broad definition involves many issues from partnerships between traditional and/or distance universities and HEI with a view to offering joint certifications (for undergraduate and/or postgraduate levels) and cooperation with learning support services. This might also include collaborative activities in strategic areas of education or research through cooperation involving researchers, academics, students, management, administrative and technical personnel. 'Virtual campuses' should not be confused with e-learning platforms. | Cooperation between higher education institutions in the field of e-learning, regarding: design of joint curricula development by several universities, including agreements for the evaluation, validation and recognition of acquired competences, subject to national procedures; large–scale experiments of virtual mobility in addition to physical mobility and development of innovative dual mode curricula, based on both traditional and on-line learning methods. This broad definition involves many issues from partnerships between traditional and/or distance universities and HEI with a view to offering joint certifications (for undergraduate and/or postgraduate levels) and cooperation with learning support services. This might also include collaborative activities in strategic areas of education or research through cooperation involving researchers, academics, students, management, administrative and technical personnel. 'Virtual campuses' should not be confused with e-learning platforms. | ||
Source: http://ec.europa.eu/education/programmes/llp/guide/glossary_en.html | Source: http://ec.europa.eu/education/programmes/llp/guide/glossary_en.html | ||
At the e-learningeuropa.info portal 'Virtual Campus' is defined as "Part of a university or faculty that offers educational facilities at any time or, in theory, any place, by Internet." | |||
Source: http://www.elearningeuropa.info/main/index.php?page=glossary&abc=V | |||
At a European Commission consultation workshop held in Brussels on 23rd November 2004 | |||
entitled “The ‘e’ for our universities – virtual campus” (EACEA, 2004), one of the working | |||
groups proposed three definitions emphasising different aspects of a virtual campus. These | |||
were the: | |||
(i) Collaboration perspective: The term "virtual campus" denotes ICT-based collaboration of different partners supporting both, learning offers and research in a distributed setting. | |||
(ii) Enterprise (economic) perspective: The term "virtual campus" denotes an ICT-based | |||
distributed learning and research enterprise. | |||
(iii) Networked organisation perspective: The term "virtual campus" denotes an environment, which augments and/or integrates learning and research services offered by different partners. | |||
Source: http://ec.europa.eu/education/archive/elearning/doc/workshops/virtual%20campuses/report_en.pdf | |||
== Virtual campus definition of the BENVIC Project== | |||
The concept of a Virtual Campus refers to a specific format of distance education and on-line learning in which students, teaching staff and even university administrative and technical staff mainly 'meet' or communicate trough technical links. | |||
Source: http://www.benvic.odl.org/indexpr.html | |||
== Virtual campus definition of Wikipedia == | |||
A Virtual Campus refers to the online offerings of a college or university where college work is completed either partially or wholly online, often with the assistance of the teacher, professor, or teaching assistant. | |||
Source: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Virtual_Campus | |||
== Virtual Campus by Van Dusen == | |||
The Virtual Campus is a metaphore for the teaching, learning and research environment created by the convergence of new powerful instruction and communication technologies | |||
Source: E-learning in Spain: The consolidation of the earliest take-off, Albert Sangra | |||
Van Dusen (1997 | |||
== Virtual campus synonyms in other countries == | |||
=== Belgium === | |||
# "Campus Virtuel" (FR) such as for the | |||
## [http://www.elearning.ulg.ac.be/modules/freecontent/index.php?id=69 Virtual Campus of the University of Liege], [http://nettskolen.nki.no/in_english/megatrends/Liege_Article.pdf MegaTrends case study (PDF)] | |||
## [http://www.campusvirtuel.be Campusvirtuel.be] from 3 Business Schools ([http://www.solvay.edu Solvay], [http://www.hec.ulg.ac.be/EN/index.php HEC-ULg] and [http://www.uclouvain.be/en-lsm.html LSM]), article in French: [http://www.uclouvain.be/259258.html "Solvay, HEC-ULg et la LSM créent ensemble un campus virtuel"] | |||
# "Virtuele Campus" (NL) which was '''formerly''' used to describe: | |||
## [http://www.secondlifecrew.be/795/hogeschool-heeft-zijn-eigen-virtuele-campus.html a terminated school project as a Second Life campus] for [http://www.kahosl.be/site/index.php?p=/nl/page/system:index/kaho/ Catholic University College Ghent (formerly KaHo Sint-Lieven)] | |||
## [http://www.virtuelecampus.be a virtual tour and information guide of the University of Antwerp], which is now redirected to a new URL with the appropriate title " | |||
=== France === | |||
# "Université Virtuelle" | |||
# "Campus Virtuel" | |||
# "Campus numérique" | |||
# "Université Numérique (de Région)" | |||
Visit our wiki page '''[[VC definition - france|VC definition - France]]''' | |||
===United Kingdom=== | |||
The Re.ViCa wiki page on the UK, written mainly in the summer of 2008, summarises the use of “virtual campus” in UK tertiary education as follows: | |||
As a matter of historical interest, the actual phrase virtual campus is (still) used in the way it is defined in this chapter at the following UK universities and colleges: | |||
*Universities. University of Lincoln, University of London External Programme, Oxford Brookes University and Robert Gordon University. (Sheffield Hallam University used the phrase for several years but is said to feel that nowadays the phrase is insufficiently distinctive.) | |||
*Colleges. City of Bristol College, Glenrothes College, North West Institute of Further and Higher Education (Londonderry), St Helens College, and the Western Colleges Consortium. | |||
*NHS. The NHS University (NHSU) and several medical schools including at Kings College London use or used the phrase. | |||
*Ulster University’s Campus One describes itself as a virtual campus. | |||
*One supplier’s product is called the “Teknical Virtual Campus” | |||
A search – Search 1 – was done in Google on 14 May 2009 for | |||
"virtual campus" site:uk .There are 11600 hits (!) of which the first 50 have been analysed. It excludes material which is actually about virtual campuses outside the UK but which might have been described by articles published on “.uk” web sites. A second search – Search 2 – tried to establish current usage within HE/FE (post-secondary) with a tighter search: 2008 OR 2009 "virtual campus" -"virtual campus tour" site:ac.uk There are still 724 English pages. The first 150 have been reviewed. | |||
Conclusions: At the top level, although few of the original university adopters of the phrase use “virtual campus” as much or as visibly as before, it is still used for a number of departmental, consortium and private provider initiatives – and also by an increasing number of colleges. However, there are a number of uses that are out of scope – including for “virtual tours” of a physical campus and for various experiments with Second Life. Finally, it continues to be used beyond the boundaries of post-secondary education, for example in prisons and by commercial training providers in a way that would be valid if the providers were in scope for us. In more detail: | |||
# The following UK universities use the phrase “Virtual Campus” (or in some cases the short form “Virtual” – e.g. Brookes Virtual) within the usual range of Re.ViCa senses at an institutional level. It can appear in a variety of ways: in their strapline for their e-learning initiative, as a component of a URL, a link from their home page, or a regularly used phrase in their top-level narratives: University of Lincoln, University of London External Programme, Oxford Brookes University (Brookes Virtual) and Robert Gordon University. Not all these universities have it as part of their strapline for their e-learning initiative. | |||
# A number of other universities do not use in such a visible sense but the phrase appears – or has appeared – in places in their literature. These include Sheffield Hallam University, Huddersfield University. | |||
# A further number of other universities use the phrase at a departmental level: Kings College London (more than one department), Liverpool John Moores University (computing). | |||
# A few more use synonyms – online campus, global campus, etc – in this way, such as Middlesex University (Computing – Global Campus). | |||
# Many colleges use the phrase “virtual campus” at an institutional level. These include the ones already cited above: City of Bristol College, Glenrothes College, North West Institute of Further and Higher Education (now part of North West Regional College), St Helens College, and the Western Colleges Consortium (of four colleges around Bristol) – and some new arrivals such as Forth Valley College, Midlands Bible College and Wirral Metropolitan College. A number of these (new and old) used the phrase first because they bought the VLE called “Virtual Campus” from the firm Teknical, now taken over by Serco. | |||
# Consortia users of the phrase include GIS Consortium, UNIGIS and Leeds Teacher Training (SCITT). | |||
# Private (for profit) providers include Kaplan, in their guise as Kaplan Open Learning, an affiliate college of the University of Essex. | |||
# Wider uses include Prisoners Education Trust and CiREM. | |||
# Many universities use it – “out of scope” for us – to describe virtual tours of the physical campus. These include University of Aberdeen, University of Brighton, Lancaster University, University of Nottingham, University of Stirling, University of Warwick, University of Worcester and York St John University | |||
# There are several university experiments with Second Life to model a physical campus which may in time extent into our kind of virtual campus functions. These include University of East London and University of Sussex. | |||
===Spain=== | |||
A spanish definition of a virtual campus focuses on the virtual campus as a metaphore for the teaching, learning and research environment created by the convergence of new powerful instruction and communication technologies (Source: E-learning in Spain: The consolidation of the earliest take-off, Albert Sangra, Van Dusen (1997 ). | |||
===Finland=== | |||
Finnish Virtual University, one the major projects of Finnish information society activities late 1990’s and the 2000’s in higher education field, defines its own portal as a virtual campus (Finnish: virtuaalikampus) for students, teachers, researchers and administrative staff working in online education The portal links together the virtual activities of the Finnish universities and provides services that can be used by all the participants. | |||
SOCRATES Thematic Network Enhancing Engineering Education in Europe – E4 Survey of Virtual Campus and Virtual University Activities in Europe (2002) takes holistic approach and defines virtual campus as a broad conceptual framework for tools, services and facilities for students, faculty and staff. The word “campus” is used to denote the environment for the people who study, carry out research or work at the university. These elements include e learning, research activities, administrative services or other functions, i.e. complementing and supporting life on the physical university campus. | |||
The approach taken by Finnish higher education society nowadays is a logic continuum of E4 definition, following the ideas of the National Information Society Policy for 2007 -2011 (The Ubiquitous Information Society Advisory Board): the key processes and interaction are largely based on the utilisation of electronic communications and information technology. ICT applications contribute to service provision and availability and create new operating models and new skills. The key elements are communications infrastructure, user-oriented services, development of digital contents and promotion of innovation activities and telework and development of science infrastructure. The use of ICT in teaching and studying is promoted. It is not seen as a separate target area as such but merely integrated into all processes of education and development of new electronic learning environment. This approach is often described as “ICT supported university” (Finnish: TVT-tuettu yliopisto) or “digitalization of the university” in university context (Sources: Ubiquitous Information Society, Action Programme 2008–2011 Government Resolution on the Objectives of the National Information Society Policy for 2007-2011 ). | |||
===Netherlands=== | |||
In the Netherlands the term ‘virtual campus’ is synonym to ‘digital campus’ which is often referred to as ‘a digital working and learning environment’. This working and learning environment is seen from a educational perspective (not from a business point of view) and includes digital components (but is not solely an electronically environment). This definition comes close to what we nowadays call blended learning. A virtual campus encloses human – and technological- activities for educational purposes (based on: Van Elk, L. ELO-definiëring (2004). Digital University). | |||
When a closer look is taken at the definition of a virtual campus from a business perspective then it matches almost everything that is related to e-learning in general. So a virtual campus is an environment in which individuals can attend practical training sessions, anyplace, anytime, anywhere. With just-in-time support, various learning materials (audio, video, written) and learning at own pace (based on website http://www.info2people.nl/page/VirtualCampus.htm ). | |||
It is remarkable that the word ‘virtual campus’ is not used very much in the field of higher education. Although all universities have a virtual environment to offer, they most of the time use the expression ‘electronic learning environment’ or ‘portal’for virtual support services. It looks like the word ‘virtual campus’ is outdated. | |||
===Italy=== | |||
Telematic University | |||
In Italy further to the approval of the law n° 341/1990 on the restructuring of the university didactic rule (university autonomy), public-private consortia were established for distance teaching universities. Further to this law, in April 2005 the “Moratti-Stanca” Decree about “the criteria and procedures for accrediting distance education courses of the state and non state universities and of higher education institutions enables to issue academic titles, was enacted”. | |||
This act, commonly called the “Moratti-Stanca” Decree, since it was enacted by the then Minister of Education, University and Research, Ms Letizia Moratti, with the then Minister for Innovation and Technologies, Mr. Lucio Stanca, concretely implements the institution of the Telematic universities, authorised to issue academic titles. | |||
In Italy distance education courses are established and implemented by state and non state universities and make use of computer-based and Telematic technologies in accordance with the technical requirements indicated by the “Moratti-Stanca” Decree. These universities have to be organised “according to the most advanced computer-based and Telematic technologies and are aimed at issuing academic titles envisage by laws currently in force”. The academic titles “can be issued by university institutions promoted by public and private bodies and acknowledge according to the criteria and procedures envisaged by the Decree”. There are specific rules as it regards the acknowledgement of study courses. More specifically, it is envisaged a Charter of Services that envisages a didactic methodology and the conclusion of a specific contract with the student. The distance education courses are characterised, as stated in the Decree: “by the use of web-based connections for the use of training materials and the development of educational activities based on the interactivity with teachers-tutors and with the other students, by the use of PC , by the continuous monitoring of the learning progress according to the selective and rigorous criteria envisaged to assure the quality of the courses and the reliability of the educational offer'' […] "The didactic organisation of the distance education courses valorises potentials of the Information and Communication Technology (ICT) at the highest degree and more specifically as it regards multimediality and interactivity in order to favour customised study paths and to optimise learning”. | |||
The Italian situation can be better understood if one takes into due account the recent history of distance higher education initiatives and the experience of renewal we had beginning Nineties with the Law n° 341/1990. The “Reform of the University Didactic Rules” that was started up caused the appearance of new higher education multimedia systems whose achievements only Consorzio NETTUNO, in which 12,000 students were enrolled, seemed to be able to build on. | |||
With the “Moratti-Stanca” Decree of April 2003 it was established that the Minister of the University could acknowledge the establishment of new Telematic universities by decree. Starting from 2004 it acknowledged 11 universities as a whole. The path undertaken by the Italian legislator was full of initiatives, even if not all of them were up to the undertaking. Actually, not all the Telematic universities acknowledged by ministerial decree were able of carrying on proposals for distance education complying with the standards set a national level. | |||
== Multicampus University (K.U.Leuven)== | == Multicampus University (K.U.Leuven)== | ||
The 'traditional university' Katholieke Universiteit Leuven ([[K.U.Leuven]]) in [[Belgium]] progressively organizes its educational support from a multicampus perspective. | |||
In recent decades, the [[K.U.Leuven]] in Belgium has become a multicampus university. As a result of the historic expansion of the university its three groups of faculties have become separate entities, geographically spread over Leuven: Human Sciences are housed in the centre of the city, Exact Sciences in the east and Medical Sciences in the north. Since 1965, the university also has an additional campus in Kortrijk, in the west of Belgium. And in 2002, thirteen institutions of higher education in Flanders have joined forces with the K.U.Leuven in the [http://associatie.kuleuven.be/eng/ K.U.Leuven Association] in order to occupy a position of strength within the new European educational landscape and to work together towards quality improvements in education. This Association has 23 different campuses. In addition the K.U.Leuven profiles itself as an international university. The institution has agreements with various universities worldwide to enable and support a growing number student and staff exchanges between campuses. Lastly, with the introduction of ICT the university is also facing an extended form of multicampus education. Online networks of student groups and/or teaching staff – sometimes linked to but often independent from the institution – are emerging, in learning communities or communities of practice. Each participant in these networks can be considered a small virtual ‘campus’, learning from home, work or through a mobile device. | In recent decades, the [[K.U.Leuven]] in Belgium has become a multicampus university. As a result of the historic expansion of the university its three groups of faculties have become separate entities, geographically spread over Leuven: Human Sciences are housed in the centre of the city, Exact Sciences in the east and Medical Sciences in the north. Since 1965, the university also has an additional campus in Kortrijk, in the west of Belgium. And in 2002, thirteen institutions of higher education in Flanders have joined forces with the K.U.Leuven in the [http://associatie.kuleuven.be/eng/ K.U.Leuven Association] in order to occupy a position of strength within the new European educational landscape and to work together towards quality improvements in education. This Association has 23 different campuses. In addition the K.U.Leuven profiles itself as an international university. The institution has agreements with various universities worldwide to enable and support a growing number student and staff exchanges between campuses. Lastly, with the introduction of ICT the university is also facing an extended form of multicampus education. Online networks of student groups and/or teaching staff – sometimes linked to but often independent from the institution – are emerging, in learning communities or communities of practice. Each participant in these networks can be considered a small virtual ‘campus’, learning from home, work or through a mobile device. | ||
| Line 47: | Line 177: | ||
===== Virtual support activities for physical mobility ===== | ===== Virtual support activities for physical mobility ===== | ||
Ultimately, multicampus education is also about a range of virtual support activities with regard to real, physical mobility. A large range of actions can be mentioned here. At the early, preparatory phase of a physical student (or staff) exchange, multicampus support can be given through the set up of community websites for future exchange students where they can meet current students who help them find housing, give them information etc. Within the Association K.U.Leuven such a platform is being created and tested for new foreign students to find a ‘(virtual) buddy’ . There is also the opportunity for teaching staff to meet the interested new students online, for a language ‘pre-selection’ or just a first get-together. This has been tested as a pilot in the REVE project for the Erasmus Mundus Master in Adapted Physical Activity (Rajagopal et. al., 2006; Bijnens H. et. al., 2006). After the exchange, the aforementioned communities can continue to live on as a virtual alumni platform; or students could be examined at a distance through virtual mobility (video communication). | Ultimately, multicampus education is also about a range of virtual support activities with regard to real, physical mobility. A large range of actions can be mentioned here. At the early, preparatory phase of a physical student (or staff) exchange, multicampus support can be given through the set up of community websites for future exchange students where they can meet current students who help them find housing, give them information etc. Within the Association K.U.Leuven such a platform is being created and tested for new foreign students to find a ‘(virtual) buddy’ . There is also the opportunity for teaching staff to meet the interested new students online, for a language ‘pre-selection’ or just a first get-together. This has been tested as a pilot in the [[REVE]] project for the Erasmus Mundus Master in Adapted Physical Activity (Rajagopal et. al., 2006; Bijnens H. et. al., 2006). After the exchange, the aforementioned communities can continue to live on as a virtual alumni platform; or students could be examined at a distance through virtual mobility (video communication). | ||
=== Source === | === Source === | ||
[[Bijnens]] H., '''[[De Gruyter]] J.''', [[Op de Beeck]] I., [[Bacsich]] P., [[Reynolds]] S., [[Van Petegem]] W., Re-defining virtual campuses: from a “fully-fletched” virtual campus to a blended model. Paper accepted for the EDEN conference. Lisbon, June 11-14, 2008. | [[Bijnens]] H., '''[[De Gruyter]] J.''', [[Op de Beeck]] I., [[Bacsich]] P., [[Reynolds]] S., [[Van Petegem]] W., Re-defining virtual campuses: from a “fully-fletched” virtual campus to a blended model. Paper accepted for the EDEN conference. Lisbon, June 11-14, 2008. | ||
---- | ---- | ||
> [[Glossary]] | > [[Glossary]] | ||
<br> | |||
> [[Main Page]] | |||
[[Category:Definienda]] | |||
Latest revision as of 20:28, 14 February 2023
(Legacy pages currently being reviewed) In a hurry? See Programmes (for online higher education, i.e. Virtual Campuses)
This entry covers virtual campus for universities and for colleges - but not for schools - see virtual school.
Overview
The phrase "virtual campus" became prominent around 1997, when various universities launched their versions of a virtual campus. It is often applied to a single university which has a virtual university “fringe” round a physical campus, but there are some totally virtual campuses, such as the Open University of Catalonia. Now there are at least 10 virtual campus operations in the UK and many more elsewhere. Increasingly a university may no longer use the phrase "virtual campus" while still in fact having one.
Defining “Virtual Campus” – A boundary approach
Overview
Although the phrase ‘virtual campus’ is an important concept in the field of education, there is no theoretical framework for it. This chapter focuses on the development of such a theoretical framework. Similar to the work Stoof, Martens, Van Merrienboer & Bastiaens (2002) did for the concept of competence, we propose the boundary approach for virtual campuses, an aid to support stakeholders in the field of e-learning in thinking about the concept ‘virtual campus’. Here the concept of the ‘virtual campus’is being explored by focusing on its dimensions. This holds the quest for one absolute definition of it is abandoned and that instead definitions are being valued against their degree of viability. The expression "virtual campus" became prominent around 1997, when various universities launched their versions of a virtual campus. It is often applied to a single university which has a virtual university “fringe” round a physical campus, but there are some totally virtual campuses, such as the Open University of Catalonia. Now there are at least 10 virtual campus operations in the UK and many more elsewhere. Increasingly a university may no longer use the phrase "virtual campus" while still in fact having one.
The boundary approach for the concept of virtual campus
As the previous section shows there are a lot of variables involved defining the concept of the virtual campus. Depending on the context, the target group, the different goals and the technology involved a definition of ‘virtual campus’ can be formulated. The partners in the project group of the ReVica project do not want to give one single definition of the concept of the virtual campus. Since there will never be one right answer on the question what an virtual campus is,we suggest to use a conceptual representation aid as is shown in figure 1 to discuss the concept of the virtual campus. Figure 1 show the concept of a virtual campus as an amoeba-like form. The amoeba represents the virtual campus as a limited and demarcated concept, which is expressed by drawing its boundary. The boundary is being shaped by two opposing forces, being visualized as arrows (Based on the work of Stoof, Martens, Van Merriënboer & Bastiaens, 2002, p 352). From inside the figure, forces expand the boundary. This process is labeled as the ‘inside-out approach’ of the concept of the virtual campus. These are dimensions that define and construct the concept of the virtual campus. In Re.ViCa we aim to take virtual campus as synonymous with large-scale e-learning initiative. This ‘large-scale e-learning initiative’ is the inside-out dimension.
On the other hand, the forces from outside the figure reduce the boundary. This outside-in approach focuses on the selection of terms that best express the intended meaning of the virtual campus (so it clarifies the relationships). In Re.ViCa we avoid the issue of giving distance e-learning a privileged position over campus-based e-learning but this begs the question of what is large-scale? Here we suggest some indicators, these are all outside in dimensions, which suggest large-scale - note that not all of them need to be satisfied. An e-learning initiative in a university - or consortium of universities - is major if it has many (but not necessarily all) of the following characteristics:
- It requires at least one per cent of the institutional budget (this is a rule of thumb taken from Activity Based Costing theory that it is pointless to track from the top any initiatives below that level of expenditure).
- The person responsible (as the majority proportion of his/her job) for leading that initiative has a rank and salary at least equivalent to that of a university full professor at Head of Department level, or equivalent rank of administrative or technical staff (usually an Assistant Director) - and ideally that of Dean or full Director.
- There is a specific department to manage and deliver the iniative with a degree of autonomy from mainstream IT, library, pedagogic or quality structures.
- Progress of the initiative is overseen by a Steering Group chaired by one of the most senior managers in the institution (in UK terms, a Pro-Vice Chancellor).
- The initiative is part of the institution's business plan and is not totally dependent on any particular externally funded project
- There are strategy, planning and operational documents defining the initiative and regularly updated
- The head of the institution (Vice-Chancellor, Rector, President, etc) will from time to time in senior meetings be notified of progress and problems with the initiative
- The head of the institution is able to discuss the initiative in general terms with equivalent heads of other institutions - in the way that he/she would be able to discuss a new library, laboratory or similar large-scale development
As said before as a project group we do not want to take the arrogant view to present one final definition of the virtual campus, Time will catch up on us when we do that and our work will become obsolete. For the time being we present a working definition, that involves large scale initiatives (an inside out dimension) which are recognizable on the list of characteristics above. The boundary approach makes it easier to change the definition in the future and discuss new opinions.
Virtual campus definition of the European Commission
Cooperation between higher education institutions in the field of e-learning, regarding: design of joint curricula development by several universities, including agreements for the evaluation, validation and recognition of acquired competences, subject to national procedures; large–scale experiments of virtual mobility in addition to physical mobility and development of innovative dual mode curricula, based on both traditional and on-line learning methods. This broad definition involves many issues from partnerships between traditional and/or distance universities and HEI with a view to offering joint certifications (for undergraduate and/or postgraduate levels) and cooperation with learning support services. This might also include collaborative activities in strategic areas of education or research through cooperation involving researchers, academics, students, management, administrative and technical personnel. 'Virtual campuses' should not be confused with e-learning platforms.
Source: http://ec.europa.eu/education/programmes/llp/guide/glossary_en.html
At the e-learningeuropa.info portal 'Virtual Campus' is defined as "Part of a university or faculty that offers educational facilities at any time or, in theory, any place, by Internet."
Source: http://www.elearningeuropa.info/main/index.php?page=glossary&abc=V
At a European Commission consultation workshop held in Brussels on 23rd November 2004
entitled “The ‘e’ for our universities – virtual campus” (EACEA, 2004), one of the working
groups proposed three definitions emphasising different aspects of a virtual campus. These
were the:
(i) Collaboration perspective: The term "virtual campus" denotes ICT-based collaboration of different partners supporting both, learning offers and research in a distributed setting.
(ii) Enterprise (economic) perspective: The term "virtual campus" denotes an ICT-based distributed learning and research enterprise.
(iii) Networked organisation perspective: The term "virtual campus" denotes an environment, which augments and/or integrates learning and research services offered by different partners.
Source: http://ec.europa.eu/education/archive/elearning/doc/workshops/virtual%20campuses/report_en.pdf
Virtual campus definition of the BENVIC Project
The concept of a Virtual Campus refers to a specific format of distance education and on-line learning in which students, teaching staff and even university administrative and technical staff mainly 'meet' or communicate trough technical links.
Source: http://www.benvic.odl.org/indexpr.html
Virtual campus definition of Wikipedia
A Virtual Campus refers to the online offerings of a college or university where college work is completed either partially or wholly online, often with the assistance of the teacher, professor, or teaching assistant.
Source: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Virtual_Campus
Virtual Campus by Van Dusen
The Virtual Campus is a metaphore for the teaching, learning and research environment created by the convergence of new powerful instruction and communication technologies
Source: E-learning in Spain: The consolidation of the earliest take-off, Albert Sangra
Van Dusen (1997
Virtual campus synonyms in other countries
Belgium
- "Campus Virtuel" (FR) such as for the
- Virtual Campus of the University of Liege, MegaTrends case study (PDF)
- Campusvirtuel.be from 3 Business Schools (Solvay, HEC-ULg and LSM), article in French: "Solvay, HEC-ULg et la LSM créent ensemble un campus virtuel"
- "Virtuele Campus" (NL) which was formerly used to describe:
- a terminated school project as a Second Life campus for Catholic University College Ghent (formerly KaHo Sint-Lieven)
- a virtual tour and information guide of the University of Antwerp, which is now redirected to a new URL with the appropriate title "
France
- "Université Virtuelle"
- "Campus Virtuel"
- "Campus numérique"
- "Université Numérique (de Région)"
Visit our wiki page VC definition - France
United Kingdom
The Re.ViCa wiki page on the UK, written mainly in the summer of 2008, summarises the use of “virtual campus” in UK tertiary education as follows: As a matter of historical interest, the actual phrase virtual campus is (still) used in the way it is defined in this chapter at the following UK universities and colleges:
- Universities. University of Lincoln, University of London External Programme, Oxford Brookes University and Robert Gordon University. (Sheffield Hallam University used the phrase for several years but is said to feel that nowadays the phrase is insufficiently distinctive.)
- Colleges. City of Bristol College, Glenrothes College, North West Institute of Further and Higher Education (Londonderry), St Helens College, and the Western Colleges Consortium.
- NHS. The NHS University (NHSU) and several medical schools including at Kings College London use or used the phrase.
- Ulster University’s Campus One describes itself as a virtual campus.
- One supplier’s product is called the “Teknical Virtual Campus”
A search – Search 1 – was done in Google on 14 May 2009 for "virtual campus" site:uk .There are 11600 hits (!) of which the first 50 have been analysed. It excludes material which is actually about virtual campuses outside the UK but which might have been described by articles published on “.uk” web sites. A second search – Search 2 – tried to establish current usage within HE/FE (post-secondary) with a tighter search: 2008 OR 2009 "virtual campus" -"virtual campus tour" site:ac.uk There are still 724 English pages. The first 150 have been reviewed. Conclusions: At the top level, although few of the original university adopters of the phrase use “virtual campus” as much or as visibly as before, it is still used for a number of departmental, consortium and private provider initiatives – and also by an increasing number of colleges. However, there are a number of uses that are out of scope – including for “virtual tours” of a physical campus and for various experiments with Second Life. Finally, it continues to be used beyond the boundaries of post-secondary education, for example in prisons and by commercial training providers in a way that would be valid if the providers were in scope for us. In more detail:
- The following UK universities use the phrase “Virtual Campus” (or in some cases the short form “Virtual” – e.g. Brookes Virtual) within the usual range of Re.ViCa senses at an institutional level. It can appear in a variety of ways: in their strapline for their e-learning initiative, as a component of a URL, a link from their home page, or a regularly used phrase in their top-level narratives: University of Lincoln, University of London External Programme, Oxford Brookes University (Brookes Virtual) and Robert Gordon University. Not all these universities have it as part of their strapline for their e-learning initiative.
- A number of other universities do not use in such a visible sense but the phrase appears – or has appeared – in places in their literature. These include Sheffield Hallam University, Huddersfield University.
- A further number of other universities use the phrase at a departmental level: Kings College London (more than one department), Liverpool John Moores University (computing).
- A few more use synonyms – online campus, global campus, etc – in this way, such as Middlesex University (Computing – Global Campus).
- Many colleges use the phrase “virtual campus” at an institutional level. These include the ones already cited above: City of Bristol College, Glenrothes College, North West Institute of Further and Higher Education (now part of North West Regional College), St Helens College, and the Western Colleges Consortium (of four colleges around Bristol) – and some new arrivals such as Forth Valley College, Midlands Bible College and Wirral Metropolitan College. A number of these (new and old) used the phrase first because they bought the VLE called “Virtual Campus” from the firm Teknical, now taken over by Serco.
- Consortia users of the phrase include GIS Consortium, UNIGIS and Leeds Teacher Training (SCITT).
- Private (for profit) providers include Kaplan, in their guise as Kaplan Open Learning, an affiliate college of the University of Essex.
- Wider uses include Prisoners Education Trust and CiREM.
- Many universities use it – “out of scope” for us – to describe virtual tours of the physical campus. These include University of Aberdeen, University of Brighton, Lancaster University, University of Nottingham, University of Stirling, University of Warwick, University of Worcester and York St John University
- There are several university experiments with Second Life to model a physical campus which may in time extent into our kind of virtual campus functions. These include University of East London and University of Sussex.
Spain
A spanish definition of a virtual campus focuses on the virtual campus as a metaphore for the teaching, learning and research environment created by the convergence of new powerful instruction and communication technologies (Source: E-learning in Spain: The consolidation of the earliest take-off, Albert Sangra, Van Dusen (1997 ).
Finland
Finnish Virtual University, one the major projects of Finnish information society activities late 1990’s and the 2000’s in higher education field, defines its own portal as a virtual campus (Finnish: virtuaalikampus) for students, teachers, researchers and administrative staff working in online education The portal links together the virtual activities of the Finnish universities and provides services that can be used by all the participants. SOCRATES Thematic Network Enhancing Engineering Education in Europe – E4 Survey of Virtual Campus and Virtual University Activities in Europe (2002) takes holistic approach and defines virtual campus as a broad conceptual framework for tools, services and facilities for students, faculty and staff. The word “campus” is used to denote the environment for the people who study, carry out research or work at the university. These elements include e learning, research activities, administrative services or other functions, i.e. complementing and supporting life on the physical university campus. The approach taken by Finnish higher education society nowadays is a logic continuum of E4 definition, following the ideas of the National Information Society Policy for 2007 -2011 (The Ubiquitous Information Society Advisory Board): the key processes and interaction are largely based on the utilisation of electronic communications and information technology. ICT applications contribute to service provision and availability and create new operating models and new skills. The key elements are communications infrastructure, user-oriented services, development of digital contents and promotion of innovation activities and telework and development of science infrastructure. The use of ICT in teaching and studying is promoted. It is not seen as a separate target area as such but merely integrated into all processes of education and development of new electronic learning environment. This approach is often described as “ICT supported university” (Finnish: TVT-tuettu yliopisto) or “digitalization of the university” in university context (Sources: Ubiquitous Information Society, Action Programme 2008–2011 Government Resolution on the Objectives of the National Information Society Policy for 2007-2011 ).
Netherlands
In the Netherlands the term ‘virtual campus’ is synonym to ‘digital campus’ which is often referred to as ‘a digital working and learning environment’. This working and learning environment is seen from a educational perspective (not from a business point of view) and includes digital components (but is not solely an electronically environment). This definition comes close to what we nowadays call blended learning. A virtual campus encloses human – and technological- activities for educational purposes (based on: Van Elk, L. ELO-definiëring (2004). Digital University). When a closer look is taken at the definition of a virtual campus from a business perspective then it matches almost everything that is related to e-learning in general. So a virtual campus is an environment in which individuals can attend practical training sessions, anyplace, anytime, anywhere. With just-in-time support, various learning materials (audio, video, written) and learning at own pace (based on website http://www.info2people.nl/page/VirtualCampus.htm ). It is remarkable that the word ‘virtual campus’ is not used very much in the field of higher education. Although all universities have a virtual environment to offer, they most of the time use the expression ‘electronic learning environment’ or ‘portal’for virtual support services. It looks like the word ‘virtual campus’ is outdated.
Italy
Telematic University In Italy further to the approval of the law n° 341/1990 on the restructuring of the university didactic rule (university autonomy), public-private consortia were established for distance teaching universities. Further to this law, in April 2005 the “Moratti-Stanca” Decree about “the criteria and procedures for accrediting distance education courses of the state and non state universities and of higher education institutions enables to issue academic titles, was enacted”. This act, commonly called the “Moratti-Stanca” Decree, since it was enacted by the then Minister of Education, University and Research, Ms Letizia Moratti, with the then Minister for Innovation and Technologies, Mr. Lucio Stanca, concretely implements the institution of the Telematic universities, authorised to issue academic titles. In Italy distance education courses are established and implemented by state and non state universities and make use of computer-based and Telematic technologies in accordance with the technical requirements indicated by the “Moratti-Stanca” Decree. These universities have to be organised “according to the most advanced computer-based and Telematic technologies and are aimed at issuing academic titles envisage by laws currently in force”. The academic titles “can be issued by university institutions promoted by public and private bodies and acknowledge according to the criteria and procedures envisaged by the Decree”. There are specific rules as it regards the acknowledgement of study courses. More specifically, it is envisaged a Charter of Services that envisages a didactic methodology and the conclusion of a specific contract with the student. The distance education courses are characterised, as stated in the Decree: “by the use of web-based connections for the use of training materials and the development of educational activities based on the interactivity with teachers-tutors and with the other students, by the use of PC , by the continuous monitoring of the learning progress according to the selective and rigorous criteria envisaged to assure the quality of the courses and the reliability of the educational offer […] "The didactic organisation of the distance education courses valorises potentials of the Information and Communication Technology (ICT) at the highest degree and more specifically as it regards multimediality and interactivity in order to favour customised study paths and to optimise learning”. The Italian situation can be better understood if one takes into due account the recent history of distance higher education initiatives and the experience of renewal we had beginning Nineties with the Law n° 341/1990. The “Reform of the University Didactic Rules” that was started up caused the appearance of new higher education multimedia systems whose achievements only Consorzio NETTUNO, in which 12,000 students were enrolled, seemed to be able to build on. With the “Moratti-Stanca” Decree of April 2003 it was established that the Minister of the University could acknowledge the establishment of new Telematic universities by decree. Starting from 2004 it acknowledged 11 universities as a whole. The path undertaken by the Italian legislator was full of initiatives, even if not all of them were up to the undertaking. Actually, not all the Telematic universities acknowledged by ministerial decree were able of carrying on proposals for distance education complying with the standards set a national level.
Multicampus University (K.U.Leuven)
The 'traditional university' Katholieke Universiteit Leuven (K.U.Leuven) in Belgium progressively organizes its educational support from a multicampus perspective. In recent decades, the K.U.Leuven in Belgium has become a multicampus university. As a result of the historic expansion of the university its three groups of faculties have become separate entities, geographically spread over Leuven: Human Sciences are housed in the centre of the city, Exact Sciences in the east and Medical Sciences in the north. Since 1965, the university also has an additional campus in Kortrijk, in the west of Belgium. And in 2002, thirteen institutions of higher education in Flanders have joined forces with the K.U.Leuven in the K.U.Leuven Association in order to occupy a position of strength within the new European educational landscape and to work together towards quality improvements in education. This Association has 23 different campuses. In addition the K.U.Leuven profiles itself as an international university. The institution has agreements with various universities worldwide to enable and support a growing number student and staff exchanges between campuses. Lastly, with the introduction of ICT the university is also facing an extended form of multicampus education. Online networks of student groups and/or teaching staff – sometimes linked to but often independent from the institution – are emerging, in learning communities or communities of practice. Each participant in these networks can be considered a small virtual ‘campus’, learning from home, work or through a mobile device.
Enhancing or replacing physical mobility with virtual mobility
The current structure of the university thus challenges the K.U.Leuven to organize and support its education with attention for communication and collaboration between the various campuses. Today this is most often realized through physical mobility: staff and/or student move between different locations. This is the case for interdisciplinary courses between Leuven’s three groups of faculties and for staff mobility between Kortrijk and Leuven. It is also the most common form for international exchanges. Yet the university is progressively supporting initiatives that replace or enhance physical with virtual mobility, seeking to integrate aspects of ‘virtual campuses’ into traditional education to stimulate collaboration between the sites of the Association, to support student and/or staff exchanges in Europe or in the world, to enhance communication with developing countries or to sustain virtual learning communities.
Joint course materials
At a basic level (virtual/blended) multicampus education in Leuven is revealed in initiatives that create, offer and localize joint course materials. While teaching staff and students remain at their own campus for the entire course, specific course modules learning materials are used that have been developed, at a distance, by an inter-institutional (multicampus) teaching team. These course materials are often offered on a common website, a databank or a virtual learning environment. Recently there are also teachers who (co-)develop or use ‘Open Educational Resources’.
Pooled infrastructure
Not only course materials are collaboratively created or shared. Also (laboratory)-infrastructure is shared between locations to avoid a double set up of equipment. In some cases this pooled infrastructure is also virtual. Some (dangerous) laboratory experiments or experiments that require students and staff to be at different locations (students watch a complex surgical operation) can now happen thanks to virtual support to bridge the distance between the actual experiment and the audience. The infrastructure of the experiment itself is in a limited number of cases entirely digital by means of a simulation on a common virtual platform.
Joint learning activities
Furthermore, multicampus education can be about joint learning activities. For the ‘Student Business Game’ for instance, students from different institutions f the Association K.U.Leuven play a business game on their own campus after which the winning teams compete with each other via videoconferencing before a jury of teaching and company staff. Joint learning activities can also be about e-coaching, about writing an academic paper at a distance or student placements. All activities invite multiple sites to collaborate in the creation, delivery or support of the activity, with the help of technology. At K.U.Leuven joint learning activities are particularly interesting for interdisciplinary modules, courses or programs, such as activities involving both learners studying medicine or nursing, industrial or civil engineering, etc.
Joint courses
Building on joint learning activities, another type of multicampus are joint courses. A joint course can be (a) a course developed by one campus (institution) and offered to students at another campus (institution), (b) a course developed by one institution and used but adapted by another institution or (c) a jointly developed course offered to students of all involved institutions (Haake et al., 2006). One variation of this type are virtual seminars: co-created or co-delivered seminars set up as a single course, or in a series of courses - broadcasted over multiple sites using ICT (videoconferencing, web conferencing, streaming, etc) . The KULeuven has a strong expertise and long tradition in organizing virtual seminars. The ‘Pentalfa’ project for instance is a multidisciplinary, post-graduate distance learning initiative of the Faculty of Medicine, aimed to offer (extra) training broadcasted to various hospitals of the Flemish Hospital Network K.U.Leuven. It is currently in its 8th year and there are plans to enhance the initiative with an international component. The university is also looking into the use of virtual seminars for knowledge exchange and networking between the institutions of the Association and beyond (society in general, companies, alumni, etc.).
Multicampus programmes
Next, multicampus education is also revealed in the offer of a complete, ‘multicampus’ programme, which many institutions can be contributing in. A number of Bachelors and Masters are already set up within the Association K.U.Leuven, involving multiple teaching teams from different institutions. The challenge is to streamline these programs around a common denominator, yet with respect to any local specificities of each campus involved. Virtual initiatives – joint learning materials, joint learning activities, joint courses – all play a vital part in this. Eventually a completely virtual multicampus programme comes close to the traditional form of distance education, as offered by the Open University for instance. From the perspective of more and better flexibility in education, it could be interesting to bring distance and regular education together. Regular programs could put forward a number of distance learning courses (and vice versa), in replacement of or as an enhancement to their offer: they could support or realize the transition between certain bachelors and masters in a flexible way, (work) students could enhance their own study package with a number of distance education courses. In Flanders, the current offers of both the regular universities and the Open University are still entirely separate from each other. Yet under certain conditions the Open University does already allow its students to take courses from other universities in addition to the curriculum of the own education. K.U.Leuven is currently studying the opportunity to present this interpretation of multicampus to its students.
Virtual support activities for physical mobility
Ultimately, multicampus education is also about a range of virtual support activities with regard to real, physical mobility. A large range of actions can be mentioned here. At the early, preparatory phase of a physical student (or staff) exchange, multicampus support can be given through the set up of community websites for future exchange students where they can meet current students who help them find housing, give them information etc. Within the Association K.U.Leuven such a platform is being created and tested for new foreign students to find a ‘(virtual) buddy’ . There is also the opportunity for teaching staff to meet the interested new students online, for a language ‘pre-selection’ or just a first get-together. This has been tested as a pilot in the REVE project for the Erasmus Mundus Master in Adapted Physical Activity (Rajagopal et. al., 2006; Bijnens H. et. al., 2006). After the exchange, the aforementioned communities can continue to live on as a virtual alumni platform; or students could be examined at a distance through virtual mobility (video communication).
Source
Bijnens H., De Gruyter J., Op de Beeck I., Bacsich P., Reynolds S., Van Petegem W., Re-defining virtual campuses: from a “fully-fletched” virtual campus to a blended model. Paper accepted for the EDEN conference. Lisbon, June 11-14, 2008.