Welcome to the Virtual Education Wiki ~ Open Education Wiki
Indonesia: Difference between revisions
(→Indonesia in a nutshell: picture added) |
NikkiCortoos (talk | contribs) m (adapted to merged template) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
'' | <!-- ''by authorname authorsurname'' --> | ||
== Partners situated in Indonesia== | == Partners and Experts situated in Indonesia== | ||
None. | None. | ||
| Line 24: | Line 24: | ||
* Jakarta is the country's special capital region. | * Jakarta is the country's special capital region. | ||
== Education in Indonesia == | |||
=== Indonesia education policy === | |||
=== Indonesia education system === | |||
== Schools in Indonesia == | |||
<!-- cover pre-primary, primary and secondary (all kinds including vocational) --> | |||
<!--- please include an introduction to schools and a list of schools. If there are too many schools in this country, link to an external list of all the schools (on Ministry’s website or Wikipedia) and list the most important ones (well-known school or exemplar) --> | |||
<!-- make sure you include private schools (non-profit, e.g. foundations and for-profit) --> | |||
<!-- include a section on homeschooling if applicable --> | |||
== Higher education == | == Further and Higher education == | ||
=== Universities in Indonesia=== | === Universities in Indonesia=== | ||
| Line 49: | Line 60: | ||
== | == Education reform == | ||
=== | <!-- focus on the last 10 years at most --> | ||
=== Schools === | |||
=== Post-secondary === | |||
== Administration and finance == | == Administration and finance == | ||
=== Schools === | |||
<!-- describe any issues of school fees or other costs if state schools are not free --> | |||
=== Post-secondary === | |||
<!-- divide into universities, polytechnics and colleges if need be --> | |||
<!-- for colleges, describe the student fees regime if colleges charge student fees --> | |||
Not covered, except to note that there are public and private universities. | Not covered, except to note that there are public and private universities. | ||
== Quality assurance == | == Quality assurance, inspection and accreditation == | ||
=== Schools === | |||
<!-- describe the inspection agencies --> | |||
=== Post-secondary === | |||
<!-- subdivide as necessary - QA for HE is usually very different from QA for colleges --> | |||
<!-- describe the accreditation regime and the QA agency or agencies --> | |||
No information in general. | No information in general. | ||
| Line 67: | Line 104: | ||
However, see [http://www.irrodl.org/index.php/irrodl/article/view/340/774 The Practice of a Quality Assurance System in Open and Distance Learning: A case study at Universitas Terbuka Indonesia (The Indonesia Open University)] for a case study of [[Universitas Terbuka]]. | However, see [http://www.irrodl.org/index.php/irrodl/article/view/340/774 The Practice of a Quality Assurance System in Open and Distance Learning: A case study at Universitas Terbuka Indonesia (The Indonesia Open University)] for a case study of [[Universitas Terbuka]]. | ||
== | == Information society == | ||
Not covered. | |||
== | == ICT in education initiatives == | ||
=== Virtual initiatives in schools === | |||
<!-- include virtual schools, virtual classes, schools consuming virtual classes, and other initiatives including not-schools and services for homeschoolers --> | |||
<!-- create a separate wiki page per "school" and add here a short introduction and link to the separate school wiki page. --> | |||
=== | === Virtual initiatives in post-secondary education === | ||
<!-- for important countries you will want to divide this into universities, polytechnics and colleges --> | |||
<!-- include virtual campuses and virtual universities (distance education) as well as on-campus initiatives --> | |||
== References == | == References == | ||
| Line 96: | Line 141: | ||
[[Category:Countries with Programmes]] | [[Category:Countries with Programmes]] | ||
[[Category:Countries in merged template]] | |||
[[Category:VISCED]] | |||
Revision as of 09:55, 19 September 2012
Partners and Experts situated in Indonesia
None.
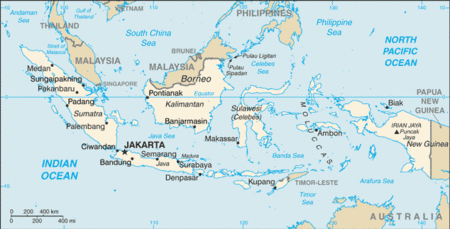
Indonesia in a nutshell
(Sourced from http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Indonesia)
The Republic of Indonesia (Indonesian: Republik Indonesia), is a country in Southeast Asia. Comprising 17,508 islands, it is the world's largest archipelagic state. With a population of 222 million people in 2006, it is the world's fourth most populous country and the most populous Muslim-majority nation, although officially it is not an Islamic state.
Indonesia is a republic, with an elected parliament and president.
The nation's capital city is Jakarta. The country shares land borders with Papua New Guinea, East Timor and Malaysia. Other neighboring countries include Singapore, the Philippines, Australia, and the Indian territory of the Andaman and Nicobar Islands.
Administratively, Indonesia consists of 33 provinces, five of which have special status. Each province has its own political legislature and governor. The provinces are subdivided into regencies and cities, which are further subdivided into subdistricts, and again into village groupings. Following the implementation of regional autonomy measures in 2001, the regencies and cities have become the key administrative units, responsible for providing most government services. The village administration level is the most influential on a citizen's daily life, and handles matters of a village or neighborhood through an elected village chief.
The provinces of Aceh, Jakarta, Yogyakarta, Papua, and West Papua have greater legislative privileges and a higher degree of autonomy from the central government than the other provinces.
- The Acehnese government, for example, has the right to create an independent legal system; in 2003, it instituted a form of Sharia (Islamic law).
- Yogyakarta was granted the status of Special Region in recognition of its pivotal role in supporting Indonesian Republicans during the Indonesian Revolution.
- Papua, formerly known as Irian Jaya, was granted special autonomy status in 2001.
- Jakarta is the country's special capital region.
Education in Indonesia
Indonesia education policy
Indonesia education system
Schools in Indonesia
Further and Higher education
Universities in Indonesia
The Wikipedia List of universities in Indonesia lists 84 universities, although the accuracy of the list is not clear, around a third of the entries have further detail or web sites.
Some 57 of the universities are public, with 27 being private.
In e-learning circles, the best known is Universitas Terbuka, Indonesia's Open University.
Polytechnics in Indonesia
No information.
Education reform
Schools
Post-secondary
Administration and finance
Schools
Post-secondary
Not covered, except to note that there are public and private universities.
Quality assurance, inspection and accreditation
Schools
Post-secondary
No information in general.
However, see The Practice of a Quality Assurance System in Open and Distance Learning: A case study at Universitas Terbuka Indonesia (The Indonesia Open University) for a case study of Universitas Terbuka.
Information society
Not covered.
ICT in education initiatives
Virtual initiatives in schools
Virtual initiatives in post-secondary education
References
- E-LEARNING IN INDONESIAN EDUCATION SYSTEM, by Mohammad Ali (Indonesia University of Education) - http://gauge.u-gakugei.ac.jp/apeid/apeid04/country_papers/indonesia.pdf
- Indonesia – Developing Higher Education Information Network, by Dr Soekartawi (Professor, Brawijaya University) - http://www.digitallearning.in/articles/article-details.asp?articleid=2200&typ=COUNTRY%20FOCUS